Azure Cosmos DB Blog
The latest news, updates and technical insights from the Azure Cosmos DB team
Latest posts

Maximize Azure Cosmos DB Performance with Azure Advisor Recommendations
In the first post of this series, we introduced how Azure Advisor helps Azure Cosmos DB users uncover opportunities to optimize efficiency and make smarter decisions. This follow-up dives deeper into one of the most important categories of guidance: performance. If you've ever dealt with skewed workloads, unexpected RU consumption, or queries that don’t scale as expected, Azure Advisor surfaces exactly the insights you need to diagnose and improve them. In this post, you’ll learn what performance recommendations Advisor provides, why they matter, and how you can use them to enhance the speed, reliability, a...

Building AI-Powered Apps with Azure Cosmos DB and the Vercel AI SDK
The Vercel AI SDK is an open-source TypeScript toolkit that provides the core building blocks for integrating AI into any JavaScript application. It works with 20+ AI providers out of the box—including OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, Mistral, and more—so you can write your code once and switch providers by changing a single import. At its core, the SDK handles streaming (responses appear word-by-word instead of making users wait), tool calling (allowing the AI to invoke your functions, such as querying a database), and multi-step agentic reasoning, where the AI chains multiple tool calls together to a...

How to Enable Microsoft Entra ID for Azure Cosmos DB (NoSQL)
Strengthen Identity Security and Eliminate Account Keys Identity is becoming the new security perimeter. As organizations modernize their cloud applications, long‑lived secrets and shared keys introduce unnecessary risk. Azure Cosmos DB now fully supports Microsoft Entra ID for both control plane and data plane access, giving customers a secure, passwordless, least‑privilege alternative to legacy key‑based authentication. This blog walks through why customers are moving to Entra ID, what changes when you disable local authentication, and how to configure modern RBAC for Cosmos DB. Why Move to Microsoft Entra...

Part 2: Building a Python CRUD API with Azure Functions and Azure Cosmos DB
Series: Building Serverless Applications with Azure Functions and Azure Cosmos DB In the first post of this series, we focused on establishing the fundamentals of serverless architecture by building and deploying a simple HTTP API using Azure Functions and FastAPI. The post centred on serverless compute, showing how Azure Functions handles execution, scaling, and infrastructure management while FastAPI provides a modern, developer-friendly API framework. In this post, we extend that foundation by introducing serverless data. You’ll build a Python-based CRUD inventory API and persist data using Azure Cosmos DB...
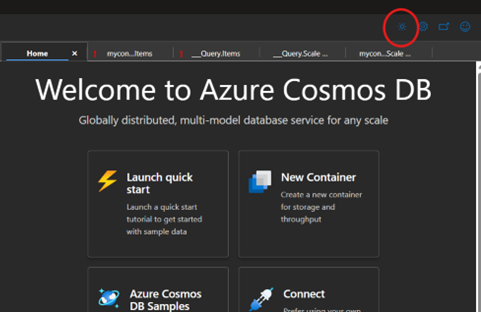
Azure Cosmos DB Data Explorer now supports Dark Mode
If you spend time in the Azure Portal’s using Azure Cosmos DB Data Explorer, you know it’s a “lots of screens, lots of tabs, lots of work happening” kind of place. So I’m excited to share a small upgrade that makes a big difference: Dark Mode is now supported in Cosmos DB Data Explorer. It just works with Azure Portal Dark Mode If you already have Dark Mode enabled in the Azure Portal, Data Explorer will automatically switch to dark with it. No extra setup, no separate preference buried in a panel somewhere. If you want to switch on the on demand, you can also use the sun/moon toggle in the Data Explorer...

Azure Cosmos DB TV Recap – From Burger to Bots – Agentic Apps with Cosmos DB and LangChain.js | Ep. 111
In Episode 111 of Azure Cosmos DB TV, host Mark Brown is joined by Yohan Lasorsa to explore how developers can build agent-powered applications using a fully serverless architecture. This episode focuses on a practical, end-to-end example that demonstrates how transactional application data and AI-driven experiences can coexist on a single platform without introducing additional infrastructure or operational overhead. The session walks through a sample application inspired by a familiar business scenario: a simple ordering system. What begins as a traditional REST-based business API evolves into an agent-enabl...

Accelerate Your Cosmos DB Infrastructure with GitHub Copilot CLI and Azure Cosmos DB Agent Kit
Modern infrastructure work is increasingly agent driven, but only if your AI actually understands the platform you’re deploying. This guide shows how to turn GitHub Copilot CLI into an Azure Cosmos DB aware infrastructure expert by loading the Azure Cosmos DB Agent Kit. In under a minute, you’ll give Copilot deep, opinionated knowledge of Azure Cosmos DB best practices so it can review, generate, and optimize your Terraform, Bicep, Docker, and CI/CD configurations directly from your terminal. TL;DR — Get Started in 30 Seconds That's it! Copilot CLI now has expert-level Azure Cosmos DB infrastructure knowl...

Azure Cosmos DB TV Recap: Supercharging AI Agents with the Azure Cosmos DB MCP Toolkit (Ep. 110)
In Episode 110 of Azure Cosmos DB TV, host Mark Brown is joined by Sajeetharan Sinnathurai to explore how the Azure Cosmos DB MCP Toolkit is changing the way developers build, deploy, and scale AI agents using real application data. As agentic AI systems evolve, one challenge continues to surface: securely and consistently connecting AI agents to operational data—without rewriting integration logic for every platform. This episode takes a deep dive into how the Model Context Protocol (MCP), along with Azure Azure Cosmos DB’s implementation, addresses that challenge. Why MCP Matters for AI Agents At its cor...

Introducing the Azure Cosmos DB Agent Kit: Your AI Pair Programmer Just Got Smarter
The Azure Cosmos DB Agent Kit is an open-source collection of skills that teaches your AI coding assistant (GitHub Copilot, Claude Code, Gemini CLI) expert-level Azure Cosmos DB best practices. Install with one command, get production-ready guidance instantly. The Challenge Every Azure Cosmos DB Developer Faces You're building a new application with Azure Cosmos DB. You've got your data, you've got your queries, but then come the questions that keep you up at night: These aren't trivial questions. Poor decisions here can mean the difference between a blazing-fast application and one that...
