Why Data Governance Matters
In today’s data-driven world, governance isn’t just a technical requirement—it’s foundational to successful business operations. Good governance ensures data is not only accurate and compliant but also discoverable and usable at scale. At the heart of this approach lies robust, high-quality metadata, which transforms raw data into valuable, reusable information assets. Without well-defined context and clear naming standards, data quickly becomes fragmented, duplicated, and ultimately underutilized.
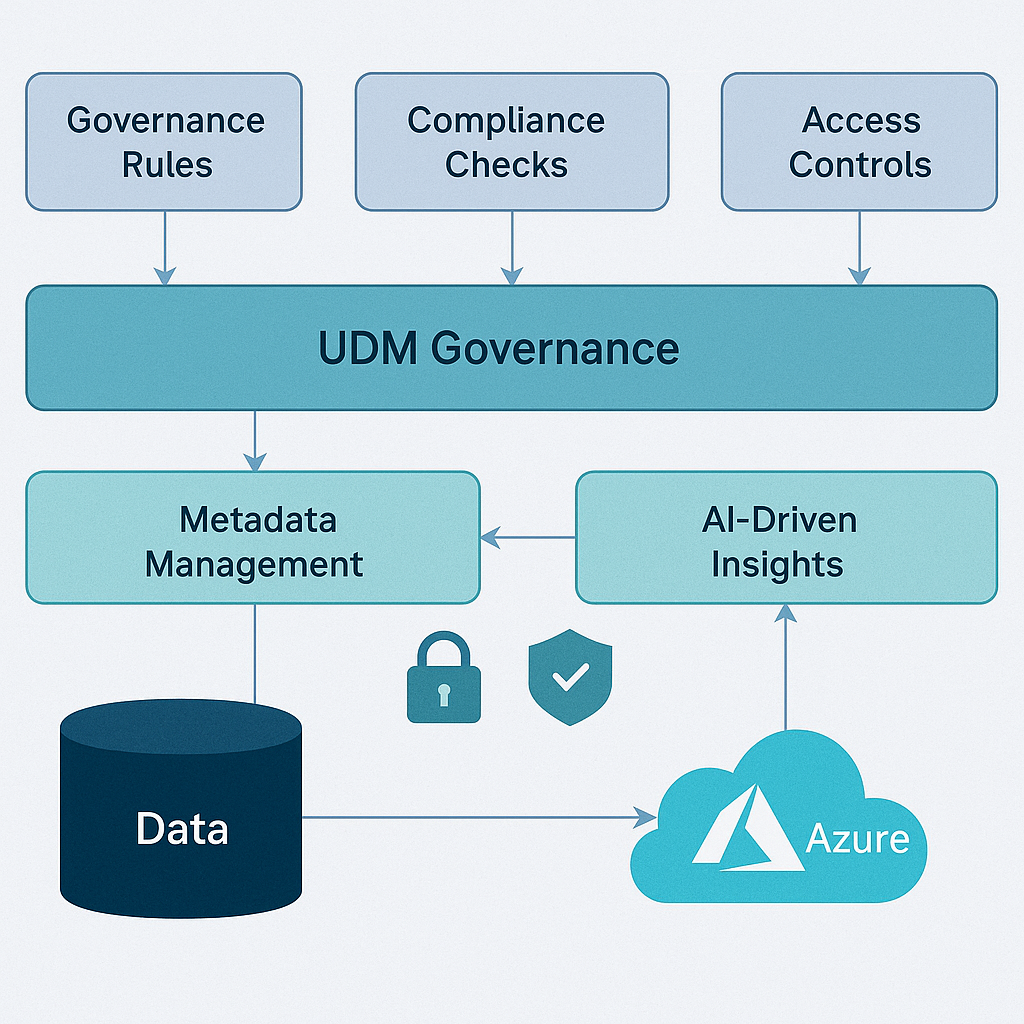
The Unified Data Model (UDM) is designed to address these challenges directly by embedding structured governance throughout the entire data lifecycle. With governance practices built into its core, UDM ensures your data assets remain discoverable, secure, compliant, and scalable as your organization grows and evolves.
Data Model Governance at Scale
Governance in large-scale data systems involves more than just setting rules—it’s about systematically managing metadata, automating compliance checks, enforcing access controls, and enabling transparent auditing. Effective governance prevents inefficiencies, duplication, and fragmentation that can hinder business growth and innovation. Well-governed data isn’t just beneficial—it’s essential.
Data assets created without consistent governance often serve immediate needs but quickly become obstacles to scalability and reusability. In contrast, governed assets, like those managed through UDM, enable broader use cases, driving productivity and innovation across your entire organization.
Embedding Governance Rules in UDM
One of the foundational aspects of governance in UDM is the enforcement of clear naming conventions and standardized schema definitions. Proper naming conventions might seem trivial, but they profoundly impact usability, compliance, and long-term maintainability. For instance, names that avoid spaces, team-specific jargon, redundancies, or excessively long descriptions significantly improve asset discoverability.
Consider the difference: an asset named “Office365Storage” quickly becomes obsolete if the team or project changes, whereas a simple, descriptive name like “Storage” remains meaningful over time. Similarly, avoiding spaces and redundancies ensures easy discoverability and prevents data pipeline failures.
Standardized schema definitions, such as clearly defined Profiles, Extensions, and Dimensions within UDM, further reinforce these governance principles. By minimizing redundancy and adhering to structured schemas, organizations can maintain data integrity and usability at scale.
Automating Compliance Checks
Automated compliance checks in UDM play a pivotal role in maintaining data privacy, security, and regulatory compliance. Through automated processes, UDM ensures that personally identifiable information (PII) is classified correctly, sensitive data is secured appropriately, and regulatory standards like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA are continuously met.
These automated governance measures reduce manual oversight, lowering the risk of human error. They ensure data remains compliant, secure, and trustworthy, providing peace of mind that regulatory audits will reveal adherence rather than deficiencies.
Access Control: Balancing Accessibility and Security
Effective governance also involves controlling who can access and modify data. UDM provides robust, role-based access controls, ensuring only authorized personnel can alter critical data assets. Roles such as Admin, Contributor, and Viewer are clearly defined, creating clarity around responsibilities and permissions.
For example, within a Game Developer Profile, the Data Governance Team may exclusively manage core attributes like Developer ID and Country, whereas Finance and Marketing teams have tailored access to revenue and engagement metrics respectively. This targeted approach ensures sensitive data remains secure without unnecessarily hindering legitimate access and collaboration.
Ensuring Transparency Through Auditability
Another critical element of governance is transparency—knowing precisely who modified data, when, and why. UDM integrates comprehensive audit logging and versioning, providing historical context for every data change. This feature not only aids in regulatory compliance but also simplifies troubleshooting and data recovery processes.
When an issue arises, version control makes it possible to roll back to previous states, mitigating the risk of irreversible data loss. This auditability builds trust across the organization, ensuring that data integrity is consistently maintained.
Leveraging AI to Enhance Metadata Governance
One exciting development in UDM governance is the integration of Large Language Models (LLMs). These AI tools significantly enhance metadata management by detecting acronyms and ensuring they are clearly defined within the context of their use. This kind of governance check is virtually impossible through traditional automated methods due to the inherent variability of acronyms.
Additionally, LLMs ensure asset descriptions are comprehensive enough for any user to understand their purpose, even without prior knowledge. By leveraging AI, organizations can maintain higher metadata quality, making data more accessible and understandable for everyone.
Real-World Insights: Microsoft’s Governance Journey
Microsoft’s experience implementing UDM highlights the immense value of proactive governance. We learned that establishing governance from the outset is far more efficient than retroactively applying standards. Our integration of LLMs, particularly for acronym detection and description enrichment, significantly improved the quality and clarity of our metadata, proving invaluable in our large-scale environment.
While governance initiatives require upfront effort, the benefits—reduced duplication, improved compliance, and higher overall data quality—far outweigh these initial investments.
Best Practices for Sustainable Data Governance
To build a sustainable governance practice, organizations should assign clear data ownership, enforce schema validation, thoroughly document metadata, regularly audit governance practices, and balance accessibility with security. These best practices help ensure data remains compliant, usable, and valuable over the long term.
Conclusion: Governance as a Strategic Advantage
Effective data governance isn’t merely about compliance—it’s a strategic advantage that supports operational excellence and business innovation. UDM’s structured, AI-enhanced governance framework enables organizations to maintain data that is not only compliant and secure but also scalable and highly usable across diverse scenarios.
As organizations increasingly recognize the importance of data governance, proactive and structured approaches like UDM will become indispensable for sustained success.
Have thoughts or experiences you’d like to share about your governance journey? We’d love to hear from you in the comments below!





0 comments