UPDATE 9/22: read the General Availability announcement.
Some of the top asks we have received on Azure Active Directory were for better sorting, counting, and filtering capabilities. We are excited to announce that we are now providing these capabilities on Azure Active Directory objects to developers through Microsoft Graph! In addition to addressing these important requests, we’ve added the ability to provide keyword-based searches.
In the past, if you’ve tried to filter and sort users in the same request, using a query like this:
GET https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0/users?$filter=startswith(displayName, 'al')&$orderby=displayName&$select=id,displayName
You might have seen the following response:
"error": { "code": "Request_UnsupportedQuery", "message": "Sorting not supported for current query." }
Now, this will result in a sorted list of users, with a new @odata.count property:
"@odata.context": "https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/$metadata#users(id,displayName)", "@odata.count": 2, "value": [ { "id": "4782e723-f4f4-4af3-a76e-25e3bab0d896", "displayName": "Alex Wilber" }, { "id": "c03e6eaa-b6ab-46d7-905b-73ec7ea1f755", "displayName": "Allan Deyoung" } ]
To achieve this, you need to:
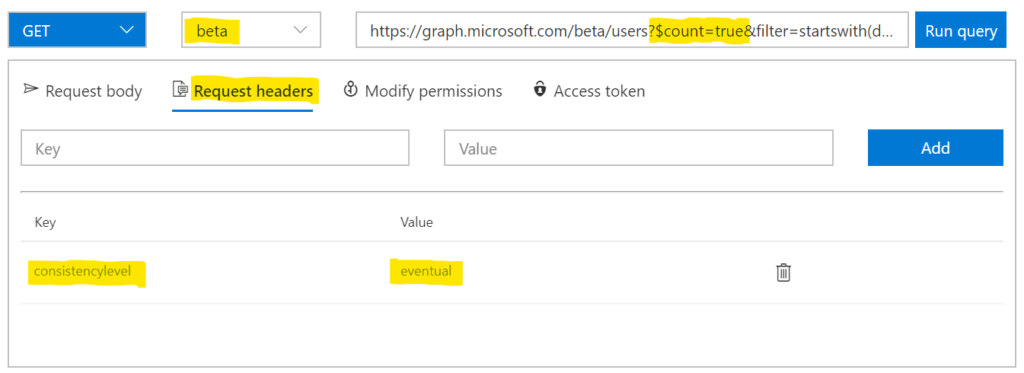
- Select the beta endpoint
- Add
$count=truein the QueryString - Add
ConsistencyLevel = eventualto the Request headers
Supported Objects
In the table below there are all the objects and related links that currently have the new advanced querying capabilities.
| Object | Links |
| Users | Member Of, Transitive Member Of, Owned Objects, Registered Devices, Owned Devices, Direct Reports |
| Groups | Members, Transitive Members, Owners |
| Applications | Member Of, Transitive Member Of |
| Service Principals | Member Of, Transitive Member Of |
| Devices | Member Of, Transitive Member Of, Registered Users, Registered Owners |
| Org Contacts | Member Of, Transitive Member Of, Registered Users, Registered Owners |
| Administrative Units | Members |
What is eventual consistency?
Azure Active Directory stores multiple copies of data to handle large read volume and provide high availability. When data is updated, the change will eventually be applied to all the copies.
$search and $count queries require the client to opt-in for eventual consistency by setting the header ConsistencyLevel = eventual.
For example, this means that when you add a user, you need to wait for all the copies to be updated to search or count them.
Sample Queries
Count the number of users, groups, applications, contacts, devices, service principals in a tenant, answering questions like:
◾ How many users are in the tenant?
GET https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/users/$count
◾ How many guest users are in the tenant, and who are they? Note: $count can also be a QueryString parameter.
GET https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/users/?$count=true&$filter=userType eq ‘Guest’
◾ How many members are in the engineering group (including transitive and direct members of a group)?
GET https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/groups/{group-id}/transitiveMembers/$count
Note: A group can contain nested groups, so we are using the transitiveMembers linked property to include all the nested groups’ members.
Search terms using tokenization. We are using a tokenization approach for our searches, detailed as follows:
- Spaces:
hello worldwill be tokenized inhelloandworld - Different casing:
HelloWorldandhelloWORLDwill be tokenized inhelloandworld - Special characters:
hello.worldwill be tokenized inhello,.andworld - Characters and Numbers:
hello123will be tokenized inhelloand123
Note: tokenized search is currently limited to displayName and description properties for now. All the other properties default to the startsWith behavior.
We currently don’t offer true substring searches because it will affect the overall search performance. Searching for world will not find helloworld.
◾ Search for users with “de” in the displayName
GET https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/users?$count=true&$search="displayName:de"
◾ Search for all users in a with “al” in the displayName or with mail starting with ‘admin’, sorted by displayName
GET https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/users?$count=true&$search="displayName:al" OR "mail:admin"&$orderBy=displayName
◾ Search for service principals with “team” in the displayName
GET https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/servicePrincipals?$count=true&$search="displayName:team"
◾ Search in a group transitively for all members with “br” in the displayName
GET https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/groups/{group-id}/transitiveMembers/microsoft.graph.user/?$count=true&$search="displayName:br"
Note: OData Cast provides a way to trim the results to a specific object type. Group members can be of the following types: users, applications, service principals, devices. In the previous example, specifying /microsoft.graph.user in the URL will return only the users in the group.
Sorting can be combined with filter or search, but is limited to displayName and userPrincipalName properties for now.
◾ Sort users in building 18 by displayName:
GET https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/users?$count=true&$orderby=displayName&$filter=startswith(officeLocation, '18')
As always, you can send multiple requests at the same time using JSON batching.
Try it now!
We’ve heard your feedback and have addressed some of the top requests on UserVoice such as:
- Support the $count operator for user and group objects
- Enable $filter on group members
- Enable combining filter and orderBy on users endpoint
- Support $count for group members and owners
We cannot wait to see what you can create with these new features. To try our queries, just click the “GET” link in the examples above.
As you use our APIs, please let us know what other objects, properties and fields you need to query to enable your scenarios in this brief survey and UserVoice.

0 comments