Many apps require adding user authentication. This often means enabling users to sign into existing Microsoft, Facebook, Google, and (now) Apple Sign-In accounts.
Microsoft Authentication Library (MSAL) provides an excellent turn-key solution to adding authentication to your app. Additionally, there is even support for Xamarin apps in their client NuGet package.
However, if you are looking for a way to easily integrate Xamarin social authentication into a new or existing ASP.NET (or other) web app, Xamarin.Essentials has you covered!
Authentication at the Backend
Many authentication providers only offer explicit or “two-legged” authentication flows to ensure better security. This means you will need a ‘secret’ from the provider to complete the authentication flow. Unfortunately, mobile apps are not a great place to store secrets. Anything stored in a mobile app’s code or otherwise is generally considered insecure. The best practice here, is to use a web backend as a middle layer between your mobile app and the authentication provider.
We strongly recommend against using older mobile-only authentication libraries and patterns which do not leverage a web backend in the authentication flow.
There are a lot of moving parts to this type of flow, but that doesn’t mean it needs to be difficult!
Web Authenticator API
In Xamarin.Essentials 1.5.1 we are introducing the WebAuthenticator API. This is designed to do the heavy lifting of opening a URL in the browser. Then waiting for that browser session to redirect to your app’s callback URI. In other words: dealing with a typical external authentication flow.
The API is simple. It is a single method AuthenticateAsync which takes two parameters. The url that starts the authentication flow, and the Uri that your app is registered to handle the callback on. The result is a WebAuthenticatorResult which includes any query parameters parsed from the callback URI.
var authResult = WebAuthenticator.AuthenticateAsync(
new Uri("https://mysite.com/mobileauth/Microsoft"),
new Uri("myapp://"));
var accessToken = authResult?.AccessToken;
The Web Authenticator will take care of opening a Safari view controller on iOS or a Custom Tab on Android. This will display the authentication URL to your user. When the user completes the flow, and your server calls back to the callback URI, the result is returned. If the user cancels the flow at any time, a null result is returned.
On iOS we take advantage of ASWebAuthenticationSession to handle this. Yet gracefully fall back to using SFAuthenticationSession or SFSafariViewController depending on the iOS version at runtime. On Android, this uses Custom Tabs to launch a browser intent. On UWP, we are using WebAuthenticationBroker. For each platform, we strive to deliver the best native experience possible.
Mobile Platform Setup
Each platform handles navigating in web browsers for authentication flows a little differently. As well as requires some specific setting up.
iOS
On iOS you will need to add your app’s callback URI pattern to your Info.plist. As a best practice, consider using Universal App Links to register your app’s callback URI.
Additionally, you will also need to override your AppDelegate‘s OpenUrl method to call into Essentials:
public override bool OpenUrl(UIApplication app, NSUrl url, NSDictionary options)
{
if (Xamarin.Essentials.Platform.OpenUrl(app, url, options))
return true;
return base.OpenUrl(app, url, options);
}
Android
Android requires an Intent Filter setup to handle your callback URI. This is easily accomplished by subclassing the WebAuthenticatorCallbackActivity class:
const string CALLBACK_SCHEME = "myapp";
[Activity(NoHistory = true, LaunchMode = LaunchMode.SingleTop)]
[IntentFilter(new[] { Intent.ActionView }, Categories = new[] { Intent.CategoryDefault, Intent.CategoryBrowsable }, DataScheme = CALLBACK_SCHEME)]
public class WebAuthenticationCallbackActivity : Xamarin.Essentials.WebAuthenticatorCallbackActivity
{
}
In your MainActivity, add a call to Essentials in your OnResume:
protected override void OnResume()
{
base.OnResume();
Xamarin.Essentials.Platform.OnResume();
}
UWP
For UWP, declare your callback URI in your Package.appxmanifest file:
<Extensions>
<uap:Extension Category="windows.protocol">
<uap:Protocol Name="myapp">
<uap:DisplayName>My App</uap:DisplayName>
</uap:Protocol>
</uap:Extension>
</Extensions>
Apple Sign In
For using social authentication in your app, chances are you are also adding Apple Sign In. We have you covered on iOS, Android, and UWP.
First, configure your app to use Apple Sign In.
For iOS 13 and higher, use the AppleSignInAuthenticator.AuthenticateAsync() method. This will call the native Apple Sign in API’s under the hood so users get the best experience possible on these devices. Write your shared code to use the right API at runtime like this:
var scheme = "..."; // Apple, Microsoft, Google, Facebook, etc.
WebAuthenticatorResult r = null;
if (scheme.Equals("Apple")
&& DeviceInfo.Platform == DevicePlatform.iOS
&& DeviceInfo.Version.Major >= 13)
{
// Use Native Apple Sign In API's
r = await AppleSignInAuthenticator.AuthenticateAsync();
}
else
{
// Web Authentication flow
var authUrl = new Uri(authenticationUrl + scheme);
var callbackUrl = new Uri("xamarinessentials://");
r = await WebAuthenticator.AuthenticateAsync(authUrl, callbackUrl);
}
var accessToken = r?.AccessToken;
For non-iOS 13 devices, this will start the web authentication flow. This can also be used to enable Apple Sign In on Android and UWP devices.
Web Authentication with ASP.NET
It is possible to use the WebAuthenticator API with any web backend. However, using ASP.NET Core makes this process super easy.
Set up all desired providers just like you would setup any external social authentication provider.
There are two additional things needed for this example to work:
- Use
.AddCookies()in your Startup.cs.AddAuthentication()call - All providers must be configured with
.SaveTokens = true;
To include Apple Sign In, use the AspNet.Security.OAuth.Apple NuGet package. View the full Startup.cs sample in the Essentials GitHub repository.
Adding a Custom Mobile Auth Controller
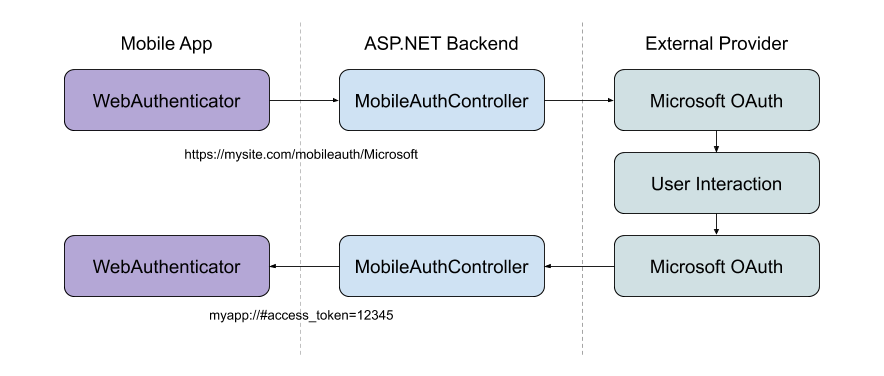
With a mobile authentication flow, we typically want to initiate the flow directly to a provider that the user has chosen. (Such as: clicking a “Microsoft” button on the sign-in screen of an app.) We also want to be able to return relevant information to our app at a specific callback URI to end the authentication flow.
To achieve this we can use a custom API Controller:
[Route("mobileauth")]
[ApiController]
public class AuthController : ControllerBase
{
const string callbackScheme = "myapp";
[HttpGet("{scheme}")] // eg: Microsoft, Facebook, Apple, etc
public async Task Get([FromRoute]string scheme)
{
// 1. Initiate authentication flow with the scheme (provider)
// 2. When the provider calls back to this URL
// a. Parse out the result
// b. Build the app callback URL
// c. Redirect back to the app
}
}
The purpose of this controller is to infer the scheme (provider) that the app is requesting. As well as initiate the authentication flow with the social provider. When the provider calls back to the web backend, the controller parses out the result and redirects to the app’s callback URI with parameters.
Sometimes, you may want to return things like the provider’s access_token back to the app. This can be done via the callback URI’s query parameters. Alternatively, you may want to create your own identity on your server and pass back your own token to the app. What and how you do this part is up to you!
Check out the full controller sample in the Essentials repository.
Get Started with Authentication
Xamarin.Essentials’ Web Authenticator API gives you the ability to easily add an authentication flow into your app using any web backend. ASP.NET core makes it extremely simple to plug in popular social authentication providers to connect your app with.
Check out the Xamarin.Forms and ASP.NET Core samples for more information. As well as our awesome, new WebAuthenticator documentation to get started today!

Hi,
How can I get external user’s information such as name surname and email? it is nonsense if I ask user this information while using social login. Could you give an example please? thanks in advance.
Can I use this with IdentityServer4?
Hi Jon, thanks for sharing this article. Just a
couple of questions. Does the Authorize attribute works in the web API? Do you need to send the token in every request from the the app? Thank you.
Not exactly using the sample provided here. This particular ASP.NET sample is just passing back the access token from Google/Facebook/Apple/whatever and is just illustrating how you would replace the native login components for these providers with this solution.
It’s certainly possible to implement your own logic on the ASP.NET controller which gets an identity and access token for your web app instead of the social provider itself, and then send that back to the client.
I have everything working, but have problems getting FullName for Apple. I'm using iOS 13, when I check Properties of authentication result, there values for "email" and "name" are null. Also, it would be OK for me to get the name on the servers side in another API using obtained access token, but I don't see any API from Apple to get it, like I would do for Facebook with https://graph.facebook.com/me or for Google with https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v1/userinfo.
Anyone was able to get Name of the user?
Updated:Read more
After debugging through source code of Xamarin.Essentials, I discovered two things in this code from AppleSignInAuthenticator:
Great work,
I managed to implement it based on your sample, and Apple SignIn is working, but I am struggling with Facebook. I am constantly getting “URL blocked: This redirect failed because the redirect URI is not white-listed in the app's client OAuth...“.
In facebook app Basic Settings I have set up App domains to "app.domain.com", also in Facebook login settings I have set up Valid OAuth Redirect URIs to "https://app.domain.com/WebAuth/mobileauth". Client OAuth Login set to Yes; Web OAuth Login set to Yes; YesNo Force Web OAuth Reauthentication set to No; Embedded Browser OAuth Login set to Yes; Login from...
I have implemented a Web authentication login, but Cookies are not maintaining in iOS sfsafariviewcontroller. whereas the Chrome custom tab maintains the cookies across the application.
Hi,
we are trying to implement Essentials.WebAuthenticator and it works great when signing with AppleID. The problem that we are having is that when trying to use sign in with google, the code works in Android, but not with iOS. the problem that we are having is that after the Webview opens, the user types his email and password, google sends back the authentication token but our callback URL is displayed on the webView instead of it closing and returning the parameters.
the code that works in Android but not iOS is
Strings ClientRedirectURI = "https://www.company.com/oauthcallback";
string urlcall = URLCreator(Strings.ClientAuthorizeUrl,...
http:// and https:// url’s are special in mobile apps and typically to use them, require that you validate them with apple with Universal App Links, and App Links for Android. It’s not catching these probably because you have not done this process to validate the URL’s for your app.
Im using web authenticator in my xamarin forms app. How to perform signout? I wrote another endpoint to perform the signout., but the next call still returns the active session.
I have been trying to use this code with IdentityServer4 for the authentication service and just cant seem to get it to work, any hints?
if you found a solution please post it here
Checkout: https://www.davidbritch.com/2020/04/authentication-from-xamarinforms-app_8.html
Thank you!!! 😀
Jon, This is a great capability, thank you!
I have been trying to modify the sample code to implement the authentication services as an Azure Function.
I have a working Azure Function setup in a VS2019 Function project, and added the nuget for Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.MicrosoftAccount provider to the project.
I implemented a startup method shown below, to configure the services. But when I call the builder.Services.AddAuthentication(...) with the provider setup, it fails with the following exception:
Code:
[assembly: WebJobsStartup(typeof(MyApp.Functions.Startup))]Read more
namespace MyApp.Functions
{
public class Startup : IWebJobsStartup //, IExtensionConfigProvider
{
void IWebJobsStartup.Configure(IWebJobsBuilder builder)
{
//builder.Services.AddControllers();
builder.Services.AddAuthentication(o => { o.DefaultScheme = CookieAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme; });
I am not sure that that library is compatible with Azure Functions as it requires ASP.NET Core. You can spin that up like the article points out and a sample here: https://github.com/xamarin/Essentials/blob/develop/Samples/Sample.Server.WebAuthenticator/Controllers/MobileAuthController.cs
We do have a sample of Apple ID with Azure Functions that may help you out to give you some insight: https://github.com/Redth/Xamarin.AppleSignIn.Sample/tree/master/AppleSignInAzureFunction
Read next
Virtual Xamarin and .NET Events in April
Embedded Fonts: Custom Fonts in Xamarin.Forms
Stay informed