Introduction: Why Agent Onboarding Matters
As AI systems evolve, organizations increasingly rely on networks of autonomous agents to deliver sophisticated services, such as automating workflows and powering conversational assistants. However, scaling these agentic systems introduces challenges, including overlapping roles and unclear descriptions. Such ambiguities can result in inaccurate orchestration, confusion, and errors, ultimately degrading the user experience.
For enterprise-grade AI, scalability and reliability are non-negotiable. Without a disciplined onboarding process, maintaining accuracy and user trust becomes nearly impossible.
Our Approach: A Structured, Multi-Layered Onboarding Process
To tackle these challenges, we designed a comprehensive agent onboarding process that prioritizes clarity, oversight, and rigorous evaluation. In a recent deployment for a major ecommerce platform, our digital assistant intelligently routed customer queries to specialized AI agents—streamlining interactions and boosting operational efficiency.
Our solution uses a two-layer architecture:
- Semantic Cache: Rapidly filters agents using vectorized sample utterances, narrowing down candidates based on user requests.
- LLM-Based Orchestrator: Analyzes context and intent to select and invoke the most suitable agent(s), enabling nuanced, multi-agent interactions.
This layered approach ensures that only the most relevant agents are shortlisted for each task, optimizing both accuracy and scalability. The high-level architecture below illustrates the process:
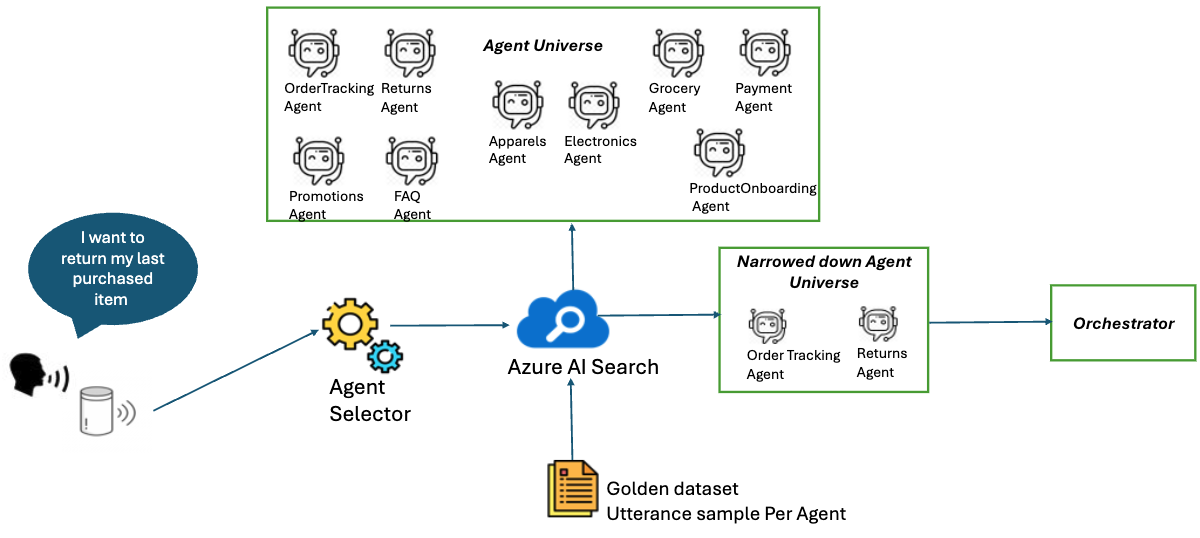
For a details exploration of the orchestration process, the challenges faced, and the lessons learned, check out our earlier blog post, Patterns for Building a Scalable Multi-Agent System. This resource offers essential context and insights that enrich the onboarding strategies outlined in this article.
How Do Semantic Cache and LLM Orchestrator Work Together?
Each agent specializes in a distinct service—such as order tracking, promotions, or payments. The semantic cache acts as a fast, first-pass filter, using vector embeddings of sample utterances to shortlist agents. The LLM orchestrator then applies deeper contextual analysis to select and invoke the best-fit agent(s). For multi-intent requests, the orchestrator can coordinate several agents, enabling richer, more dynamic interactions.
By enforcing unique names, descriptions, and capabilities for every agent—and evaluating their impact before production—we maintain system integrity and scalability throughout onboarding.
The Onboarding Process: Step-by-Step
Agent onboarding is a multi-stage, data-driven process managed by authorized reviewers to ensure accountability and consistency. Decisions are guided by a golden dataset containing user queries, chat histories, expected selected agents, and final LLM responses. This structured approach enables objective evaluation and continuous improvement. The onboarding process includes:
- Uniqueness Checks: Verifying agent names and descriptions to prevent duplication.
- Utterance Evaluation: Comparing sample utterances to avoid functional overlap.
- Temporary Semantic Cache Integration: Testing in a pre-production environment to assess agent interactions.
- System-Wide Response Evaluation: Ensuring the new agent does not introduce ambiguity or degrade performance.
- Golden Dataset Updates: Benchmarking and maintaining authoritative data for future evaluations.
Each step is designed to catch conflicts or ambiguities early, reducing troubleshooting and preserving system reliability.
Authorization and Oversight: Ensuring Accountability
All agent changes—whether additions, updates, or removals—require formal review and authorization. This oversight maintains a detailed change log, accelerates issue resolution, and ensures only vetted agents enter production.
Section 1: Initial Checks
Guaranteeing Agent Uniqueness
The first step in the onboarding process is to ensure that each agent has a unique name and a clearly distinct description. Duplicate names or similar descriptions can lead to selection errors and confusion. For instance, if TVAgent has the description “Choose me to learn about TV shows and schedules,” and TVProgramAgent has the description “Choose me to learn about TV programs and timings,” the similarity could confuse the LLM when both options are presented for selection.
def is_agent_name_unique(new_name, existing_names):
return new_name not in existing_names
# Example usage:
if not is_agent_name_unique("WeatherAgent", ["WeatherAgent", "NewsAgent"]):
print("Agent name already exists. Please choose a different name.")Best Practices for Naming Agents
- Ensure Uniqueness: Assign each agent a unique name to avoid conflicts or errors during orchestration. Duplicate names can lead to ambiguity and selection issues.
- Be Clear and Descriptive: Choose names that clearly reflect the agent’s purpose or functionality. For example, use
CustomerSupportAgentorProductCatalogSearcherinstead of generic or unclear names. - Follow a Consistent Naming Convention: Adopt a standardized format for naming agents. This could include prefixes or suffixes to group agents by domain, team, or functionality. Examples:
Sales-LeadGenAgentHR-OnboardingAgent
- Prioritize Readability: Use formats like PascalCase or camelCase for clarity. Avoid special characters unless absolutely necessary to maintain simplicity.
Best Practices for Writing Agent Descriptions
- Be Specific and Detailed: Clearly articulate the agent’s unique capabilities, ensuring the description provides a thorough understanding of its role. Avoid ambiguous or overly generic language.
- Highlight Core Functions: Emphasize the primary tasks the agent is designed to handle. Use concise and focused language to underline its key strengths.
- Use Action-Oriented Language: Begin descriptions with action verbs to make them clear and engaging. Examples include “Assist with,” “Provide insights on,” or “Handle requests for.”
- Include Example Utterances: Provide a few sample phrases that demonstrate how users can interact with the agent. This helps set clear expectations and defines its scope.
- Ensure Semantic Distinction: Verify that the description is semantically unique compared to other agents to avoid redundancy or confusion during orchestration. Use vector embeddings to compare descriptions and calculate similarity scores (e.g., cosine similarity) to identify and resolve overlaps.
Distinct Sample Utterances
Agents are defined by sample utterances—short phrases that capture their core functions. Each utterance is vectorized (using models like text-3-small-embedding) and compared for overlap using vector similarity scores, e.g., cosine similarity. If overlap is detected, utterances are revised to ensure clear differentiation.
Section 2: Semantic Cache Integration & Evaluation
Temporary Integration and Analysis
After passing initial checks, the new agent’s utterances are temporarily added to the semantic cache for pre-integration analysis. This step assesses how the new agent interacts with existing agents and identifies potential conflicts.
Evaluation Metrics
We focus on two key metrics:
- Recall at 5: Measures whether the correct agent appears among the top five candidates selected by the semantic cache. It is calculated as:

- Agent Invoke Accuracy: Confirms that the intended agent is ultimately invoked for each request.
During the onboarding process, we conduct both semantic cache and end-to-end response evaluations to ensure that the new agent integrates seamlessly without negatively impacting the performance of existing agents. If any conflicts or performance issues are detected, we refine the agent’s utterances and/or descriptions iteratively until they align with our quality and reliability standards.
Golden Dataset Updates & Responsible AI
Once an agent passes all evaluations, its data is added to the golden dataset. This dataset is maintained with strict attention to privacy, fairness, and bias mitigation. All prompt designs and data updates follow responsible AI guardrails, supporting ongoing quality assurance and ethical standards.
Onboarding Process Diagram

Outcomes and Insights
Performance Metrics
How effective is our onboarding process in practice? During evaluations on the golden dataset, we tracked two core metrics:
- Out of a test dataset comprising 2,370 scenarios—including single-intent and multi-intent interactions across both single-turn and multi-turn conversations involving 26 agents—the system accurately identified the correct agent among the top five candidates in 98% of cases.
- The intended agent was successfully invoked in 95% of cases.
These results demonstrate strong scalability and reliability.
| Dataset Size | Recall at 5 | Agent Invoke Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| 2,370 | 98% | 95% |
The chart below illustrates cumulative agent invoke accuracy as new agents are onboarded. Performance remained consistently high—above 92%—even as the number of agents increased, demonstrating the process’s scalability and reliability.
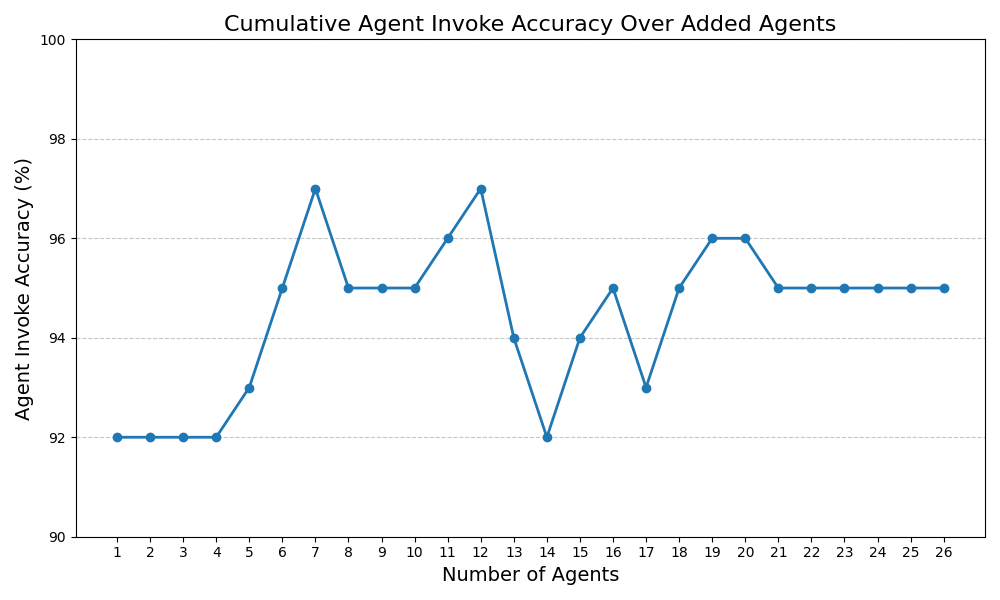
The recall at 5 metric consistently exceeded 98% during agent onboarding as well, highlighting the process’s effectiveness in accurately identifying the correct agent among top candidates as the system scaled.
Practitioner Takeaways
- Structured onboarding eliminates ambiguity: Rigorous checks for uniqueness and distinctiveness are essential for reliability as agent networks grow.
- Semantic cache accelerates selection: Filtering agents before orchestration optimizes accuracy and resource use.
- Continuous benchmarking sustains quality: Regular updates to the golden dataset and ongoing evaluations maintain high standards.
- Responsible AI is foundational: Privacy, fairness, and bias mitigation must be integral to onboarding and evaluation processes.
Conclusion
As multi-agent AI systems scale in complexity, a robust onboarding process is essential. By combining semantic cache filtering, structured onboarding, rigorous evaluation, and responsible AI practices, organizations can confidently grow their agentic ecosystems without sacrificing accuracy or reliability.
For AI practitioners and tech leads, the message is clear: invest in structured onboarding to unlock scalable, dependable multi-agent intelligence.
Next Steps
To further enhance scalability, the next step is to develop a generic agent onboarding process that can be adapted across diverse domains and platforms, streamlining integration and evaluation for any agentic system.

