Introduction
Some of the most common questions we receive from Microsoft Teams developers concern authentication to Azure Active Directory (Azure AD), single sign-on (SSO) to Azure AD, and how to access Microsoft Graph APIs from within a Microsoft Teams app. Here, we’ll explain in detail how to do these things, going above and beyond authentication basics.
The TypeScript source code shown here can be found in our comprehensive sample apps: https://github.com/OfficeDev/microsoft-teams-sample-complete-node. There’s also a C# version.
First Things First
Don’t rely on the information from tab context to establish the user’s identity, whether you get it as URL parameters to your tab content URL or by calling the microsoftTeams.getContext() function in the Microsoft Teams client SDK. A malicious actor could invoke your tab content URL with its own parameters, and a web page impersonating Microsoft Teams could load your tab content URL in an <iframe> and return its own data to the getContext() function. You should treat the identity-related information in the tab context as “hints,†and validate them before use.
The Basics
The help topic Authenticate a user in your Microsoft Teams tab covers the basics of tab authentication. Here I’ll present a working example of a static tab that requests an access token for Microsoft Graph and shows the current user’s basic profile information from Azure AD.
Configuring your Azure AD Application
To authenticate with Azure AD, you will need to register an application and configure it correctly. If your Microsoft Teams app has a bot or a compose extension, an Azure AD application was created for you when you registered your bot with the Bot Framework. If your Microsoft Teams app just has a tab, you can create a new application through the Application Registration Portal (https://apps.dev.microsoft.com).
The examples below use the OAuth2 Implicit Grant flow via the V1 endpoint, and reads the user’s profile information. Here’s how to configure your application:
1. Open the Application Registration Portal, locate your app, and click on it to see its properties.
2. For the TypeScript/Node.js and C# sample apps on GitHub, the redirect URLs will be similar to what’s below, but the hostname will be different. That is, the redirect URLs for the sample app will be https://yourhost/tab-auth/simple-end and https://yourhost/tab-auth/silent-end.
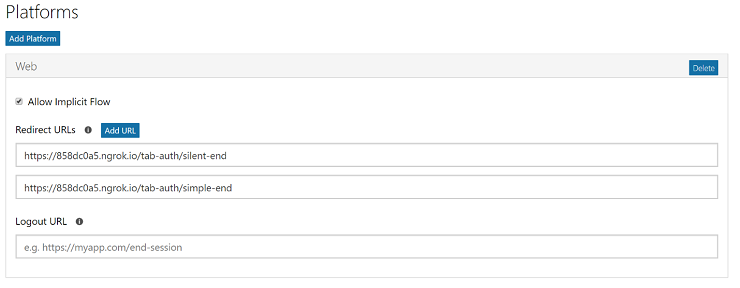
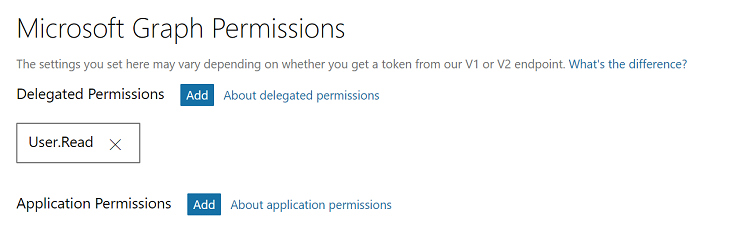
3. In the “Microsoft Graph Permissions” section, add the permissions your app requires. The examples below assume the User.Read delegated permission, which newly-created apps will have by default.
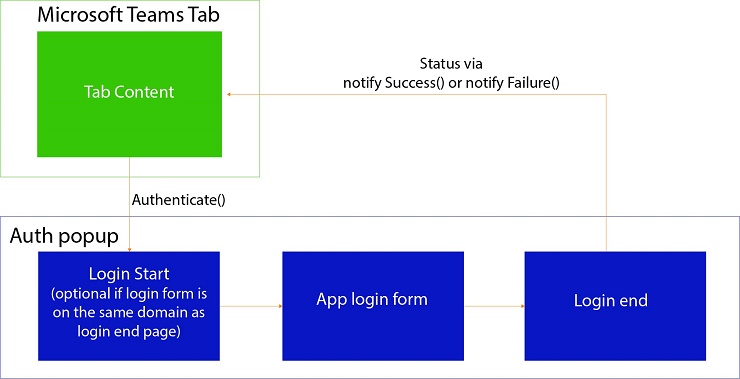
Step 1: Initiate Authentication Flow
In the tab content or configuration page, call the microsoftTeams.authenticate() function of the Microsoft Teams client SDK to launch a popup that will host the authentication flow.
microsoftTeams.authentication.authenticate({
url: window.location.origin + "/tab-auth/simple-start",
width: 600,
height: 535,
successCallback: function (result) {
getUserProfile(result.accessToken);
},
failureCallback: function (reason) {
handleAuthError(reason);
}
});
Here are some important things to understand about the above function:
- Identity providers typically don’t allow their login and consent pages to be placed in an <iframe>, so you must use a popup (such as /tab-auth/simple-start above) instead of trying to host the login experience directly in your tab.
- The URL you pass to microsoftTeams.authenticate() is the start page of your authentication flow. This page must be on a domain that’s in your validDomains list, or else the popup will not open.
- The authentication flow must start on a page that’s on your domain; don’t start it directly to your identity provider’s login or consent page. In our example, even though we’re using Azure AD, we begin at /tab-auth/simple-start rather than going directly to the Azure AD endpoint at https://login.microsoftonline.com. If you skip this step, the login popup may fail to close when you call notifySuccess() or notifyFailure().
Step 2: Navigate to the Authorization Page
Next, from your login start page (e.g. in our example, /tab-auth/simple-start), navigate to the authorization page of the identity provider. You can return an HTTP 302 response from your server, or do this client-side by returning a page with JavaScript that calls window.location.assign(). Our example does this client-side, so that it can use the “hinting†information from the Microsoft Teams client SDK function microsoftTeams.getContext() to streamline the login flow:
microsoftTeams.getContext(function (context) {
// Generate random state string and store it, so we can verify it in the callback
let state = _guid(); // _guid() is a helper function in the sample
localStorage.setItem("simple.state", state);
localStorage.removeItem("simple.error");
// Go to the Azure AD authorization endpoint
let queryParams = {
client_id: "YOUR_APP_ID_HERE",
response_type: "id_token token",
response_mode: "fragment",
resource: "https://graph.microsoft.com/User.Read openid",
redirect_uri: window.location.origin + "/tab-auth/simple-end",
nonce: _guid(),
state: state,
// The context object is populated by Teams; the upn attribute
// is used as hinting information
login_hint: context.upn,
};
let authorizeEndpoint = "https://login.microsoftonline.com/common/oauth2/authorize?" + toQueryString(queryParams);
window.location.assign(authorizeEndpoint);
});
Notes:
- As described earlier, this example uses the Azure AD OAuth2 Implicit Grant flow to get an access token for Microsoft Graph and an id token for the user. By performing the authorization in the microsoftTeams.getContext() callback function, the username field of the login prompt can be pre-filled with the user principal name (UPN) from the tab context. This saves the user from typing and may even allow the authentication flow to complete without further user interaction if the user is already logged in.
- If you’re doing client-side redirection, call window.location.assign(). The microsoftTeams.navigateCrossDomain() function is not available in the context of the authentication popup. As a result, it is not necessary to include the the identity provider’s domain (e.g., for Azure AD, login.microsoftonline.com) in the validDomains[] list in the app’s manifest.json file.
Step 3: User Sign-In and Authorization
The user signs in to the identity provider and authorizes your application. The identity provider navigates to your login callback URL (the one you specified in the Application Registration Portal, e.g. https://yourhost/tab-auth/simple-end) should determine if authentication was successful and call either the microsoftTeams.authentication.notifySuccess() or microsoftTeams.authentication.notifyFailure() functions from the Microsoft Teams client SDK.
Note: notifyFailure() has the following predefined failure reasons:
- CancelledByUser – the user closed the popup window before completing the authentication flow.
- FailedToOpenWindow – the popup window could not be opened. When running Microsoft Teams in a browser, this typically means that the window was blocked by a popup blocker.
Below is the example code of the JavaScript code in the login callback URL’s page that illustrates how to call notifySuccess() and notifyFailure():
// Split the key-value pairs passed from Azure AD
// getHashParameters is a helper function that parses the arguments sent
// to the callback URL by Azure AD after the authorization call
let hashParams = getHashParameters();
if (hashParams["error"]) {
// Authentication/authorization failed
microsoftTeams.authentication.notifyFailure(hashParams["error"]);
} else if (hashParams["access_token"]) {
// Get the stored state parameter and compare with incoming state
// This validates that the data is coming from Azure AD
let expectedState = localStorage.getItem("simple.state");
if (expectedState !== hashParams["state"]) {
// State does not match, report error
microsoftTeams.authentication.notifyFailure("StateDoesNotMatch");
} else {
// Success: return token information to the tab
microsoftTeams.authentication.notifySuccess({
idToken: hashParams["id_token"],
accessToken: hashParams["access_token"],
tokenType: hashParams["token_type"],
expiresIn: hashParams["expires_in"]
})
}
} else {
// Unexpected condition: hash does not contain error or access_token parameter
microsoftTeams.authentication.notifyFailure("UnexpectedFailure");
}
The JavaScript above on the login callback URL’s page parses the key-value pairs received from Azure AD in window.location.hash using the getHashParameters() helper function. If it finds an access_token, and the “state†value is the same as the one provided at the start of the auth flow, it returns the access token to the tab by calling notifySuccess(); otherwise it reports an error with notifyFailure(). The tab receives the result, or the failure reason, in the callback functions it provided in the call to authenticate().
“Silent” Authentication
If you want to keep your code completely client-side, you can use the Azure Active Directory Authentication Library for Javascript to attempt to acquire an Azure AD access token silently (that is, without the user ever seeing a popup dialog). Even though the ADAL.js library is optimized for working with AngularJS applications, it’s certainly usable from pure JavaScript single-page applications.
The diagram below illustrates how “silent†authentication works:
The ADAL.js library creates a hidden <iframe> for the implicit grant flow, but it specifies prompt=none so that Azure AD never shows the login page. If user interaction is required, whether because the user needs to log in or grant access to the application, Azure AD will immediately return an error that ADAL.js reports to your app. At this point your app can show a login button.
1. Include the ADAL.js library in your tab pages and configure ADAL with your client ID and redirect URL:
<script src="https://secure.aadcdn.microsoftonline-p.com/lib/1.0.15/js/adal.min.js" integrity="sha384-lIk8T3uMxKqXQVVfFbiw0K/Nq+kt1P3NtGt/pNexiDby2rKU6xnDY8p16gIwKqgI" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
// ADAL.js configuration
let config = {
clientId: "YOUR_APP_ID_HERE",
// redirectUri must be in the list of redirect URLs for the AAD app
redirectUri: window.location.origin + "/tab-auth/silent-end",
cacheLocation: "localStorage",
navigateToLoginRequestUrl: false,
};
</script>
2. In the tab’s content page:
a. Call microsoftTeams.getContext() to get the current user’s UPN. Note that we won’t be relying on the value reported in the context, but rather, use it as a login_hint in the call to Azure AD.
// Set up extra query parameters for ADAL
// - openid and profile scope adds profile information to the id_token
// - login_hint provides the expected user name
if (upn) {
config.extraQueryParameters = "scope=openid+profile&login_hint=" + encodeURIComponent(upn);
} else {
config.extraQueryParameters = "scope=openid+profile";
}
b. If ADAL has an unexpired token cached for the user, use that.
c. Otherwise, attempt to get a token silently. Call _renewIdToken(callback) for an id token, or _renewToken(resource, callback) for an access token. ADAL.js will call your callback function with the requested token, or an error if it fails.
d. If you get an error in the callback function, show a login button and fall back to an explicit login.
let authContext = new AuthenticationContext(config); // from the ADAL.js library
// See if there's a cached user and it matches the expected user
let user = authContext.getCachedUser();
if (user) {
if (user.userName !== upn) {
// User doesn't match, clear the cache
authContext.clearCache();
}
}
// Get the id token (which is the access token for resource = clientId)
let token = authContext.getCachedToken(config.clientId);
if (token) {
showProfileInformation(token);
} else {
// No token, or token is expired
authContext._renewIdToken(function (err, idToken) {
if (err) {
console.log("Renewal failed: " + err);
// Failed to get the token silently; show the login button
showLoginButton();
// You could attempt to launch the login popup here, but in browsers this could be blocked by
// a popup blocker, in which case the login attempt will fail with the reason FailedToOpenWindow.
} else {
showProfileInformation(idToken);
}
});
}
- Let ADAL.js take care of parsing the result from Azure AD by calling AuthenticationContext.handleWindowCallback(hash) in the login callback page. Next, check that we have a valid user, and call microsoftTeams.authentication.notifySuccess() or microsoftTeams.authentication.notifyFailure() to report status back to your main tab content page.
if (authContext.isCallback(window.location.hash)) {authContext.handleWindowCallback(window.location.hash);if (authContext.getCachedUser()) {microsoftTeams.authentication.notifySuccess();} else {microsoftTeams.authentication.notifyFailure(authContext.getLoginError());}}
Using an Existing Login Flow
The above examples illustrate how to perform authentication and authorization against Microsoft Active Directory. What if have an existing web application that requires authentication, and want to allow users to pin pages from that site as a tab?
For example, suppose our site is at https://example.com, and:
- We want to pin the content at https://example.com/page/1
- The app’s login page is at https://example.com/login, and after login, it goes to the path specified by the “next” query parameter.
The diagram below illustrates this flow:
There’s no source code for this flow in the Node.js and C# examples, but here’s an overview of what to do:
1. Create a post-login page at https://example.com/tab-auth-done. On this page, check if the user’s login succeeded, then call notifySuccess() or notifyFailure() accordingly.
2. Create a tab content page at https://example.com/tab-content. This page takes the URL of the actual content page as a “contentUrl” parameter.
a. On load, check if the user is logged in to the site.
b. If the user is logged in, navigate to the actual content by calling navigateCrossDomain().We recommend calling navigateCrossDomain() even if the target is actually on the same domain because Microsoft Teams validates that that domain of the target URL is in the valid domains list. This keeps your tab from navigating to an untrusted location and losing its connection to Microsoft Teams.
c. Otherwise, show a login button. In the button’s click handler, call authenticate() with the URL: https://example.com/login?next=https://example.com/tab-auth-done. If it succeeds, navigate to the actual content as above. If it fails, you might opt to show an error message, but remember to keep showing the login button so that the user can try again.
3. Configure the tab settings as follows:
a. Set contentUrl to https://example.com/tab-content?contentUrl=https://example.com/page/1, so the tab goes to the landing page first.
b. Set webUrl to https//example.com/page/1, so we go directly to the web content when the user chooses to view your tab in a browser.
Conclusion
In this article, we’ve explained how to perform authentication and authorization against Azure Active Directory, how to do single sign-on, and how to retrieve information using Microsoft Graph. This article, along with the Node.js/Typescript and C# samples, should illustrate these sophisticated and powerful techniques.
For reference, be sure to refer to these samples:
Happy authentication and authorization!

0 comments