<BoxView
x:Name="myBoxView"
Color="Red"
HeightRequest="100"
WidthRequest="{Binding Source={x:Reference myBoxView}, Path=HeightRequest}}" />
<BoxView
Color="Red"
HeightRequest="100"
Width="{Binding Source={RelativeSource Self}, Path=HeightRequest}"/>

<CollectionView
ItemsSource="{Binding Drinks}">
<CollectionView.ItemTemplate>
<DataTemplate>
<Grid>
...
<Button
Command="{Binding Source={RelativeSource AncestorType={x:Type viewmodels:RelativeSourceViewModel}}, Path=BuyCommand}"
CommandParameter="{Binding Source={RelativeSource Self}, Path=BindingContext}"
... />
</Grid>
</DataTemplate>
</CollectionView.ItemTemplate>
</CollectionView>
In this example, the BindingContext of the page is set to the RelativeSourceViewModel property of itself. The CollectionView binds to the Drinks property of the viewmodel. The DataTemplate, which defines the appearance of each item in the CollectionView, contains a Button. The button’s Command property is bound to the BuyCommand in its parent’s viewmodel.
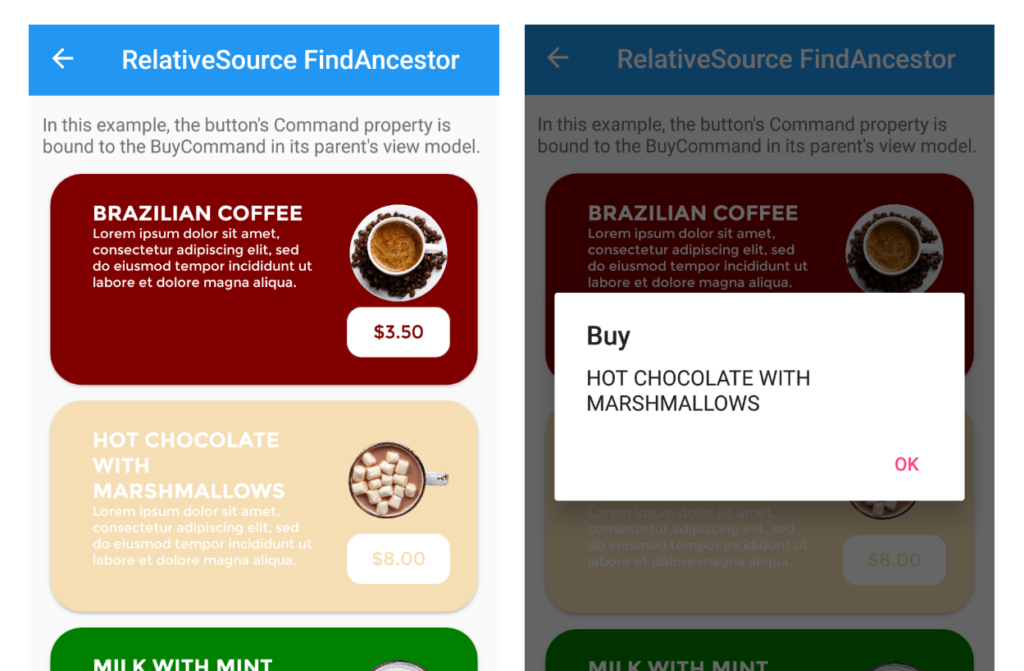
<ControlTemplate x:Key="DrinkCardViewControlTemplate">
<Grid>
<Frame
BindingContext="{Binding Source={RelativeSource TemplatedParent}}">
<StackLayout>
<Label
Text="{Binding DrinkTitle}"
... />
...
</Grid>
</Frame>
</Grid>
</ControlTemplate>
<controls:DrinkCardView
DrinkTitle="BRAZILIAN COFFEE"
DrinkDescription="Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua."
DrinkColor="Maroon"
DrinkImageSource="coffee.png"
ControlTemplate="{StaticResource DrinkCardViewControlTemplate}" />


P1, example 2:
Width=”{Binding RelativeSource={RelativeSource Self}, Path=HeightRequest}”/>
Maybe Source is the correct word?
You’re right Dmytro. It’s already changed.
Great article, I’ve been looking forward to this feature.
From which Xamarin.Forms version is this feature supported?
Hi Reed,
The first version where it was available was 4.3-pre1 https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/xamarin/xamarin-forms/release-notes/4.3/4.3.0-pre1
Excellent, this is very useful. Now we don’t have to be creating new ViewModels for specific controls in a page.