In this post, Sr. App Dev Managers Bernard Apolinario and Ajay Tanikella gives a thorough explanation of Blockchain concepts.
What is Blockchain?
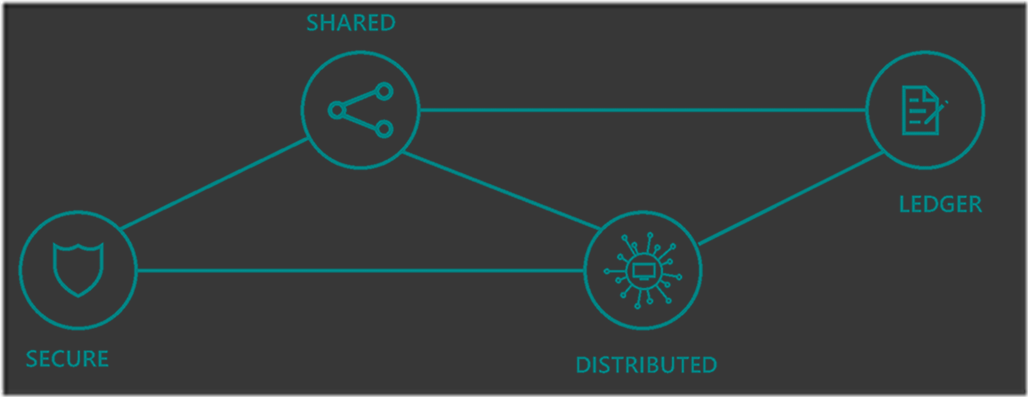
Blockchain is a Secured, Shared, Distributed ledger. It’s a concept with the following key aspects:
- Ledger: It’s a not a typical accounting ledger. It’s a ledger that tracts value exchange between two parties. Every transaction written on the ledger is immutable.
- Secured: Blockchain uses different cryptographic techniques to secure and validate transactions.
- Shared: It enables parties to share and conduct business without intermediaries.
- Distributed: Everybody on the network will have a copy of the entire chain.
Reference: https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/blog/accelerating-the-adoption-of-enterprise-blockchain/
Benefits of Blockchain
- Eliminate Intermediaries – Blockchain enables peer to peer transaction, removing the need for intermediaries such as banks, government and other traditional financial institutions.
- Reduce Fraud – Reduces fraud by bringing more transparency and improved traceability.
- Increase Efficiency – Increases efficiency by removing the middle man and lowering the transaction costs.
- Increase Resiliency – Since the ledger is distributed, a corruption of one ledger should have no impact on the other ledgers. This also negates the risk of an attack since there is no single entity to attack.
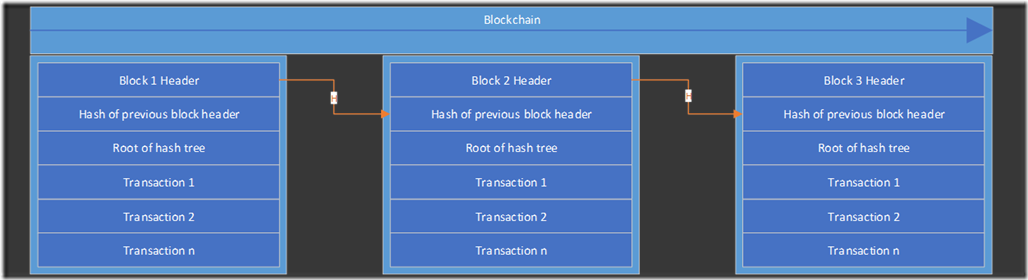
Blockchain Diagram
Different Blockchains
There are 3 different blockchains.
- Public Blockchains: Anybody can join this network.
- Example Bitcoin, Litecoin…
- Private Blockchains: One controlling party that allow access to the network. Generally, these are within an organization.
- Example: Documents to be shared between departments.
- Permissioned or Consortium or Federated Blockchains: More than one party controls the access to the network.
- Ex: Rewards Program, wherein the bank and the merchant share the info.
Blockchain Consensus Protocols
Some of popular Blockchain consensus algorithms are listed below.
- Proof of Work (PoW): A requirement where the participants perform some type of work. The work must be relatively difficult to complete but easy for the network to validate
- Proof Stake (PoS): Instead of using expensive hardware to solve the computation problem, PoS approach has no mining or requirement for work. It uses a pre-determined algorithm to identity the node that generates a new block.
- Proof of Activity (PoA): This is a combination of Proof of Work and Proof Stake. The blocks are created by the miner without any transactions using PoW. PoS is used to complete the block with the transactions.
- Proof of Burn (PoB): Instead of spending money on expensive hardware, you send the money/valuables to location that cannot be retrieved, basically burning the currency.
- Proof of Capacity (PoC): Depends on the hard disk space. The more capacity you have the more chances you will have to create the block.
- Proof of Elapsed time (PoET): Created by Intel. Like Proof of Work but consumes much less electricity. Instead of participants solving “cryptographic puzzles”, the algorithm uses a Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) to ensure blocks get produced in random lottery order, but without requiring any work.
Versions
- Version 1.0: Simple ledger that record transactions
- Version 2.0: Ledger with Smart Contracts and Logic Tier
- Version 3.0: Ledger with Smart Contracts in Cloud Servicing Multilayer Middleware and Cryplets (Microsoft Innovation)
Enterprise World
Blockchain is disruptive technology that will impact several industries. This technology will transform Financial Industry, Global Real Estate, Insurance, Auto to Government Entities and many more. Its reshaping the world with new business models. But adoption of Blockchain in the enterprise world might be little challenging because of,
- Lack of Governance
- Confidentiality
- Unable to leverage existing tools and skills
- Integration with existing system is complicated
Microsoft in Blockchain
Microsoft is thinking about blockchain at a broader level, going way beyond just cryptocurrencies. Microsoft believes that its really about the data layer that can be shared across organizations to do business in safe and secure manner
Microsoft’s commitment to bring Blockchain to enterprise world.
- Providing platform for ledgers technology
- Collaborate with delivery partners
- Built tools and resources to accelerate the development
Tools
- Confidential Consortium (Coco) framework for through put and low latency with rich and flexible confidentiality models. Microsoft plans to open source Coco framework in the future.
- App Builder (Private Preview): Provides assets and ARM templates for rapid development of blockchain POC’s on Azure. Apply Here
- Enterprise Smart Contracts: Secure, Scalable with Enterprise ready components that can be combined to create contract templates
- Blockchain as a Service (BaaS): Microsoft Platform in Azure that provides Blockchain technologies. It is available now in Microsoft’s Dev Test Labs. Click here to get started.
Additional links
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/blog/topics/blockchain/
Premier Support for Developers provides strategic technology guidance, critical support coverage, and a range of essential services to help teams optimize development lifecycles and improve software quality. Contact your Application Development Manager (ADM) or email us to learn more about what we can do for you.

0 comments