System.IO.Pipelines is a new library that is designed to make it easier to do high performance IO in .NET. It’s a library targeting .NET Standard that works on all .NET implementations.
Pipelines was born from the work the .NET Core team did to make Kestrel one of the fastest web servers in the industry. What started as an implementation detail inside of Kestrel progressed into a re-usable API that shipped in 2.1 as a first class BCL API (System.IO.Pipelines) available for all .NET developers.
What problem does it solve?
Correctly parsing data from a stream or socket is dominated by boilerplate code and has many corner cases, leading to complex code that is difficult to maintain. Achieving high performance and being correct, while also dealing with this complexity is difficult. Pipelines aims to solve this complexity.
What extra complexity exists today?
Let’s start with a simple problem. We want to write a TCP server that receives line-delimited messages (delimited by n) from a client.
TCP Server with NetworkStream
DISCLAIMER: As with all performance sensitive work, each of the scenarios should be measured within the context of your application. The overhead of the various techniques mentioned may not be necessary depending on the scale your networking applications need to handle.
The typical code you would write in .NET before pipelines looks something like this:
This code might work when testing locally but it’s has several errors:
- The entire message (end of line) may not have been received in a single call to
ReadAsync. - It’s ignoring the result of
stream.ReadAsync()which returns how much data was actually filled into the buffer. - It doesn’t handle the case where multiple lines come back in a single
ReadAsynccall.
These are some of the common pitfalls when reading streaming data. To account for this we need to make a few changes:
- We need to buffer the incoming data until we have found a new line.
- We need to parse all of the lines returned in the buffer
Once again, this might work in local testing but it’s possible that the line is bigger than 1KiB (1024 bytes). We need to resize the input buffer until we have found a new line.
Also, we’re allocating buffers on the heap as longer lines are processed. We can improve this by using the ArrayPool<byte> to avoid repeated buffer allocations as we parse longer lines from the client.
This code works but now we’re re-sizing the buffer which results in more buffer copies. It also uses more memory as the logic doesn’t shrink the buffer after lines are processed. To avoid this, we can store a list of buffers instead of resizing each time we cross the 1KiB buffer size.
Also, we don’t grow the the 1KiB buffer until it’s completely empty. This means we can end up passing smaller and smaller buffers to ReadAsync which will result in more calls into the operating system.
To mitigate this, we’ll allocate a new buffer when there’s less than 512 bytes remaining in the existing buffer:
This code just got much more complicated. We’re keeping track of the filled up buffers as we’re looking for the delimiter. To do this, we’re using a List<BufferSegment> here to represent the buffered data while looking for the new line delimiter. As a result, ProcessLine and IndexOf now accept a List<BufferSegment> instead of a byte[], offset and count. Our parsing logic needs to now handle one or more buffer segments.
Our server now handles partial messages, and it uses pooled memory to reduce overall memory consumption but there are still a couple more changes we need to make:
- The
byte[]we’re using from theArrayPool<byte>are just regular managed arrays. This means whenever we do aReadAsyncorWriteAsync, those buffers get pinned for the lifetime of the asynchronous operation (in order to interop with the native IO APIs on the operating system). This has performance implications on the garbage collector since pinned memory cannot be moved which can lead to heap fragmentation. Depending on how long the async operations are pending, the pool implementation may need to change. - The throughput can be optimized by decoupling the reading and processing logic. This creates a batching effect that lets the parsing logic consume larger chunks of buffers, instead of reading more data only after parsing a single line. This introduces some additional complexity:
- We need two loops that run independently of each other. One that reads from the
Socketand one that parses the buffers. - We need a way to signal the parsing logic when data becomes available.
- We need to decide what happens if the loop reading from the
Socketis “too fast”. We need a way to throttle the reading loop if the parsing logic can’t keep up. This is commonly referred to as “flow control” or “back pressure”. - We need to make sure things are thread safe. We’re now sharing a set of buffers between the reading loop and the parsing loop and those run independently on different threads.
- The memory management logic is now spread across two different pieces of code, the code that rents from the buffer pool is reading from the socket and the code that returns from the buffer pool is the parsing logic.
- We need to be extremely careful with how we return buffers after the parsing logic is done with them. If we’re not careful, it’s possible that we return a buffer that’s still being written to by the
Socketreading logic.
- We need two loops that run independently of each other. One that reads from the
The complexity has gone through the roof (and we haven’t even covered all of the cases). High performance networking usually means writing very complex code in order to eke out more performance from the system.
The goal of System.IO.Pipelines is to make writing this type of code easier.
TCP server with System.IO.Pipelines
Let’s take a look at what this example looks like with System.IO.Pipelines:
The pipelines version of our line reader has 2 loops:
FillPipeAsyncreads from theSocketand writes into thePipeWriter.ReadPipeAsyncreads from thePipeReaderand parses incoming lines.
Unlike the original examples, there are no explicit buffers allocated anywhere. This is one of pipelines’ core features. All buffer management is delegated to the PipeReader/PipeWriter implementations.
This makes it easier for consuming code to focus solely on the business logic instead of complex buffer management.
In the first loop, we first call PipeWriter.GetMemory(int) to get some memory from the underlying writer; then we call PipeWriter.Advance(int) to tell the PipeWriter how much data we actually wrote to the buffer. We then call PipeWriter.FlushAsync() to make the data available to the PipeReader.
In the second loop, we’re consuming the buffers written by the PipeWriter which ultimately comes from the Socket. When the call to PipeReader.ReadAsync() returns, we get a ReadResult which contains 2 important pieces of information, the data that was read in the form of ReadOnlySequence<byte> and a bool IsCompleted that lets the reader know if the writer is done writing (EOF). After finding the end of line (EOL) delimiter and parsing the line, we slice the buffer to skip what we’ve already processed and then we call PipeReader.AdvanceTo to tell the PipeReader how much data we have consumed.
At the end of each of the loops, we complete both the reader and the writer. This lets the underlying Pipe release all of the memory it allocated.
System.IO.Pipelines
Partial Reads
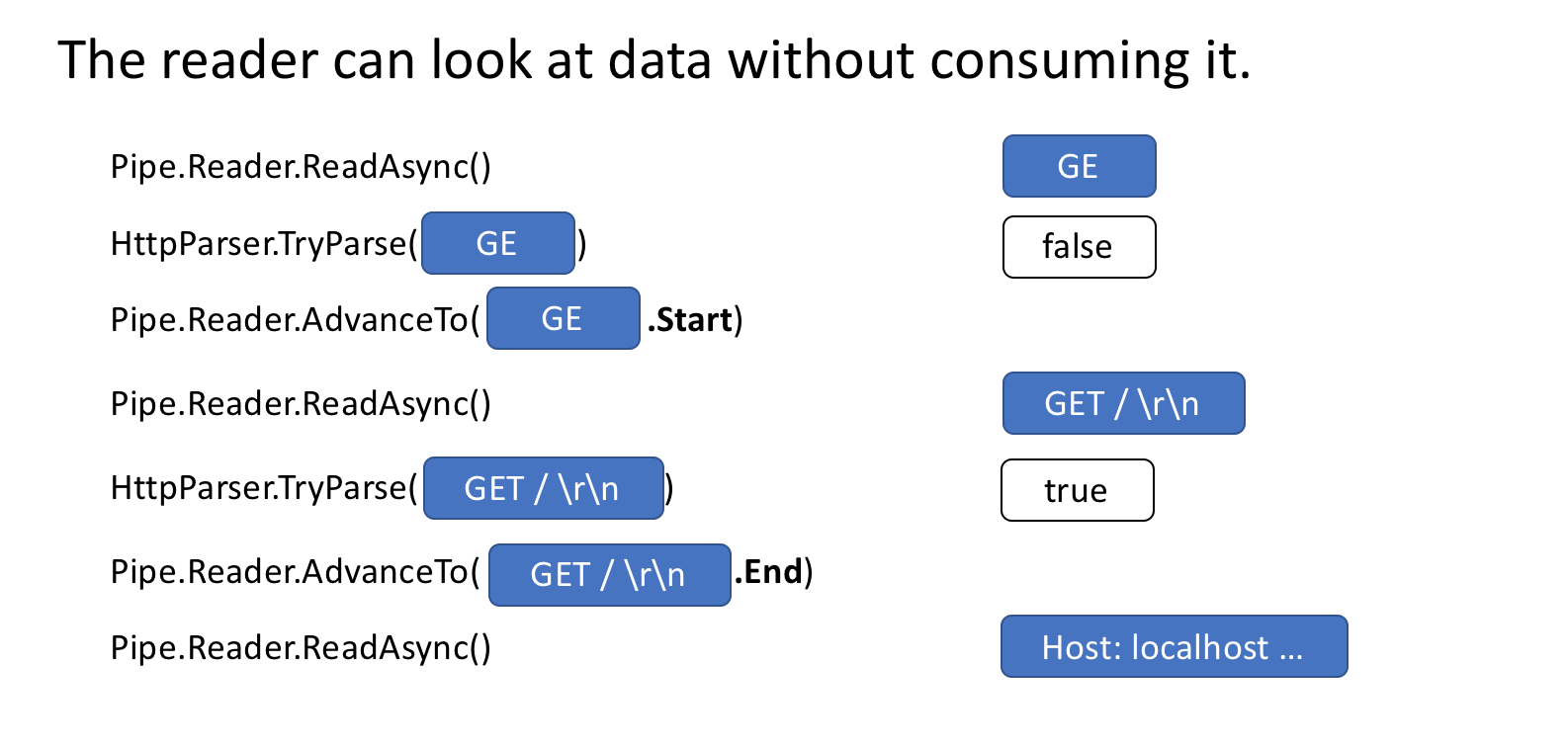
Besides handling the memory management, the other core pipelines feature is the ability to peek at data in the Pipe without actually consuming it.
PipeReader has two core APIs ReadAsync and AdvanceTo. ReadAsync gets the data in the Pipe, AdvanceTo tells the PipeReader that these buffers are no longer required by the reader so they can be discarded (for example returned to the underlying buffer pool).
Here’s an example of an http parser that reads partial data buffers data in the Pipe until a valid start line is received.
ReadOnlySequence<T>
The Pipe implementation stores a linked list of buffers that get passed between the PipeWriter and PipeReader. PipeReader.ReadAsync exposes a ReadOnlySequence<T> which is a new BCL type that represents a view over one or more segments of ReadOnlyMemory<T>, similar to Span<T> and Memory<T> which provide a view over arrays and strings.
The Pipe internally maintains pointers to where the reader and writer are in the overall set of allocated data and updates them as data is written or read. The SequencePosition represents a single point in the linked list of buffers and can be used to efficiently slice the ReadOnlySequence<T>.
Since the ReadOnlySequence<T> can support one or more segments, it’s typical for high performance processing logic to split fast and slow paths based on single or multiple segments.
For example, here’s a routine that converts an ASCII ReadOnlySequence<byte> into a string:
Back pressure and flow control
In a perfect world, reading & parsing work as a team: the reading thread consumes the data from the network and puts it in buffers while the parsing thread is responsible for constructing the appropriate data structures. Normally, parsing will take more time than just copying blocks of data from the network. As a result, the reading thread can easily overwhelm the parsing thread. The result is that the reading thread will have to either slow down or allocate more memory to store the data for the parsing thread. For optimal performance, there is a balance between frequent pauses and allocating more memory.
To solve this problem, the pipe has two settings to control the flow of data, the PauseWriterThreshold and the ResumeWriterThreshold. The PauseWriterThreshold determines how much data should be buffered before calls to PipeWriter.FlushAsync pauses. The ResumeWriterThreshold controls how much the reader has to consume before writing can resume.
PipeWriter.FlushAsync “blocks” when the amount of data in the Pipe crosses PauseWriterThreshold and “unblocks” when it becomes lower than ResumeWriterThreshold. Two values are used to prevent thrashing around the limit.
Scheduling IO
Usually when using async/await, continuations are called on either on thread pool threads or on the current SynchronizationContext.
When doing IO it’s very important to have fine-grained control over where that IO is performed so that one can take advantage of CPU caches more effectively, which is critical for high-performance applications like web servers. Pipelines exposes a PipeScheduler that determines where asynchronous callbacks run. This gives the caller fine-grained control over exactly what threads are used for IO.
An example of this in practice is in the Kestrel Libuv transport where IO callbacks run on dedicated event loop threads.
Other benefits of the PipeReader pattern:
- Some underlying systems support a “bufferless wait”, that is, a buffer never needs to be allocated until there’s actually data available in the underlying system. For example on Linux with epoll, it’s possible to wait until data is ready before actually supplying a buffer to do the read. This avoids the problem where having a large number of threads waiting for data doesn’t immediately require reserving a huge amount of memory.
- The default
Pipemakes it easy to write unit tests against networking code because the parsing logic is separated from the networking code so unit tests only run the parsing logic against in-memory buffers rather than consuming directly from the network. It also makes it easy to test those hard to test patterns where partial data is sent. ASP.NET Core uses this to test various aspects of the Kestrel’s http parser. - Systems that allow exposing the underlying OS buffers (like the Registered IO APIs on Windows) to user code are a natural fit for pipelines since buffers are always provided by the
PipeReaderimplementation.
Other Related types
As part of making System.IO.Pipelines, we also added a number of new primitive BCL types:
- MemoryPool<T>, IMemoryOwner<T>, MemoryManager<T> – .NET Core 1.0 added ArrayPool<T> and in .NET Core 2.1 we now have a more general abstraction for a pool that works over any
Memory<T>. This provides an extensibility point that lets you plug in more advanced allocation strategies as well as control how buffers are managed (for e.g. provide pre-pinned buffers instead of purely managed arrays). - IBufferWriter<T> – Represents a sink for writing synchronous buffered data. (
PipeWriterimplements this) - IValueTaskSource – ValueTask<T> has existed since .NET Core 1.1 but has gained some super powers in .NET Core 2.1 to allow allocation-free awaitable async operations. See https://github.com/dotnet/corefx/issues/27445 for more details.
How do I use Pipelines?
The APIs exist in the System.IO.Pipelines nuget package.
Here’s an example of a .NET Core 2.1 server application that uses pipelines to handle line based messages (our example above) https://github.com/davidfowl/TcpEcho. It should run with dotnet run (or by running it in Visual Studio). It listens to a socket on port 8087 and writes out received messages to the console. You can use a client like netcat or putty to make a connection to 8087 and send line based messages to see it working.
Today Pipelines powers Kestrel and SignalR, and we hope to see it at the center of many networking libraries and components from the .NET community.




Hi
in terms of speed performance how will this compare to just using udp (sending around 20k bytes)?
Hi,
This is very interesting article. Currently I am doing something similar, i.e. polling and reading and appending data manually through a virtual socket reading/writing operations. Unfortunately the virtual socket is not exposed as regular socket or pipe i.e. I cannot connect to it using or Class. I have to use https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/api/microsoft.win32.safehandles.safefilehandle?view=netframework-4.8. I am wondering if there is any way I can use this library with class. If not, can you point me to something similar for that?
Thank you
I’m not sure what the goal is. Where do you what want to use the Pipe?
Hi,
I started using the Pipe and I am coming across some issues when running multiple parallel tasks . I have different clients reading data from a socket and parsing it. Pretty common use case. Each client has its own socket channel.
When running multiple clients in parallel, I noticed that the memory being allocated by ‘GetMemory’ method of the PipeWriter gets corrupted and contains data written from another client. Somehow it seems that the Pipe is not thread or the memory location is not pinned .
I spent some time to track down the issue and here are the steps so that...
I started using the Pipe and I am coming across some issues when running multiple parallel tasks . I have different clients reading data from a socket and parsing it. Pretty common use case. Each client has its own socket channel.
That works fine as long as you have a single reader and single writer per Pipe.
When running multiple clients in parallel, I noticed that the memory being allocated by ‘GetMemory’ method of the PipeWriter gets corrupted and contains data written from another client. Somehow it seems that the Pipe is not thread or the memory location...
Hi is pipelines a part of the HttpClient library?
No it’s a standalone library.
So, from the code sample you’ve written, it’s safe the assume that the position passed into `PipeReader.AdvanceTo` is exclusive, not inclusive? The reader will mark everything before `buffer.Start` as consumed, but not including `buffer.Start`? The documentation on `PipeReader` doesn’t specify.
Good point, can you file an issue on the docs for this? https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/standard/io/pipelines.
Thanks for very good post.
i have a question, how can i build a socket server running in linux?
Hi: I sort of copied your TCP Echo sample into a messge parser TCP server. Some of the clients that are connecting to it use a persistent connection and after a while CPU is going throught the roof. Is complaining on ReadAsync and AdvanceTo (using Perfview) Any suggestions where I might start looking for a fix?(This guy is in the mix as well system.private.corelib!System.Threading.ThreadPoolWorkQueue.Dispatch())
A common issue is passing the wrong values to AdvanceTo, it’s possible you end up in a tight loop that isn’t making progress. File an issue on the repo with the code and I can take a look.
Hi,
Nice article we would use it in our application to improve WeSocket Server. One question, the data we send from client to server is protobuf serialized binary and there is no delimiter (or \n). How will I differentiate/split messages @ReadPipeAsync in such scenarios?
Do we get any help from SequenceReader (.Net Core 3.0)?
What about helper for actually using ReadOnlySequence are there anything available or should we make our own? – I’m thinking of stuff like GetInt32(), GetDouble(), GetString()
Yes, this is one of a major warts using Pipelines today, the ReadOnlySequence type is lacking helpers to make it easy to use. That’s solved in .NET Core 3.0 with SequenceReader (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/api/system.buffers.sequencereader-1?view=netcore-3.0)
This was exactly what I was looking for – very nice.
Thanks for the explaination, just a question:In a scenario where I have a TCPServer that must serve multiple peers and reply back to them (they both talk using payloads) how would you design the solution?To put it down to the simpliest and common example: how would you implement a client/server chat service?Having a single pipe that receive data from all the peers doesn't sounds good because it would mix data blocks from all the peers, while having a pipe for every client, means you need to run 2 tasks per peer (one to read from socket to pipe, and one...
2 tasks per peer is nothing especially long lived tasks (that’s the best case scenario really).