If you are involved in support or development, often you need to use secrets, passwords, or subscription keys in PowerShell scripts. These need to be kept secure and separate from your scripts but you also need access to them ALL THE TIME.
So instead of hand entering them every time they should be stored in a key store of some sort that you can access programmatically. Often off the shelf keystores are not available in your environment or are clumsy to access with PowerShell. A simple way to have easy access to these secrets with PowerShell would be helpful.
You could simply have them in plain text, on your machine only, making it relatively secure. However, there are many risks with this approach, so adding some additional security is an excellent idea.
The .NET classes sitting behind PowerShell provide some simple ways to do this. This blog will go through
- Basic encryption / decryption
- Using it day-to-day
- Your own form-based key store
Basic encryption / decryption
The protect and unprotect methods available as part of the cryptography classes are easy to use. However they use Byte arrays that we can simplify by wrapping their use in a String.
The following examples can be found at the MachineAndUserEncryption.ps1 module in my ps-community-blog repository on GitHub.
Encryption
Function Protect-WithUserKey {
param(
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[string]$secret
)
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.Security
$bytes = [System.Text.Encoding]::Unicode.GetBytes($secret)
$SecureStr = [Security.Cryptography.ProtectedData]::Protect(
$bytes, # contains data to encrypt
$null, # optional data to increase entropy
[Security.Cryptography.DataProtectionScope]::CurrentUser # scope of the encryption
)
$SecureStrBase64 = [System.Convert]::ToBase64String($SecureStr)
return $SecureStrBase64
}Just going through the lines we can see
- PowerShell needs to know about the .NET classes (I have tested under version 5 & 7 of PowerShell)
- We need to convert our string into a Byte array
- Use the .NET class to encrypt
- Convert the encrypted Byte array to a string for easy storage and retrieval
- Return that string
Decryption
Function Unprotect-WithUserKey {
param (
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[string]$enc_secret
)
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.Security
$SecureStr = [System.Convert]::FromBase64String($enc_secret)
$bytes = [Security.Cryptography.ProtectedData]::Unprotect(
$SecureStr, # bytes to decrypt
$null, # optional entropy data
[Security.Cryptography.DataProtectionScope]::CurrentUser) # scope of the decryption
$secret = [System.Text.Encoding]::Unicode.GetString($bytes)
return $secret
}Steps are identical for the decryption, using slightly different methods
- PowerShell needs to know about the .NET classes
- We need to convert our string into a Byte array
- Use the .NET class to decrypt
- Convert the encrypted Byte array to a string
- Return that string
Using it day-to-day
This is really useful if you are doing repetitive tasks that need these values. Often in a support role, investigations using API’s can speed up the process of analysis, and also provide you with a quick way to do fixes that don’t require heavy use of a GUI based environment.
Assigning a key to a secret value, and storing that in a hash table format is the simplest way to have access to these values AND keep them stored locally with a degree of security. Your code can then dynamically look up these values, and if other support people store the same key locally the same way (often with different values, think of an API password and or username pair) then your script can work for everyone.
Again, MachineAndUserEncryption.ps1 in my repository on my GitHub has functions for persisting and
using this information. For compatibility with version 5 & 7 you also need the function
ConvertToHashtableV5.
I would also recommend using Protect-WithMachineAndUserKey and Unprotect-WithMachineAndUserKey
when implementing locally, they add another layer of protection.
Your own form-based key store
If you have followed my other 2 blogs about a scalable environment and simple form development then using the resources from these we can easily create our own form to manage our secrets. In fact, if you have downloaded and installed the modules for either of those blogs (they are the same, and this blog references the same as well), you have it ready to go.
Once you have your environment set up, simply run the cmdlet:
New-EncryptKeyFormand if all is set up correctly, you should see
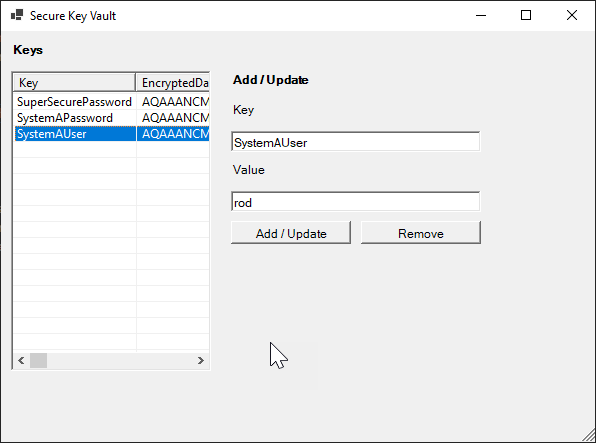
Conclusion
Balancing the pragmatic ease of use and security concerns around secrets you may need to use all day every day can be a fine balancing act. Using some simple methods, we can strike that balance and hopefully be securely productive.
Lets secure some stuff!


Nifty solution, a couple notes probably for the larger audience:
FWIW, If you don't need the machine-scoped encryption key, I believe Convertfrom-Securestring gives you the same functionality (encrypting a string w/ the windows/dotnet DPAPI without having to mess w/ dotnet types directly.). Before the SecretManagement module, I used it with just a couple lines in a $PROFILE function to save/read the encrypted form in a file locally.
The examples use a var named $SecureStr that could be a bit confusing, you might want to clarify that it is not a system.security.securestring (which is somewhat deprecated and not encrypted in-memory), but that...
That last screenshot alone suggests it’s actually good enough to use as a basic password manager. Can it be used for such a purpose?
And if it is being used as a password manager, where does the cmdlet store the keys / passwords? Any way of extracting and sharing it among others users and Windows computers?
It can be used as a basic password manager, but you need to implement all the functionality in the linked GitHub repository. That is fairly straight forward following the instructions (its a matter of downloading modules and making sure those modules are loaded when your session starts - linked blogs in the description describe this in detail).
The implementation lets you determine where the file is stored and this is at the bottom of NewEncryptKeyForm.ps1, which is currently defaulting to the current users Documents directory.
As for sharing the file, this may be pointless as the encryption is set to...
I guess if we’re from the future, we could use SecretManagement and SecretStore. ;P
Fair, very fair. Guess I know what I’ll be playing with next 🙂
I was going to ask what the difference between this article and that article were. But I’m guessing your reply answers that question! 🙂
Perhaps this segues into another article about discovering existing code repos associated with desired capabilities? Particularly how to evaluate the underlying code. I know I’ve run into that wall of preexisting code invalidating my truckload of wasted-code more often than I’d care to.
I have actually given this a fair bit of thought over the last couple of weeks. And you know what, there is a difference and I think a place for both. Often you need something simple, and the above solution is really a handful of lines that you can understand and change if you want. The (honestly) much more thorough and complete SecretManagement and SecretStore solution is scalable, extendable and all the things I would want from an industrial solution.
A good example of what a simpler solution provides is I had already extended the encryption to Machine...