Summary: Microsoft Scripting Guy, Ed Wilson, talks about using the Windows PowerShell Env: PSDrive.
 Hey, Scripting Guy! I was attending a Windows PowerShell user group meeting the other day, and I overheard someone talking about using an Environment PowerShell Drive. Huh? I did not want to ask him about this, because I would feel foolish. I have been using Windows PowerShell for a while now, but I do not have an Environmental PowerShell drive that I know of. Can you explain what this is, how I would get one, and why I would even want to use such a thing?
Hey, Scripting Guy! I was attending a Windows PowerShell user group meeting the other day, and I overheard someone talking about using an Environment PowerShell Drive. Huh? I did not want to ask him about this, because I would feel foolish. I have been using Windows PowerShell for a while now, but I do not have an Environmental PowerShell drive that I know of. Can you explain what this is, how I would get one, and why I would even want to use such a thing?
—BB
 Hello BB,
Hello BB,
Microsoft Scripting Guy, Ed Wilson, is here. My endless days of searching have finally come to an end—my new laptop finally arrived. I have taken it out of the box, and plugged it in to charge the battery, but that is about it. I know I will be spending the next several weeks setting up the thing.
Where is the Environment PowerShell drive?
To an extent, there really is no such thing as an Environment PowerShell drive. If I use the Get-PSDrive cmdlet, I see that there is a drive named Env, and a provider named Environment. This command and associated output are shown here.
PS C:\> Get-PSDrive
Name Used (GB) Free (GB) Provider Root
—- ——— ——— ——– —-
Alias Alias
C 40.70 108.00 FileSystem C:\
Cert Certificate \
D FileSystem D:\
Env Environment
Function Function
HKCR Registry HKey_Classes_Root
HKCU Registry HKEY_CURRENT_USER
HKLM Registry HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
Variable Variable
WSMan WSMan
If I use the Get-PSProvider cmdlet, I see the names of the PS Providers and the capabilities and drives associated with them as shown here.
PS C:\> Get-PSProvider
Name Capabilities Drives
—- ———— ——
Alias ShouldProcess {Alias}
Environment ShouldProcess {Env}
FileSystem Filter, ShouldProcess, Crede… {C, D}
Function ShouldProcess {Function}
Registry ShouldProcess, Transactions {HKLM, HKCU, HKCR}
Variable ShouldProcess {Variable}
Certificate ShouldProcess {Cert}
WSMan Credentials {WSMan}
Exploring the Env PowerShell drive
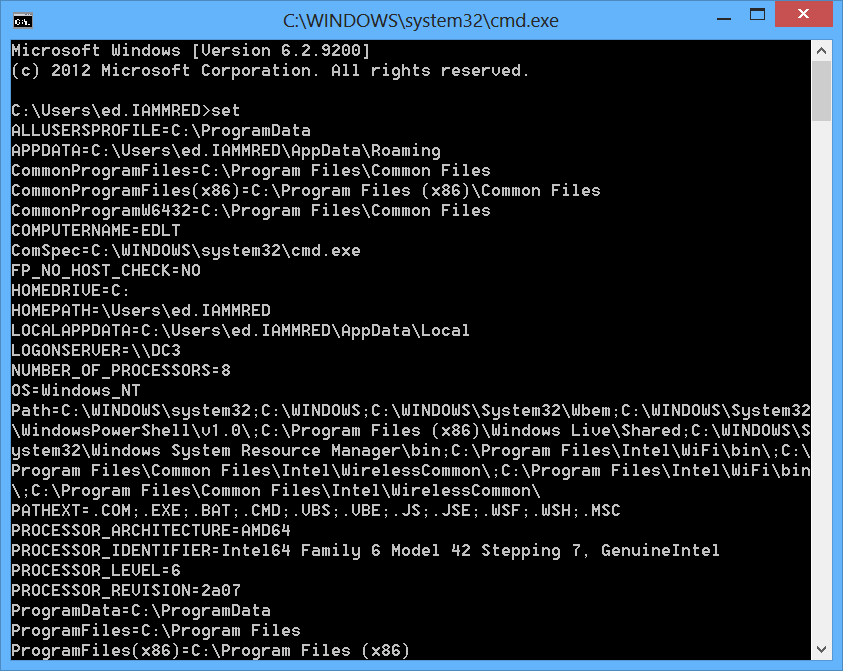
The Env drive created by the Environment PS provider provides access to the environmental variables. These are the same variables you would see if you opened a traditional CMD prompt and typed the command set. This output is shown here.
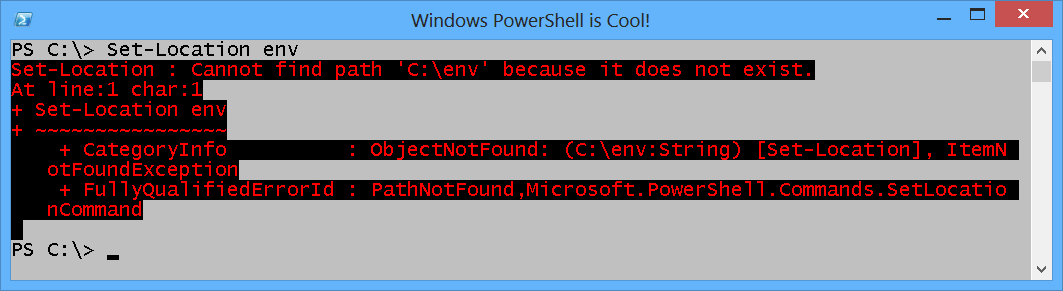
When I try to set my working location to the Env drive, an error arises. This is shown in the following image.
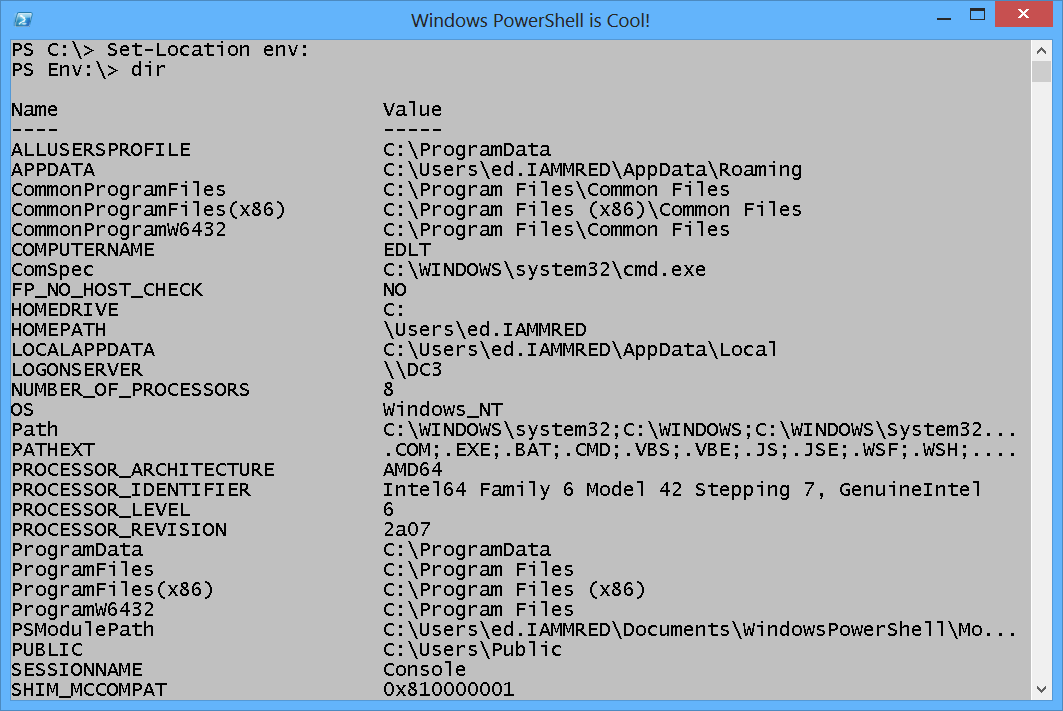
The error message is a bit misleading. It says it cannot find c:\env because it does not exist. So, I need to use drive notation and include a colon at the end of the drive name. After I set my working location to the Env drive, I can use the same type of commands I use on drive C or any other drive. This is shown here.
I can use the standard Windows PowerShell cmdlets such as Get-Item, Get-Content, Get-ChildItem, Set-Item, Set-Content to work with the Env drive. For example, I can use the Get-Item cmdlet to return the path for the temp Environment variable. This technique is shown here.
PS Env:\> Get-Item temp
Name Value
—- —–
TEMP C:\Users\ED6C0B~1.IAM\AppData\Local\Temp
I can also use the Get-Content cmdlet to retrieve the value. This technique is shown here.
PS Env:\> Get-Content temp
C:\Users\ED6C0B~1.IAM\AppData\Local\Temp
The members of the Environment variables appear here.
PS Env:\> Get-Item temp | Get-Member -MemberType *property
TypeName: System.Collections.DictionaryEntry
Name MemberType Definition
—- ———- ———-
Name AliasProperty Name = Key
PSDrive NoteProperty System.Management.Automation.PSDriveInfo PSDrive=Env
PSIsContainer NoteProperty System.Boolean PSIsContainer=False
PSPath NoteProperty System.String PSPath=Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Enviro…
PSProvider NoteProperty System.Management.Automation.ProviderInfo PSProvider=…
Key Property System.Object Key {get;set;}
Value Property System.Object Value {get;set;}
This means that I can directly access the value property as shown here.
PS Env:\> (Get-Item temp).value
C:\Users\ED6C0B~1.IAM\AppData\Local\Temp
I can also use a shortcut method to access this. This technique is shown here.
PS Env:\> $env:temp
C:\Users\ED6C0B~1.IAM\AppData\Local\Temp
This shortcut technique has the advantage of being usable from any PSDrive location as shown here.
PS Env:\> sl c:
PS C:\> $env:temp
C:\Users\ED6C0B~1.IAM\AppData\Local\Temp
BB, that is all there is to using the Env PowerShell drive. Windows PowerShell Provider Week will continue tomorrow when I will talk about working with the Alias PSDrive.
I invite you to follow me on Twitter and Facebook. If you have any questions, send email to me at scripter@microsoft.com, or post your questions on the Official Scripting Guys Forum. See you tomorrow. Until then, peace.
Ed Wilson, Microsoft Scripting Guy

0 comments