AI Shell Preview 6 is here!
We are super excited to announce the latest preview release of AI Shell. This release focuses on enhancing the user experience with new features, improved error handling, and better integration with Model Context Protocol (MCP) tools.
What’s new at a glance
- MCP client integration
- Built-in tools
Resolve-Errorcommand improvements- Aliases and flows for staying in your terminal
MCP Integration
AI Shell now acts as an MCP client, which allows you to add any MCP server to your AI Shell experience. Connecting to an MCP server massively improves the capability of your AI Shell giving you the tools that provide more relevant data or carry out actions!
Adding MCP Servers
To add an MCP server, create an mcp.json file in $HOME\.aish\ folder. The following example
shows two MCP servers: everything and filesystem. You can add any MCP servers you want.
{
"servers": {
"everything":{
"type":"stdio",
"command":"npx",
"args":["-y", "@modelcontextprotocol/server-everything"]
},
"filesystem": {
"type": "stdio",
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"-y",
"@modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem",
"C:/Users/username/"
]
}
}
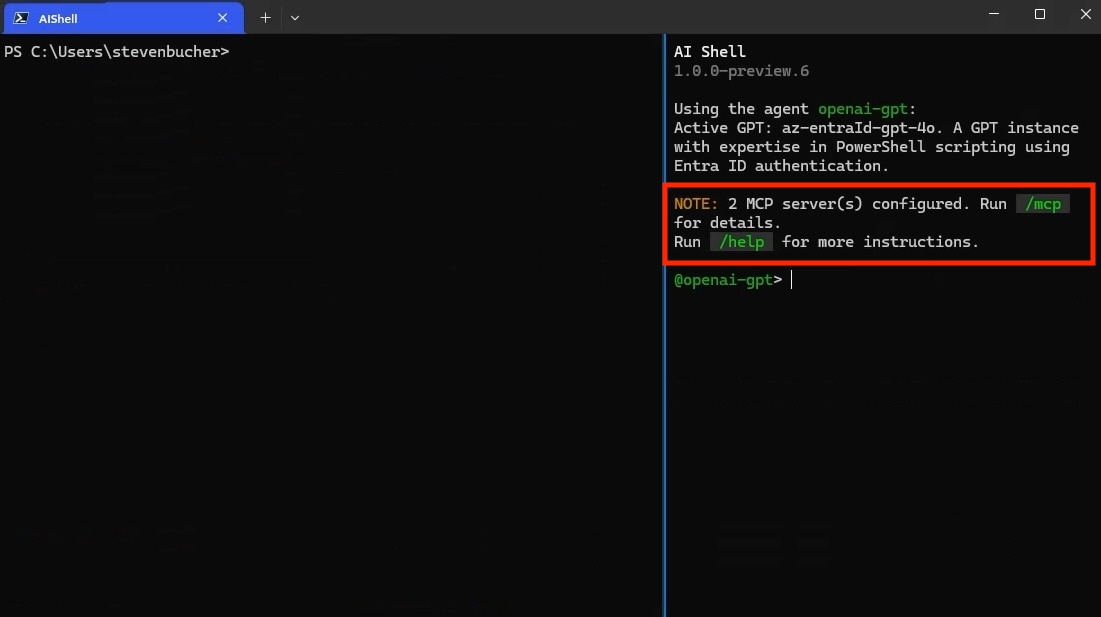
}If it’s a remote MCP server, change the type to https. You know that you have successfully added
an MCP server when you see it in the AI Shell UI. You can confirm that it’s running by checking the
status of the server through the /mcp command. Using /mcp also lists each MCP Server and the
tools available.
NOTE
You must haveNode.js or uv installed to use MCP servers that
use those command lines tools.Standalone experience with AI Shell and MCP Servers
MCP servers enhance your standalone experience with AI Shell, allowing your command line to use MCP
servers and AI to perform tasks. For example, @simonb97/server-win-cli is an MCP server that
allows you to run commands on your Windows machine, whether it be PowerShell, CMD, Git Bash, or any
configured shell you use! It also provides configuration settings to define which commands and
operations are allowed to run.
CAUTION
Please note this is a community MCP server and not an official Microsoft MCP Server. We encourage you to do your own research and testing before using it.
Additional MCP servers:
Built-in Tools for AI Shell
This release introduces built-in tools that are now accessible to agents within AI Shell. These commands are similar to MCP Server tools, but are exclusive to the AI Shell experience. These tools are designed to enhance the AI Shell experience by providing context-aware capabilities and automation features. They can be used in conjunction with the MCP servers to create a powerful AI-driven shell environment.
| Tool Name | Description |
|---|---|
get_working_directory |
Get the current working directory of the connected PowerShell session, including the provider name (e.g., FileSystem, Certificate) and the path (e.g., C:\\, cert:\\). |
get_command_history |
Get up to 5 of the most recent commands executed in the connected PowerShell session. |
get_terminal_content |
Get all output currently displayed in the terminal window of the connected PowerShell session. |
get_environment_variables |
Get environment variables and their values from the connected PowerShell session. Values of potentially sensitive variables are redacted. |
copy_text_to_clipboard |
Copy the provided text or code to the system clipboard, making it available for pasting elsewhere. |
post_code_to_terminal |
Insert code into the prompt of the connected PowerShell session without executing it. The user can review and choose to run it manually by pressing Enter. |
run_command_in_terminal |
This tool allows you to execute shell commands in a persistent PowerShell session, preserving environment variables, working directory, and other context across multiple commands. |
get_command_output |
Get the output of a command previously started with run_command_in_terminal. |
Note
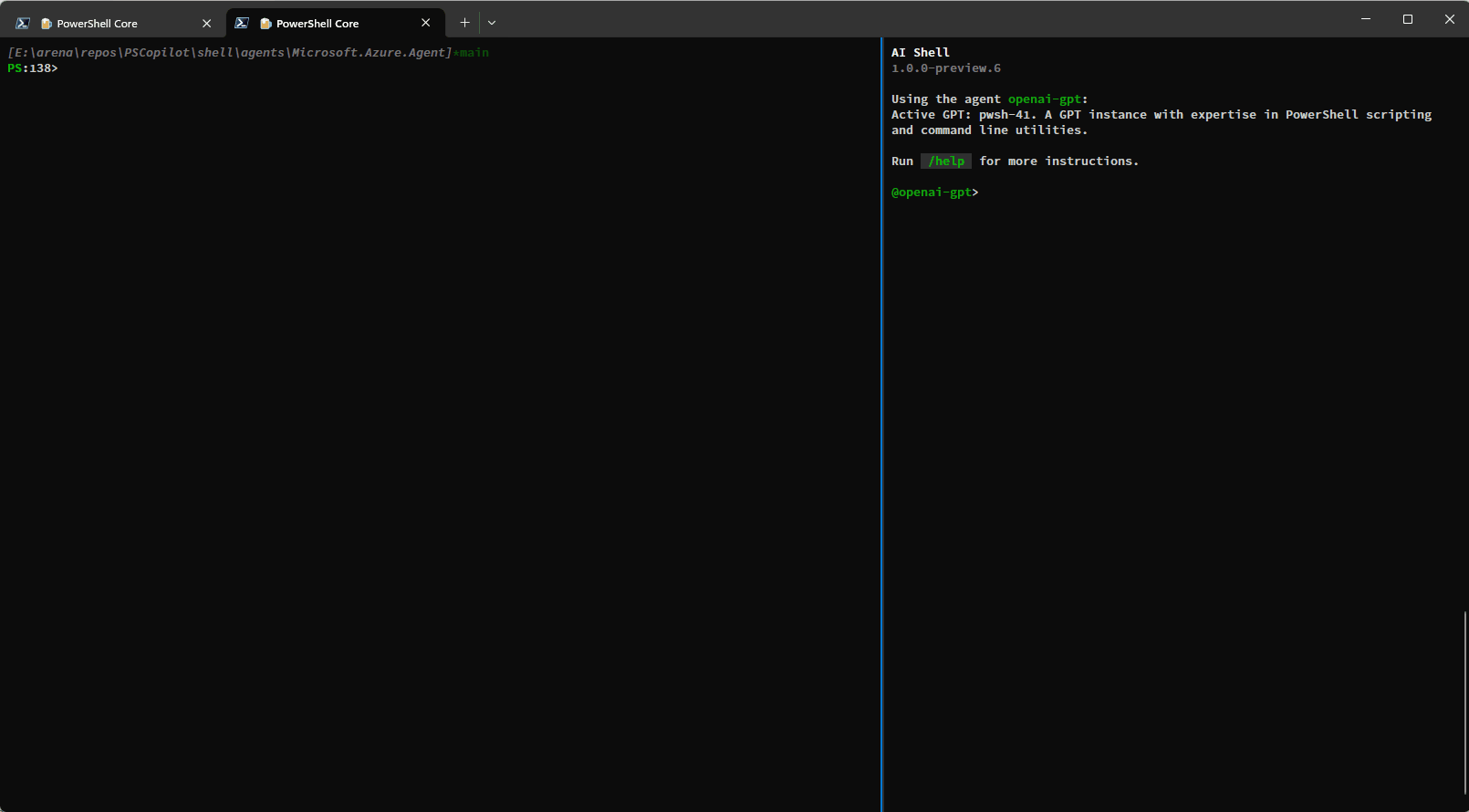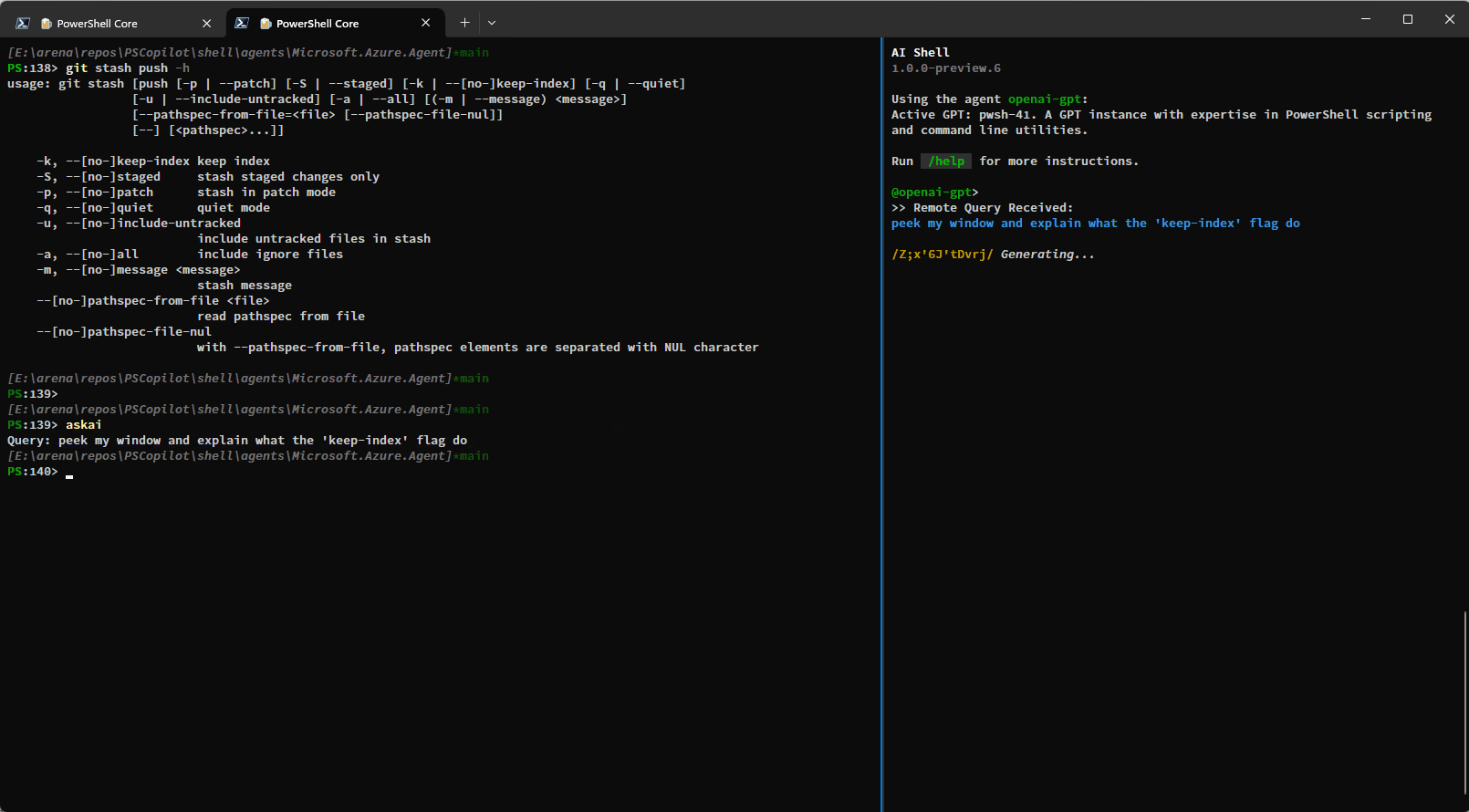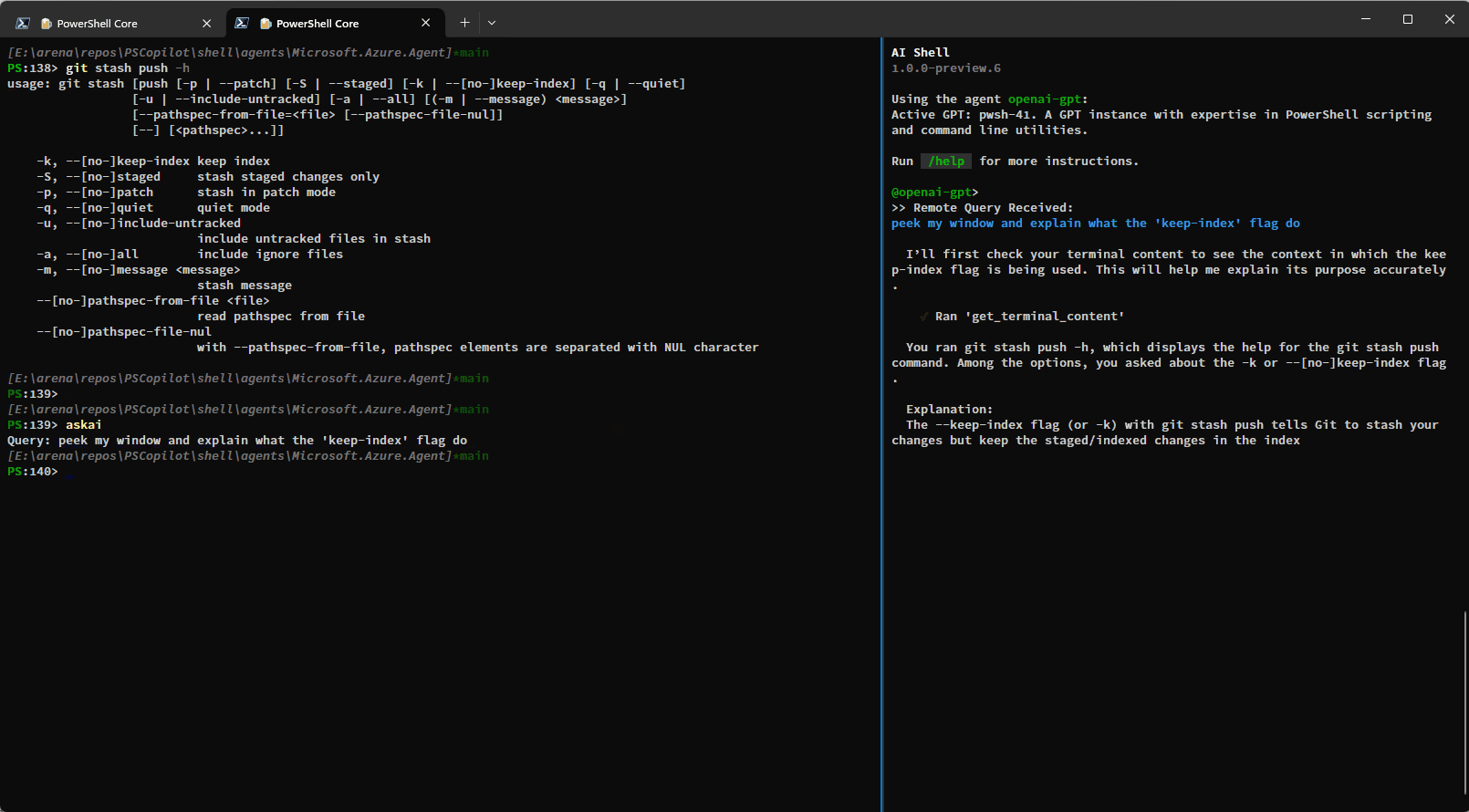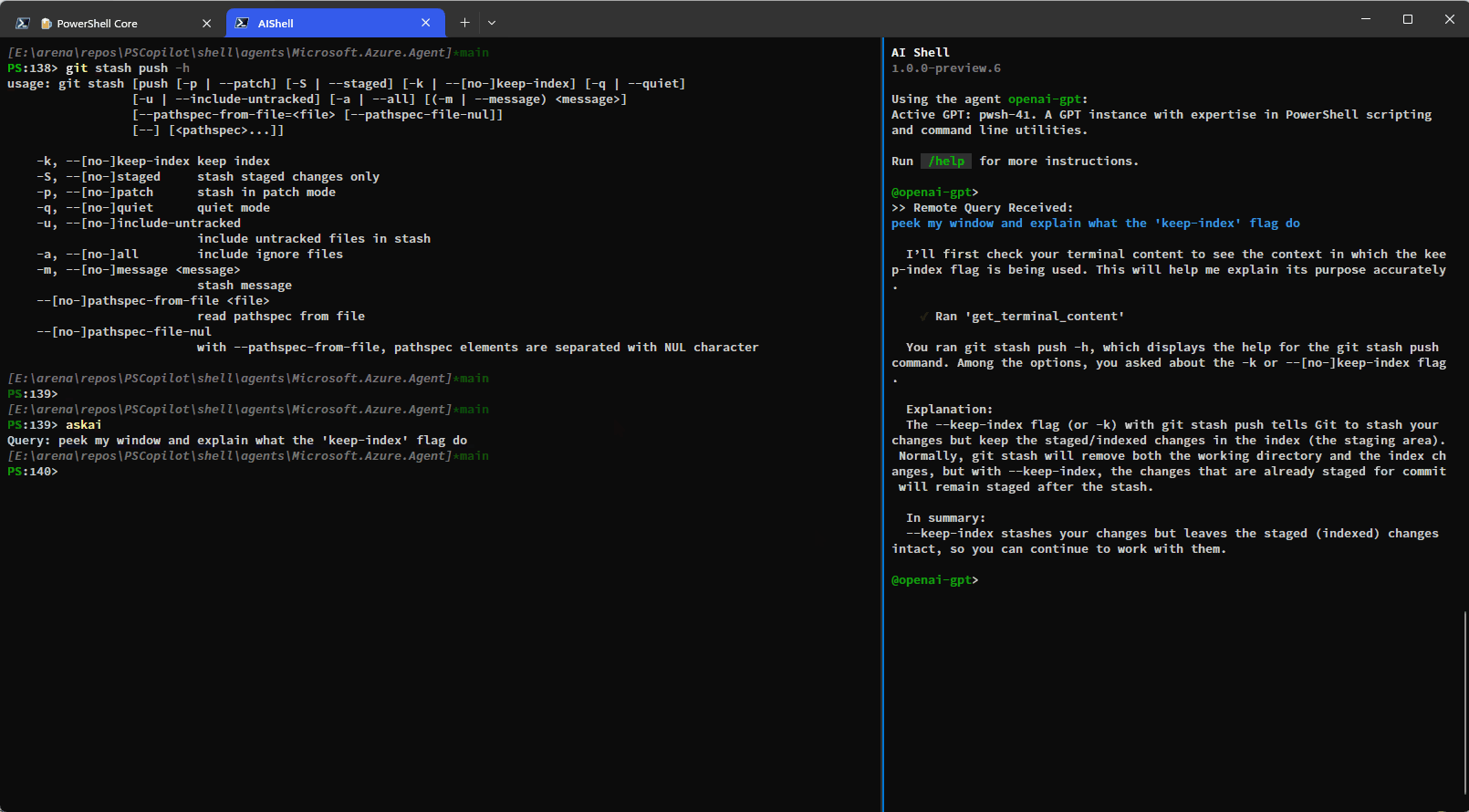
The built-in tools rely on the side-car experience with a connected PowerShell session and provide enhanced context awareness and automation capabilities.Here is a simple demo showing how you can have AI Shell run commands on your behalf using the
run_command_in_terminal tool:
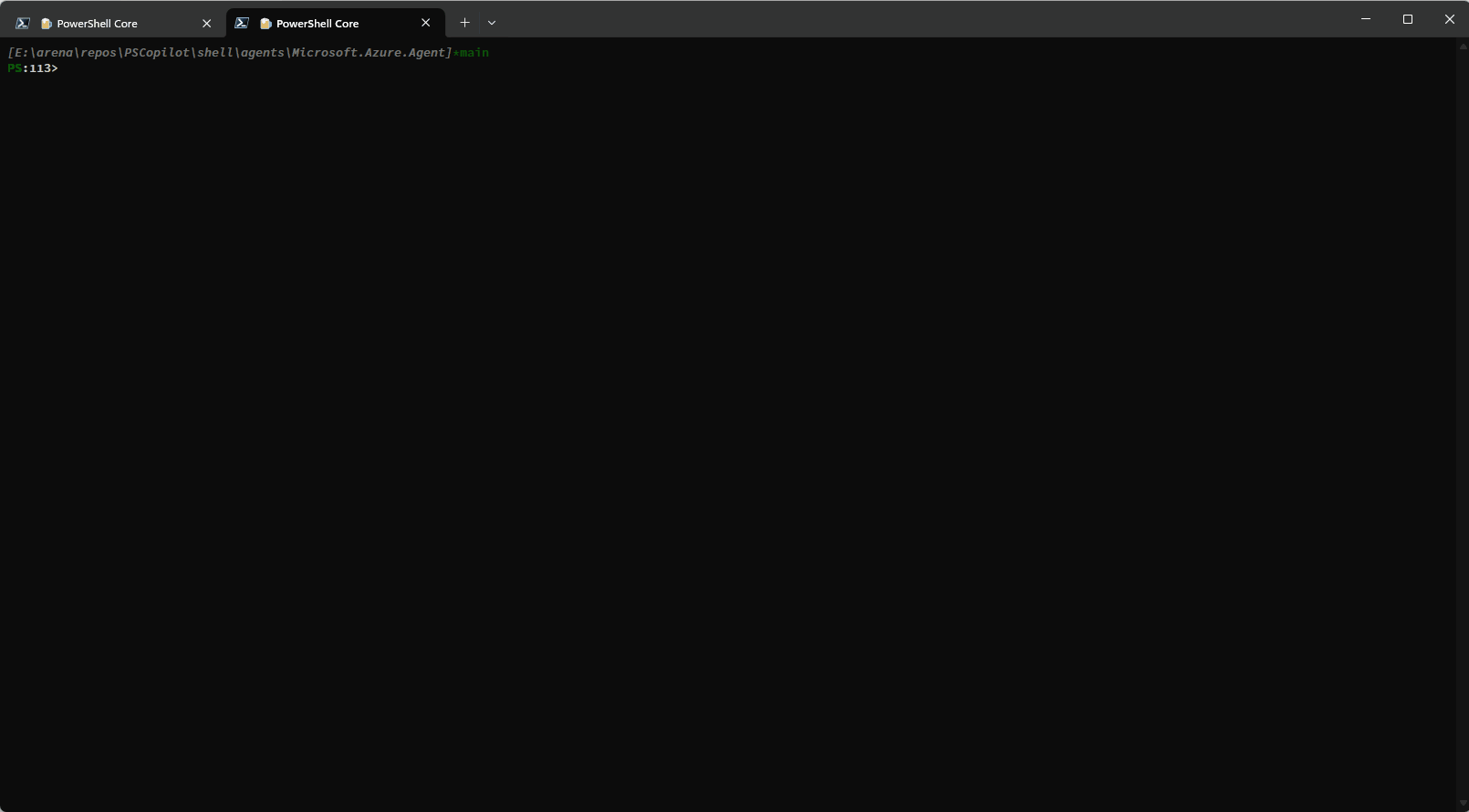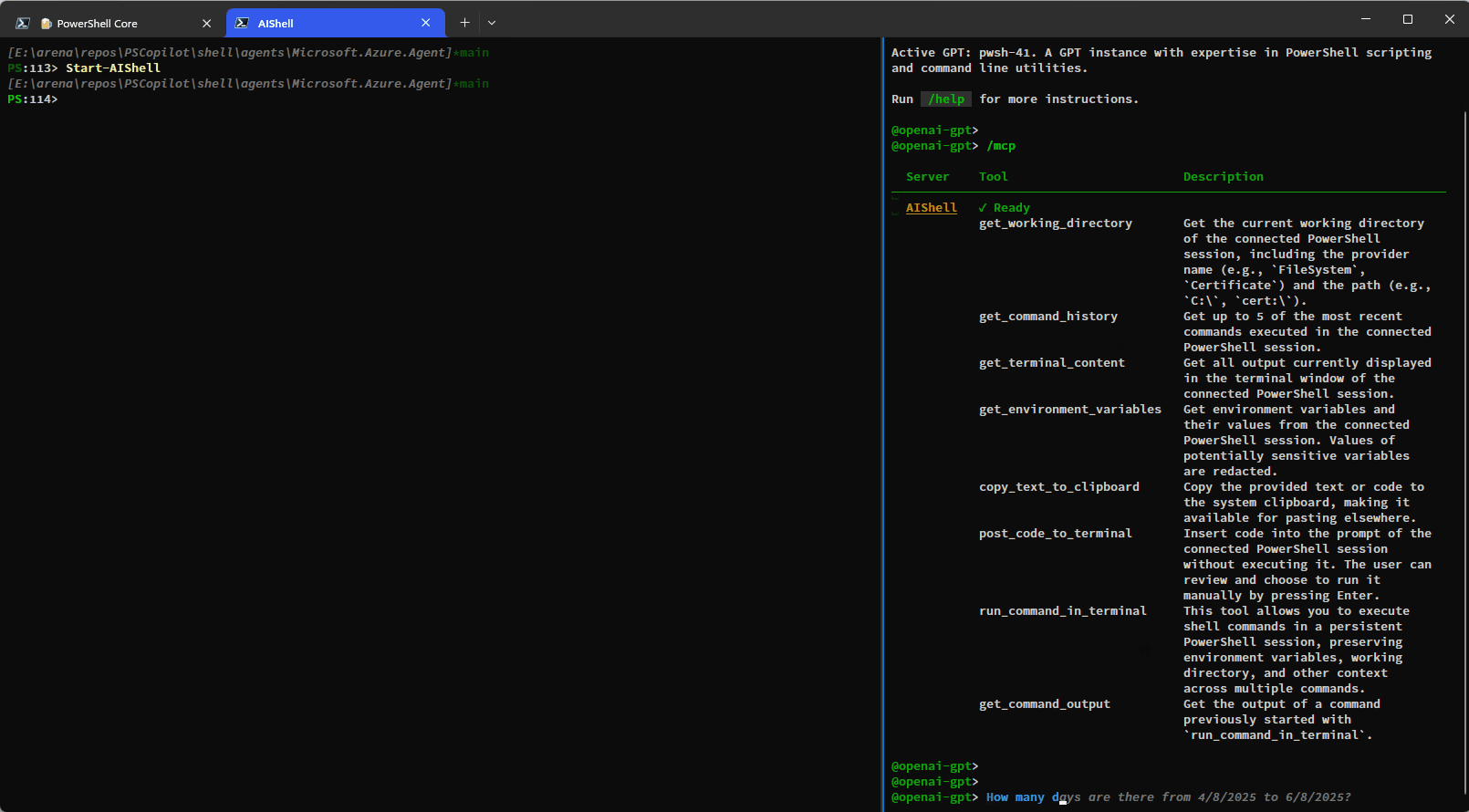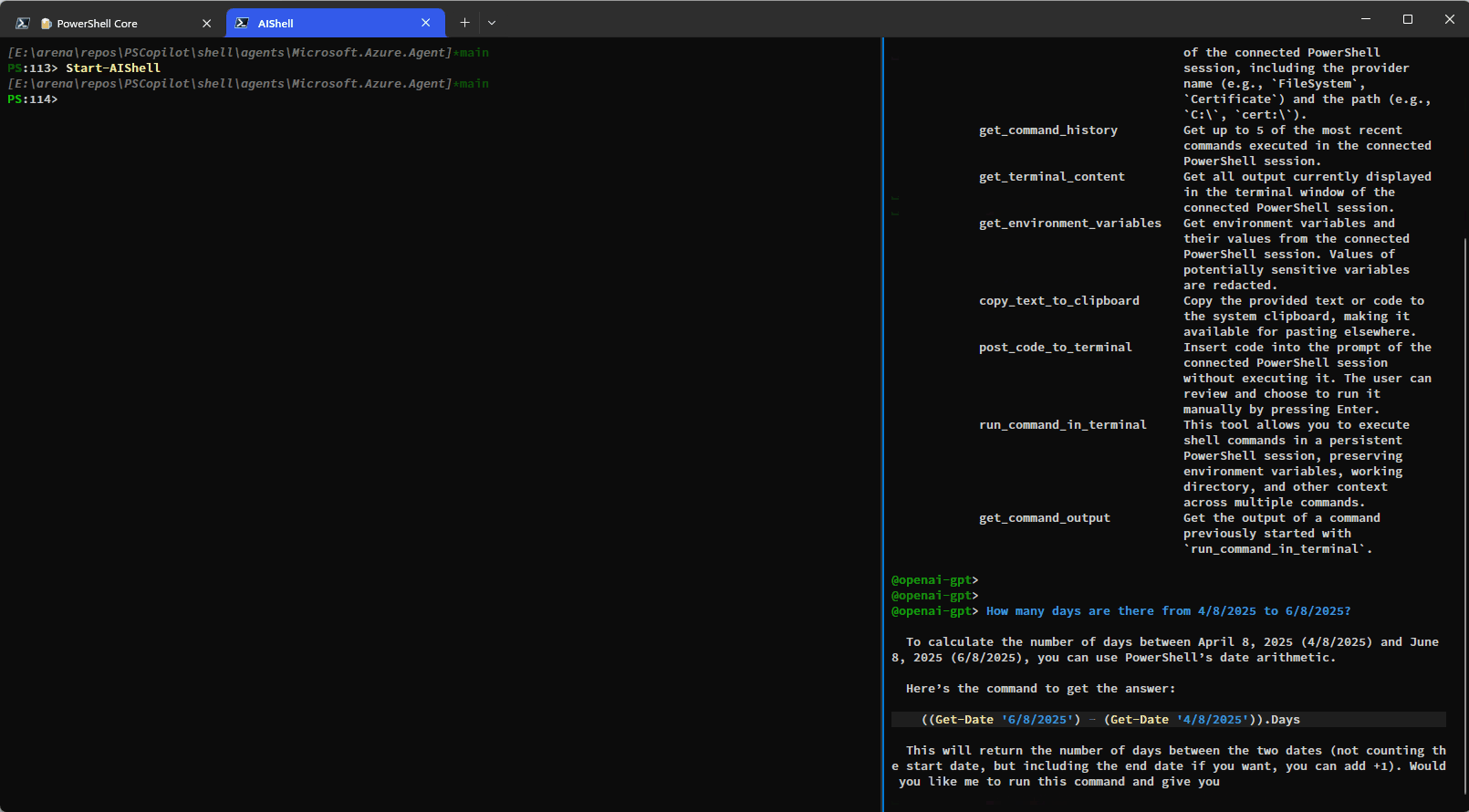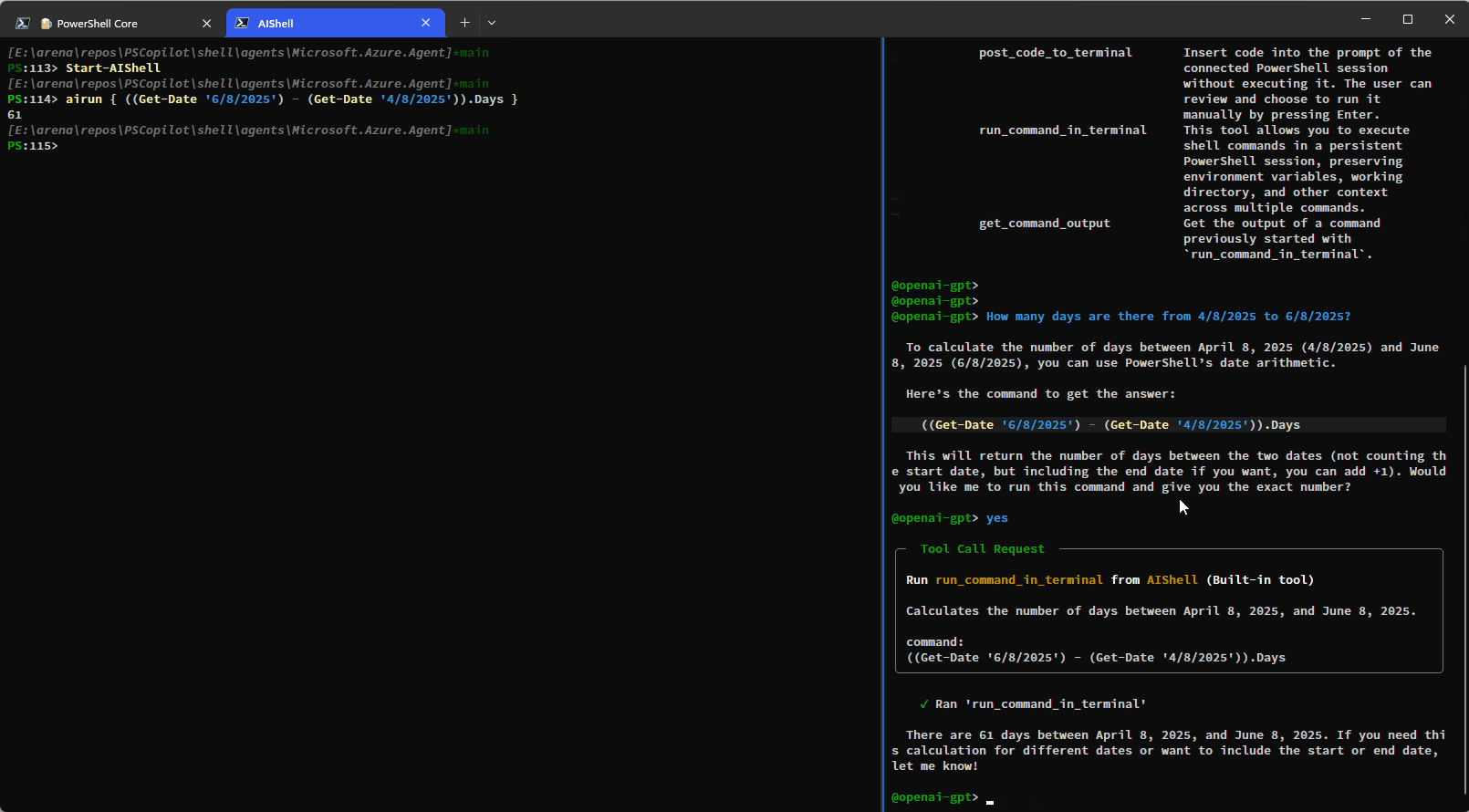
This example shows how additional context is provided to AI Shell to improve results:
You can also use the get_terminal_content tool to get the content from the connected terminal and
provide it to AI Shell to help it understand what you are trying to do:
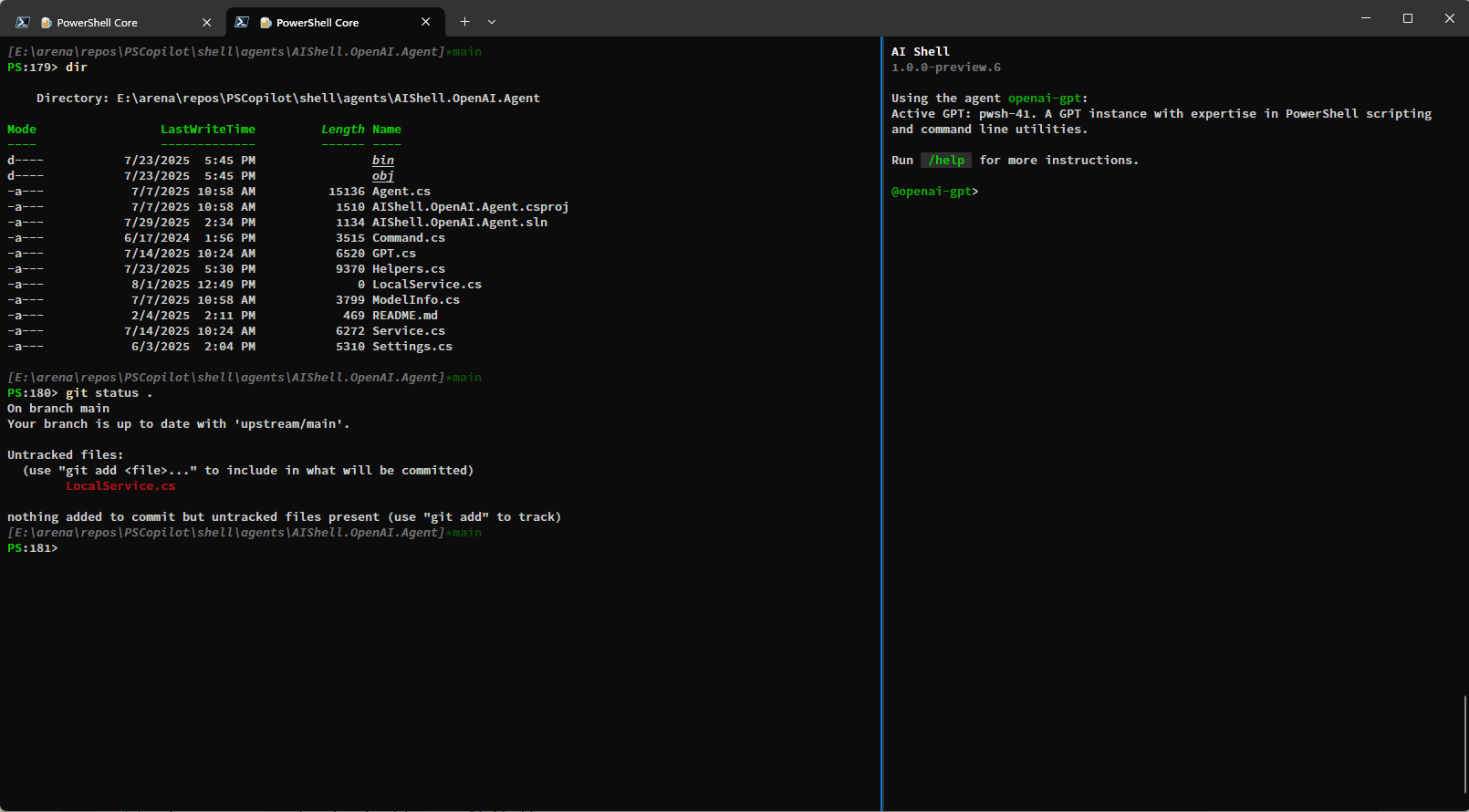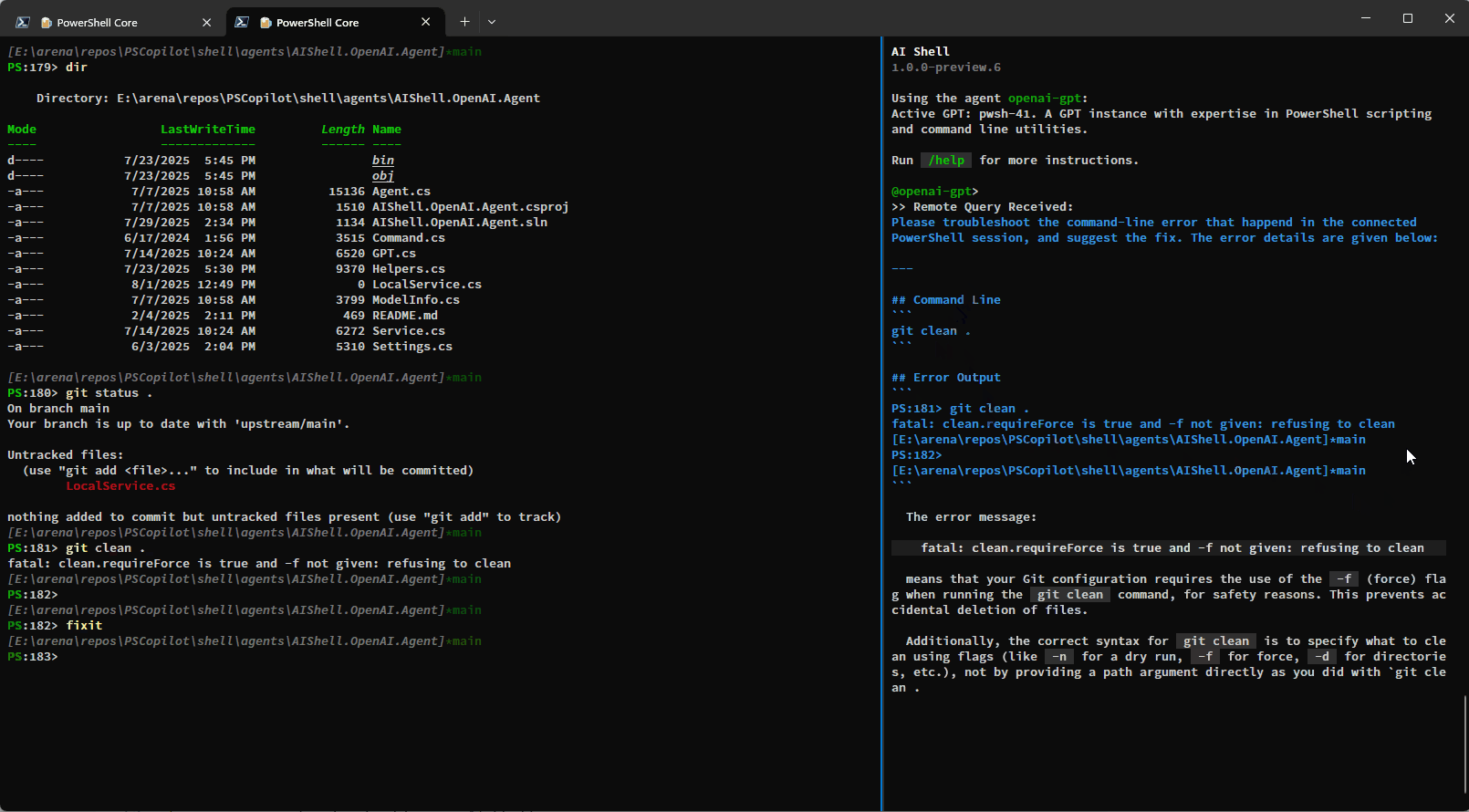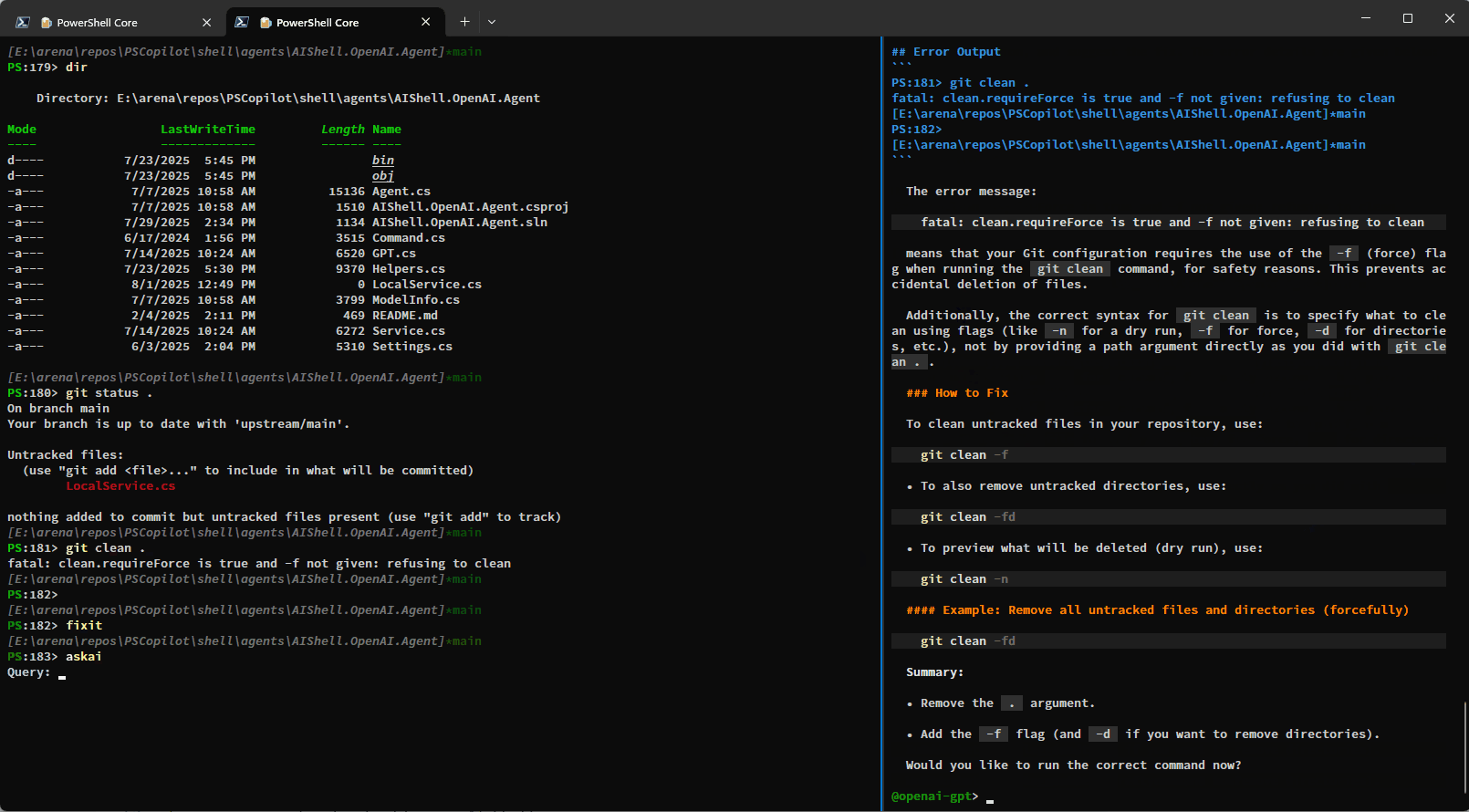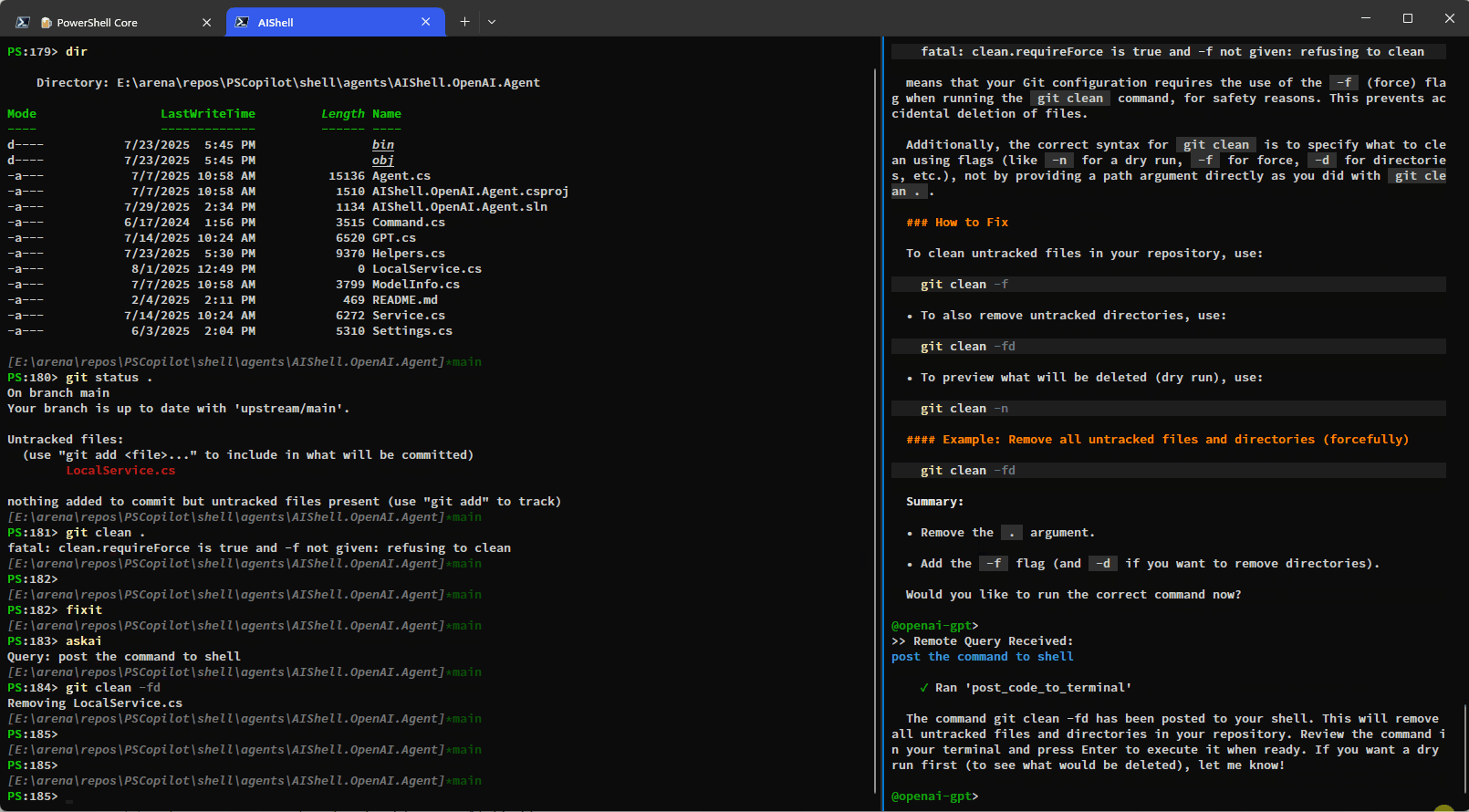
Resolve-Error Command Improvements
Previously the Resolve-Error command was only able to run after an error occurred in the previous
command. Now, Resolve-Error identifies which command the user wants to troubleshoot:
- If the last error’s command matches the most recent command in history, it’s assumed to be the one the user is interested in.
- If the last error’s command isn’t the most recent and
$LastErrorCodeis null or zero, the error likely comes from an earlier command, not the very last one. - If
$LastErrorCodeis non-zero and$?is false, the last command was a failing native command. - If
$LastErrorCodeis non-zero but$?is true, it’s unclear which command or failure the user is focused on, so the agent analyzes the terminal content to determine the relevant context.
This logic allows AI Shell to better understand what the error the user is trying to resolve is rather than requiring you to ask for AI’s help immediately after an error occurs.
Staying in your shell
The Invoke-AIShell and Resolve-Error commands allow you to stay in your working terminal to
interact with the AI Shell agent. To learn more about the parameters added, see the
previous blog post that details these features. For your convenience, these commands have
aliases that make them quicker to use.
| Command Name | Alias |
|---|---|
Invoke-AIShell |
askai |
Resolve-Error |
fixit |
How to install AI Shell
To install the latest version of AI Shell, run the following command in your PowerShell terminal:
Invoke-Expression "& { $(Invoke-RestMethod 'https://aka.ms/install-aishell.ps1') }"We hope that these enhancements make your experience with AI Shell more powerful! We are always looking for feedback and suggestions, so please submit issues or feature requests in our GitHub repository.
Thank you so much!
AI Shell Team
Steven Bucher & Dongbo Wang



0 comments