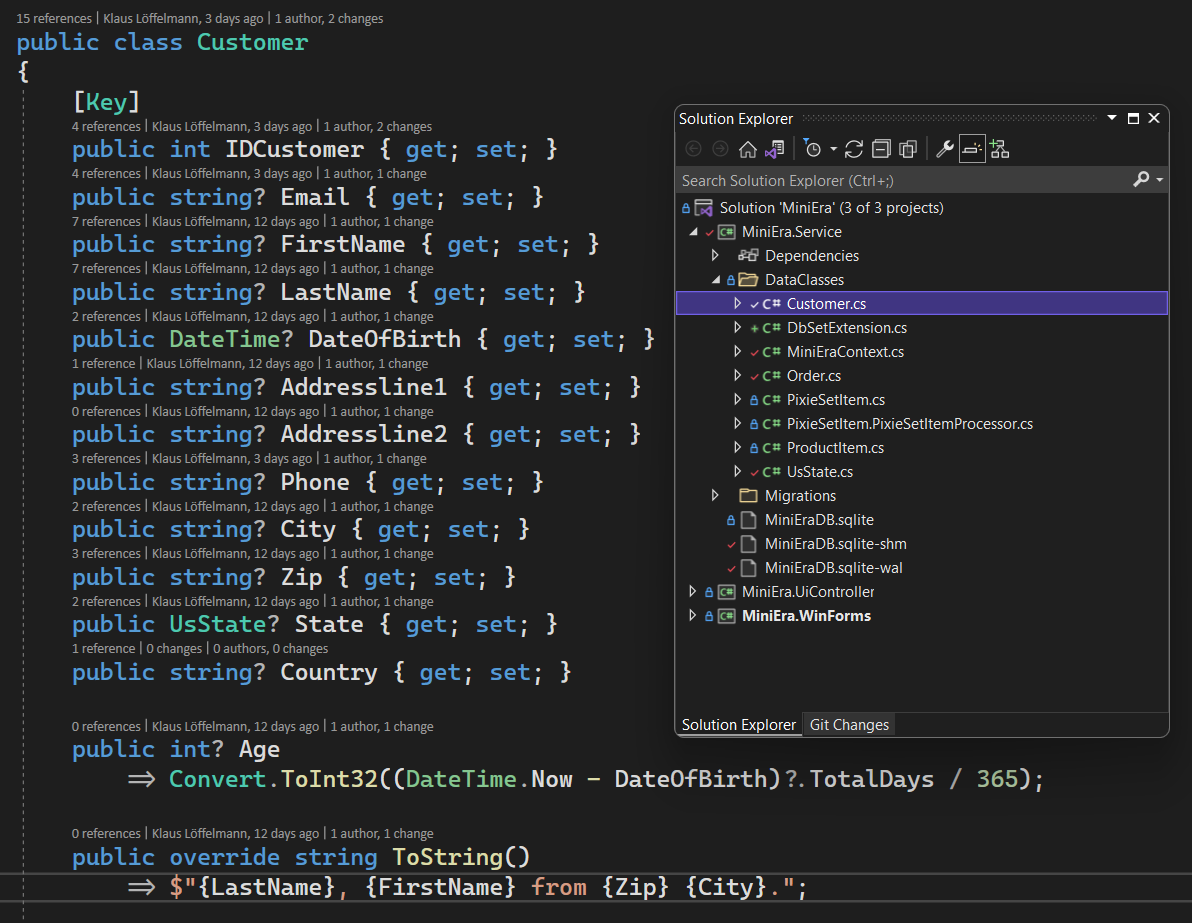
The design-time support for databinding in the new Windows Forms (WinForms) .NET Out of Process (OOP) Designer is different from the Framework Designer. The WinForms OOP Designer has a new and easier approach for hooking up data sources, focusing on Object Data Sources to support .NET based object relational mapper technologies (like the latest version of Entity Framework Core – EF Core for short) which the WinForms team recommends as a successor for Typed DataSets. This new approach was due to the completely different architecture of the new WinForms OOP Designer, which we have discussed in the previous blog post. If you haven’t read it yet, you should do so first, as it is essential for a better understanding of this post.
Why is the Data Source Tool Window unavailable in .NET projects?
Essential to databinding in WinForms .NET Framework is the Data Source Provider Service. This service runs in Visual Studio, and its responsibilities are as follows:
-
It generates and maintains Typed DataSets by connecting to a database data source (for example Microsoft SQL Server or Oracle DB Server).
-
It detects types which are designed to act either as Typed DataSet Data Sources or Object Data Sources.
-
It identifies potential Object Data Sources and sets those up in the project.
-
It discovers legacy (for example SOAP-based) web services and sets them up in a way so they can act as data sources.
-
It provides the UI functionality for the Data Source Tool Window in .NET Framework for WPF and WinForms applications. It also provides the UI Wizard to add new or maintain existing SQL Server connected data sources.
As of today, the Data Source Provider Service only works in the context of Visual Studio, which means it can only type-resolve .NET Framework assemblies and types. For .NET in its current version, the Data Source Provider Service is not able to retrieve the necessary type information as it would need to operate on the .NET Server Side (the DesignToolsServer). This is the reason that the UI stacks which used to rely on the Data Source Provider Service (WinForms, WPF) need to come up with alternatives for setting up new data sources and at the same time support legacy scenarios as well as possible. Providing feasible migration options, so that data access and databinding technologies can be migrated Form by Form, with both data source binding approaches (Typed DataSets and new ORMs based on Object Data Sources) present over a period of time, was the main driver for the new databinding functionality.
Working with legacy Typed DataSets in the OOP Designer
To decouple WinForms from the dependency to the Data Source Provider Service, there is now a new and quicker way to hook up new Object Data Sources.
That said, existing Typed DataSets definitions copied from Framework projects
can – with some limitations – be consumed by the OOP Designer even without that
service present. This means, data-bound Forms or UserControls using Typed
DataSets can be opened, and the Design Binding Picker (the drop-down editor in
the Property Browser to pick data sources for binding) will continue to provide
the necessary functionality to define the databinding of individual properties
of controls. At this time, though, no new Typed DataSets can be generated in
the context of a WinForms .NET application. It is also not possible, to
interactively update the schema for a Typed DataSet by querying the schema of
the assigned database. Necessary components (DataSet and for assigning the
data at runtime tablenameTableAdapter) to add a new binding definition can,
however, be added from the toolbox and hooked up manually – which means
maintaining legacy data-bound forms based on Typed Data Sets in .NET WinForms
projects is generally supported.
The following animated gif shows the process. Copy the Typed DataSet definition from your existing Framework project to your new .NET project and see that all necessary adapters and DataSets automatically appear in the toolbox on recompile. You see: Clicking the Typed DataSet based data source on the Picker does only set up the binding if the respective components are present in the Component Tray.
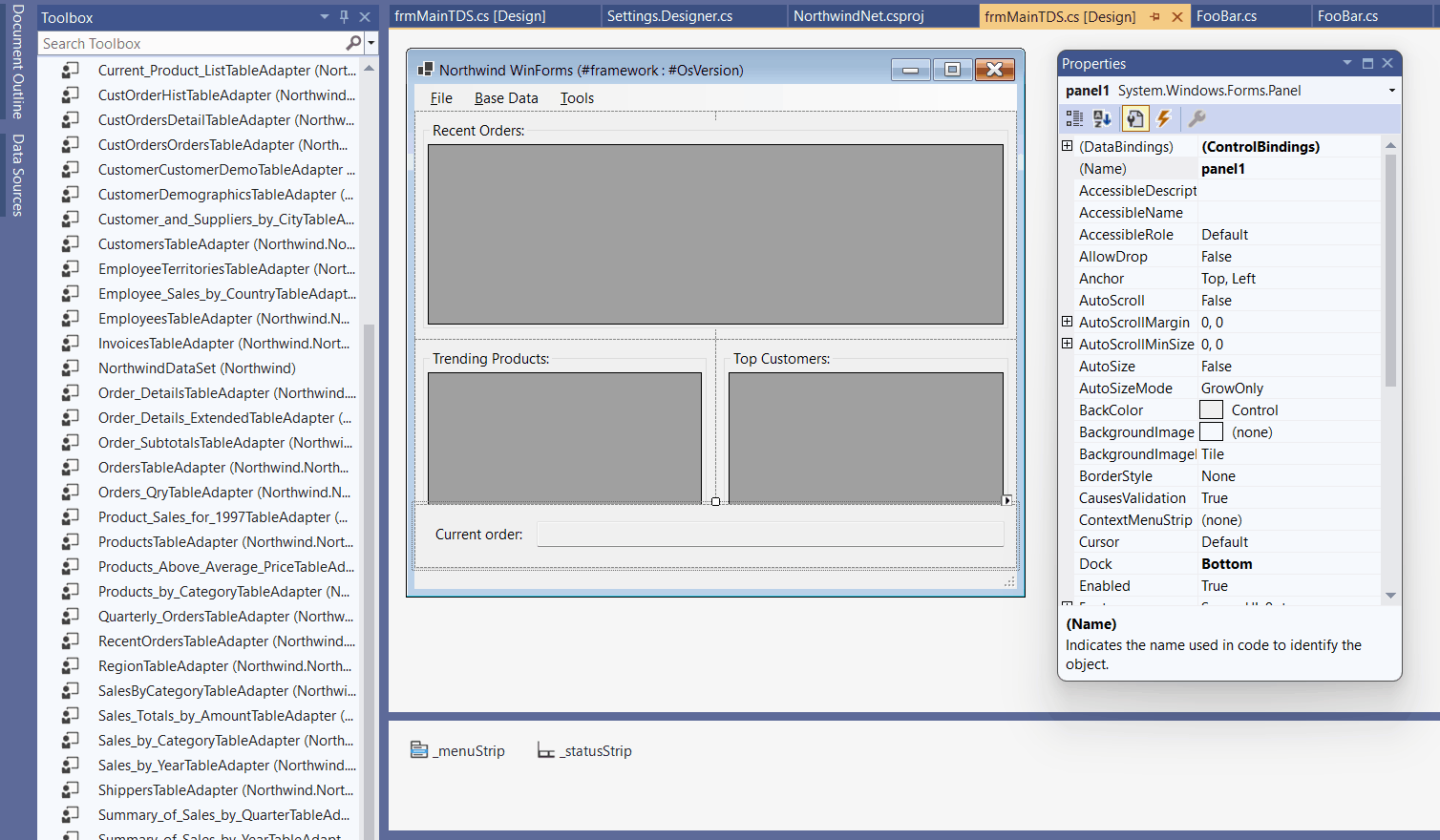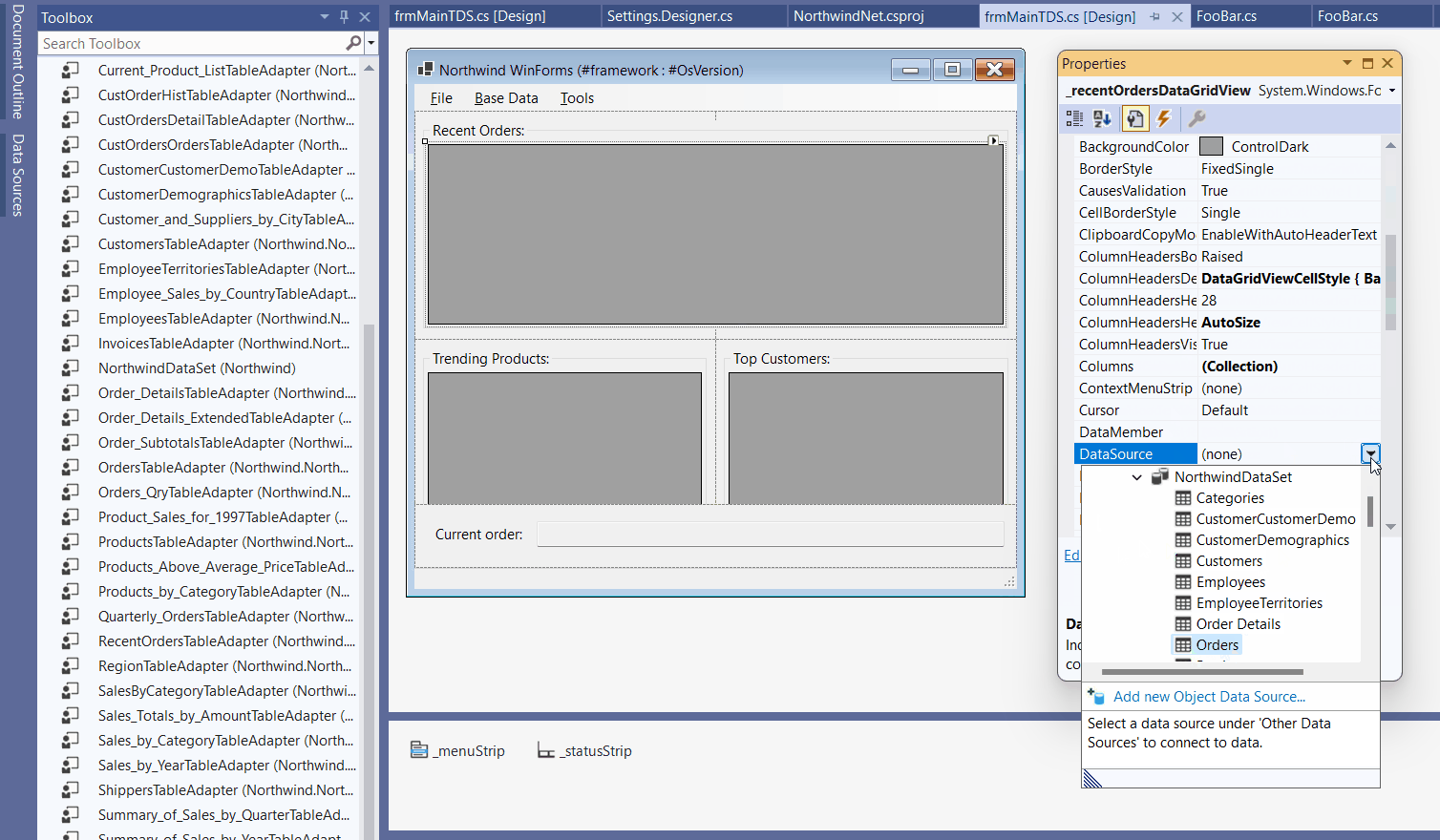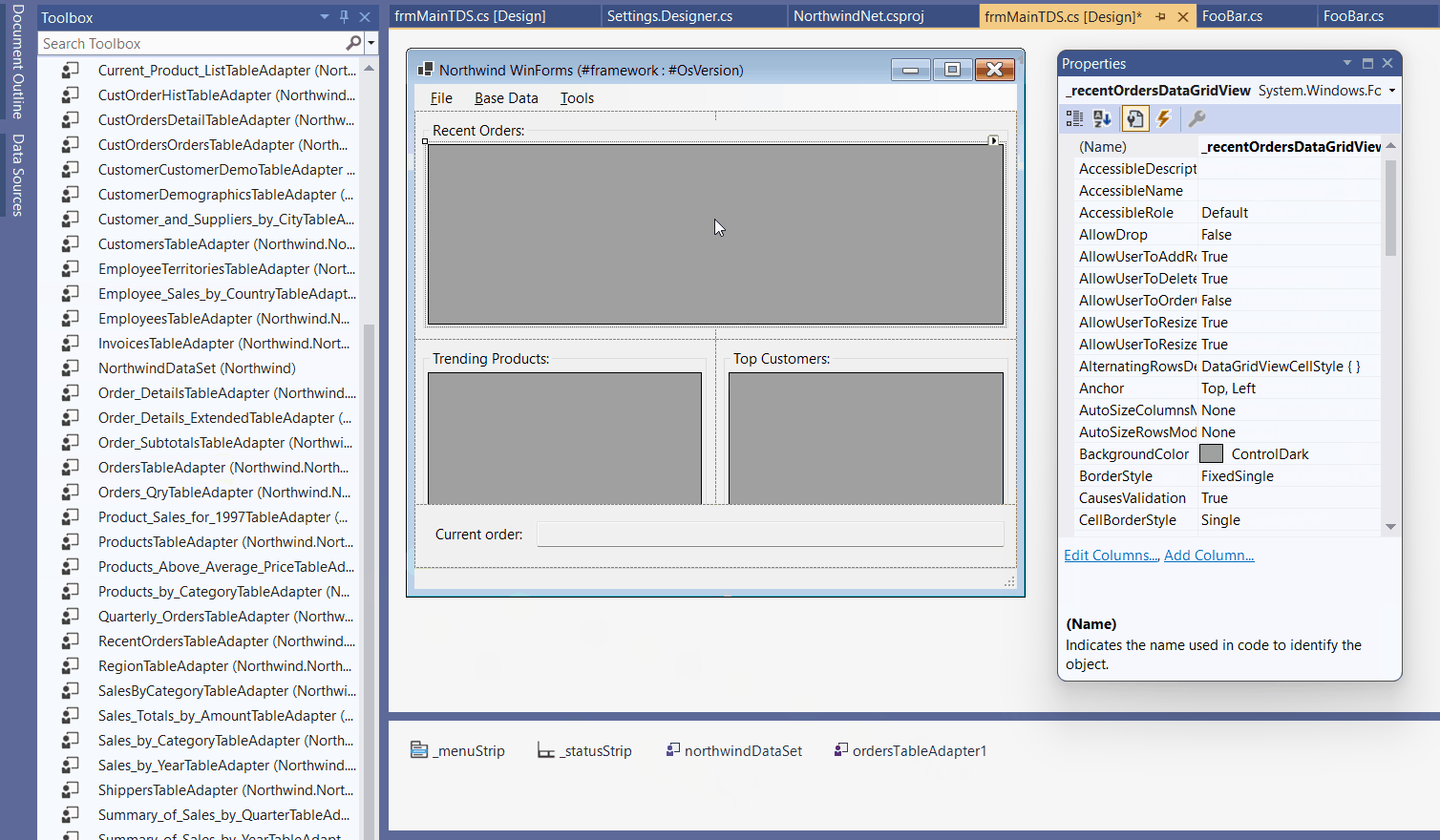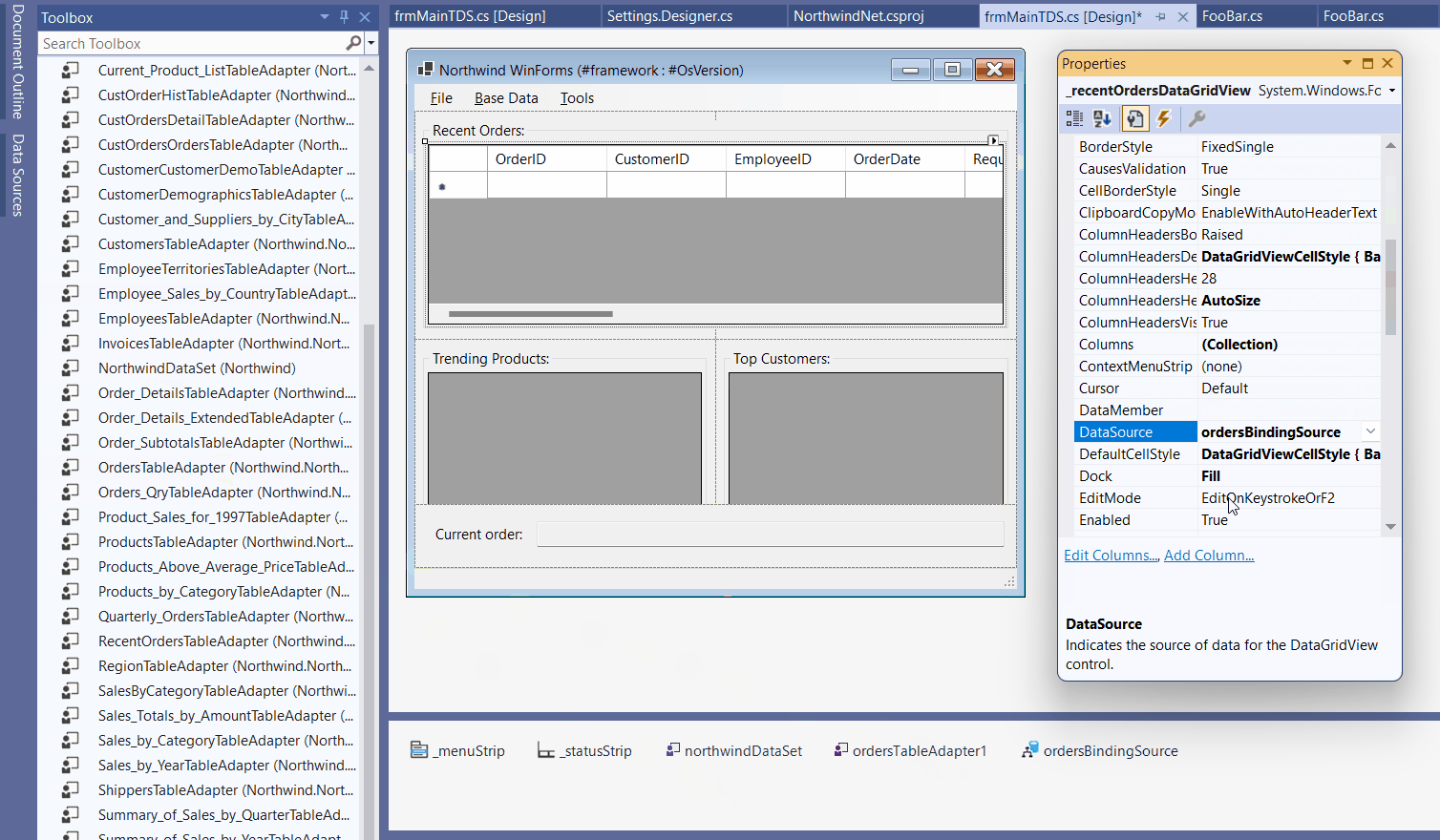
New Approaches when using Object Data Source Binding
Object Data Sources can, in contrast to Typed Data Sets, get their data through all different kind of means. One of the most popular alternatives, which is a great replacement for old-fashioned Typed DataSets, is Entity Framework Core (EF Core for short). Apart from the fact that it has greater performance and a bigger set of functionalities compared to Typed Data Sets, it also uses a different approach in dealing with the permanent task of updating and maintaining a database’s schema. While EF Core can principally be used in the same way as Typed Datasets, which are generated based on an already existing database, data objects based on EF Core can take a different more flexible and more maintenance-friendly approach, which is called Code first.
Code-first in this context means, the class definition defines the data structures/schemas, the relations between the entities (tables), and then the actual database schema is derived from this class definition: So-called migration-code updates the actual database definition on the fly. The advantage: The underlying database technologies is abstracted away: Code-first enables you to generate the schema for many different database systems: SQL Server, SQLite, Oracle Server, In-Memory databases, Cosmos, PostgreSQL, MySql – you name it!
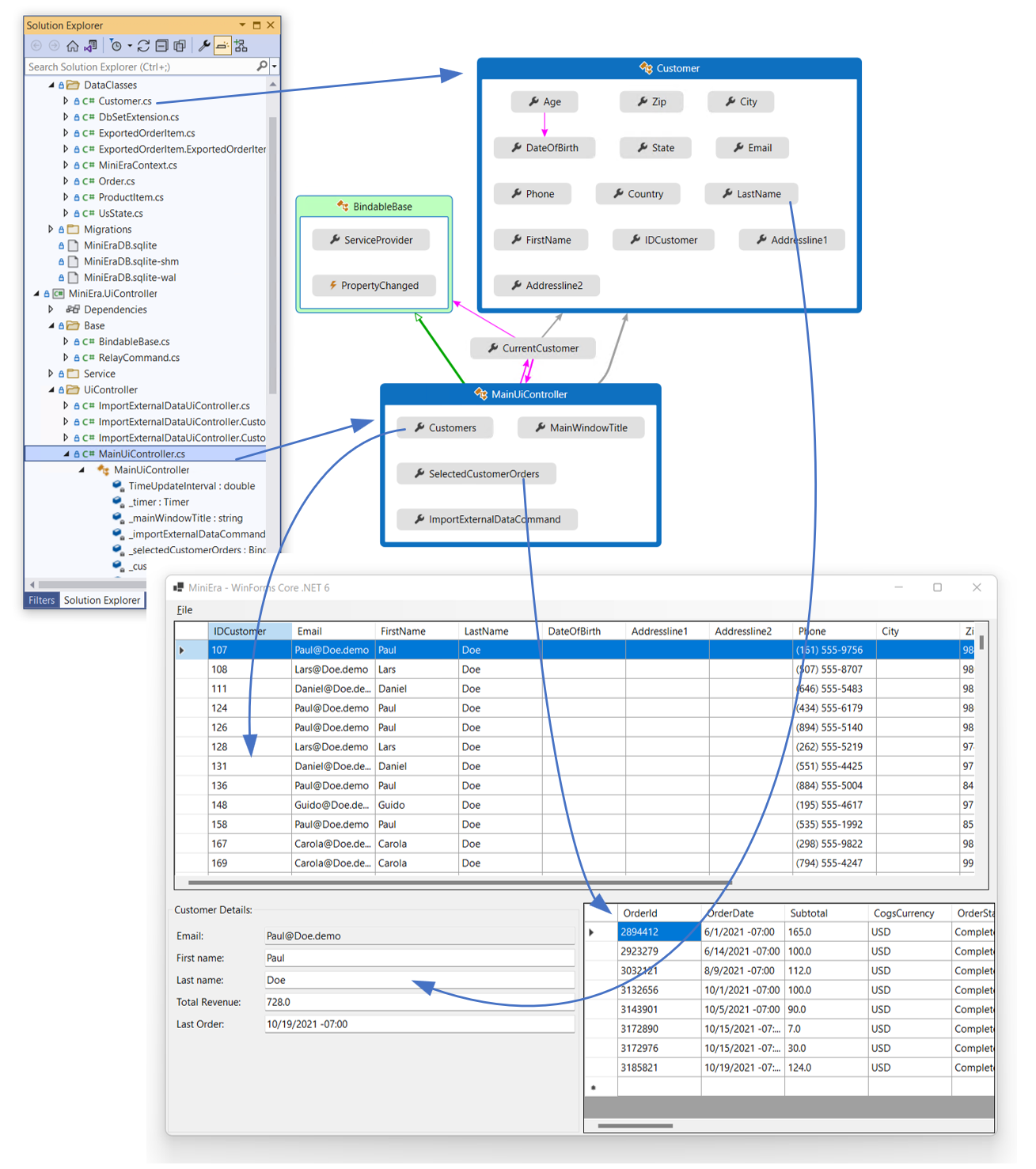
Let’s consider the following scenario: We build a .NET 6 Windows Forms application using EF Core code-first with data classes defined in a dedicated class library. This way, we can reuse the data layer code in other projects. But – in contrast what you would have done with Typed DataSets, we are not binding the EF Core data classes directly to the WinForms UI. The goal is to reduce the business logic code in the actual UI (Forms/UserControls) and get rid as much as possible of the WinForms typical “Code Behind” style. For that, we are introducing a set of properties to bind to yet another Object Data Source, which implements the business logic instead. We call this the business logic UI-controller class, or UI-controller for short. And those are the properties, we bind. A few examples:
-
Instead of setting the window title text of a Form directly in code-behind in the Form, we have a property in the UI-controller for the windows title. And that we bind.
-
A Save button should only be enabled when there actually is something to save. Instead of enabling or disabling the button in Code-Behind in the Form, we are introducing for example a `SaveButtonEnabled` property in the UI-controller, which we then bind against the `Enabled` property of the button.
-
We can even utilize a concept which originated from WPF and is called Command Binding. It’s suitable for elements like
ToolStripItems(and the derived componentsToolStripButton,ToolStripMenuItemand others) orButtoncontrols and implemented via theICommandinterface: When the user clicks on such a button in the WinForms UI, and the command property of that button is bound to a respective property in the UI-controller class, the command executes the underlying business code in the business class logic rather than in someClickevent code-behind.
A UI-controller class would look something like this:
![]()
Using a combination of data classes (which represent the Database) and UI-controller(s) in this way as Object Data Sources has some advantages:
-
Business logic reuse: The business logic is defined by business object (data source) classes independently of the UI. This means they can be reused in other scenarios. The same business objects which are used in a WinForms application could also be used for example in a Maui .NET mobile application.
-
Unit tests: Since the business logic doesn’t include any specific UI-stack dependencies, it can be unit tested way more easily. That is a big advantage over the WinForms typical code-behind approach.
-
View model/UI Controller support: Object Data Source classes can – or rather should – implement the `INotifyPropertyChanged` Interface. This enables data sources to act as UI-Controller classes (or View Models), which make them suitable to be reused in other UI Stacks.
Note: Although the binding infrastructure in WinForms is comparatively powerful, it doesn’t have the flexibility of XAML-based binding which you might know from WPF, UWP or Maui. For WinForms, you will most likely always be ending up with some Code-Behind code to support UI-Controller binding scenarios, which are otherwise difficult to implement just on the model/controller side. But that’s OK and expected. For a better reusability of code and the ability to write code, which is testable, it’s still worth the effort. And a migration to this way of binding can be easily done over time, Form by Form, so it is really feasible and can be planned for huge LOB apps. On top, we plan to further support and extend UI-controller centric scenarios in the .NET 7 time frame for WinForms projects.
The New Add Object Data Source Dialog
To use a certain class as your Object Data Source, start the binding process as you previously would:
-
Open the Design Binding Picker to add a new Object Data Source definition to your project.
-
Click on the link Add new Object Data Source to find the type you want to use as a data source in your project.
-
Use the Filter field to filter the selection by name. Note that types which implement the `INotifyPropertyChanged` interface (or derive from types which are based on that interface) are formatted in bold typeface.
-
Use the checkboxes in the dialog to include or exclude types, which are not part of your project, or to control how the types are organized in the list.
The example in the animated GIF below shows how a slightly modified
ToolStripMenuItem component can be bound this way to a Command, and in
addition a DataGridView’s DataSource to a property of a UI-controller
representing a list of customers:
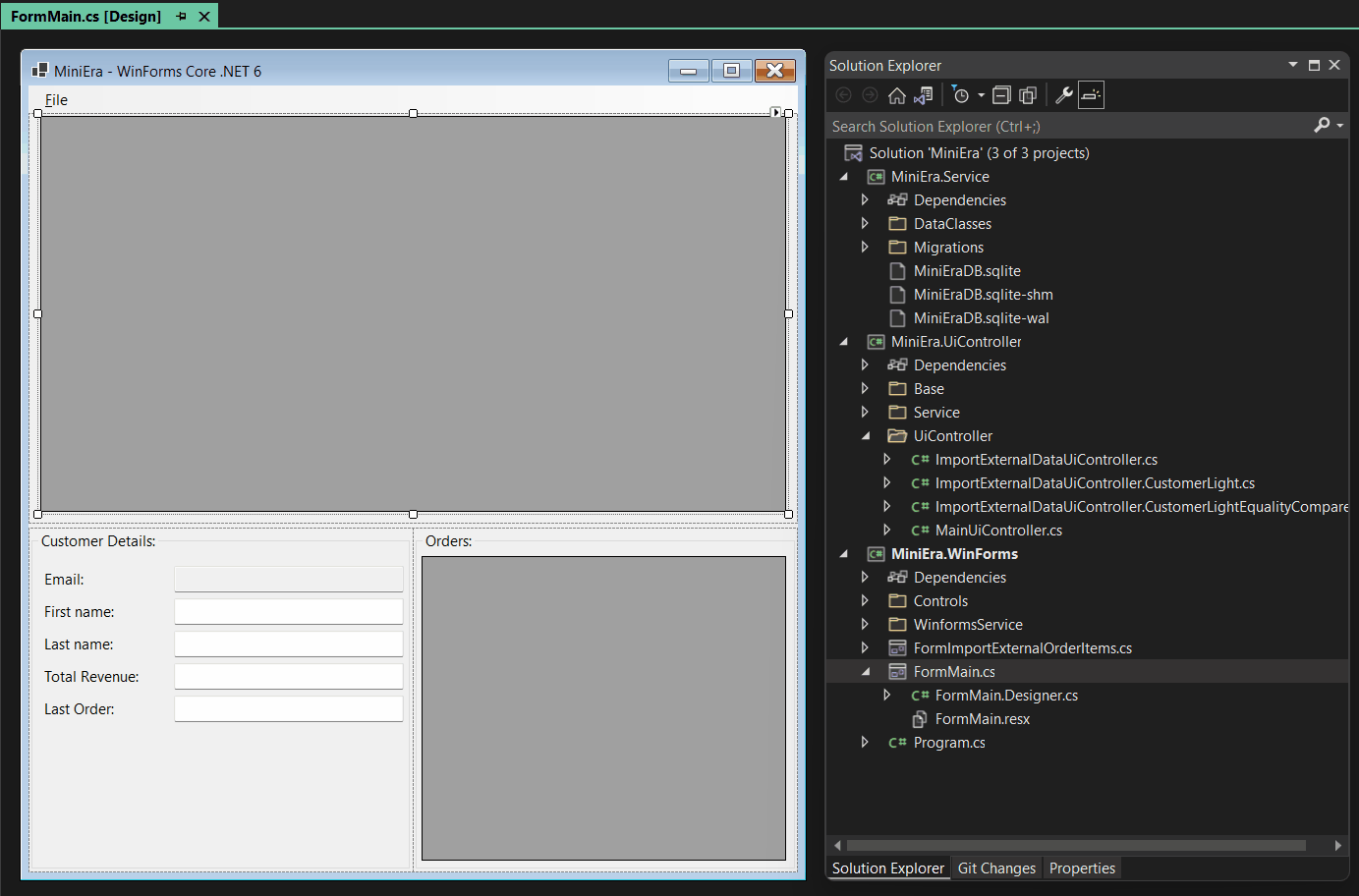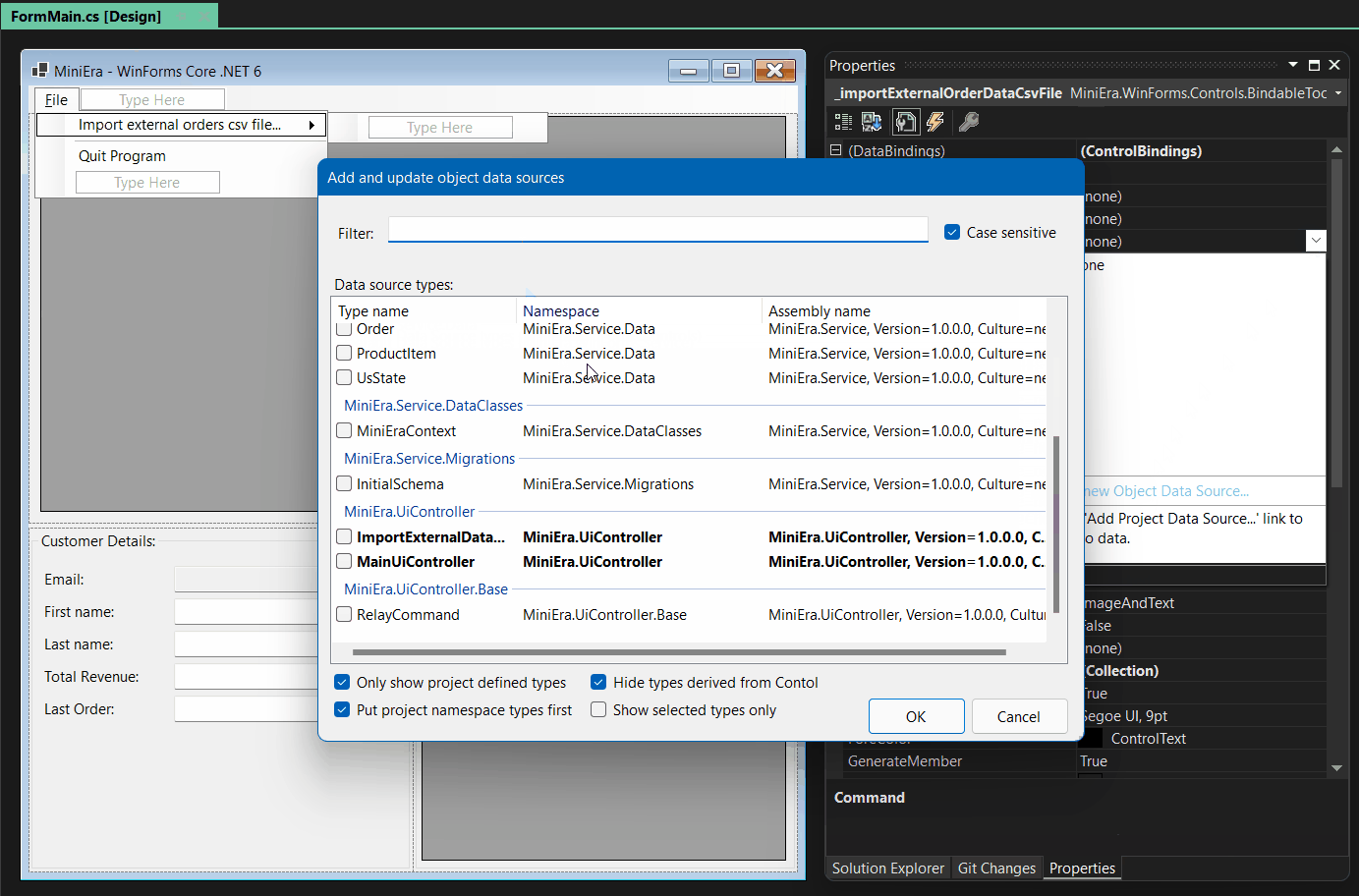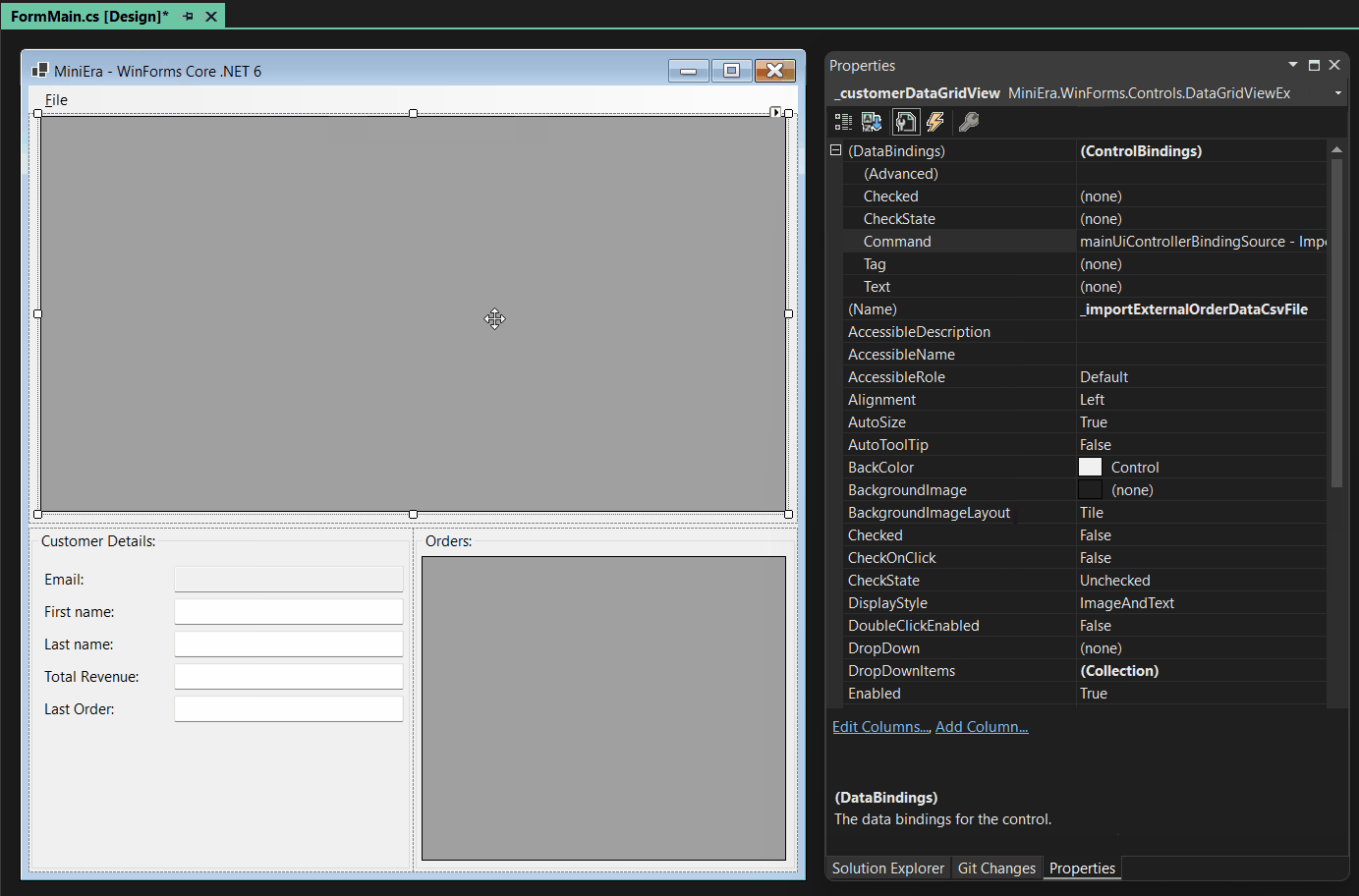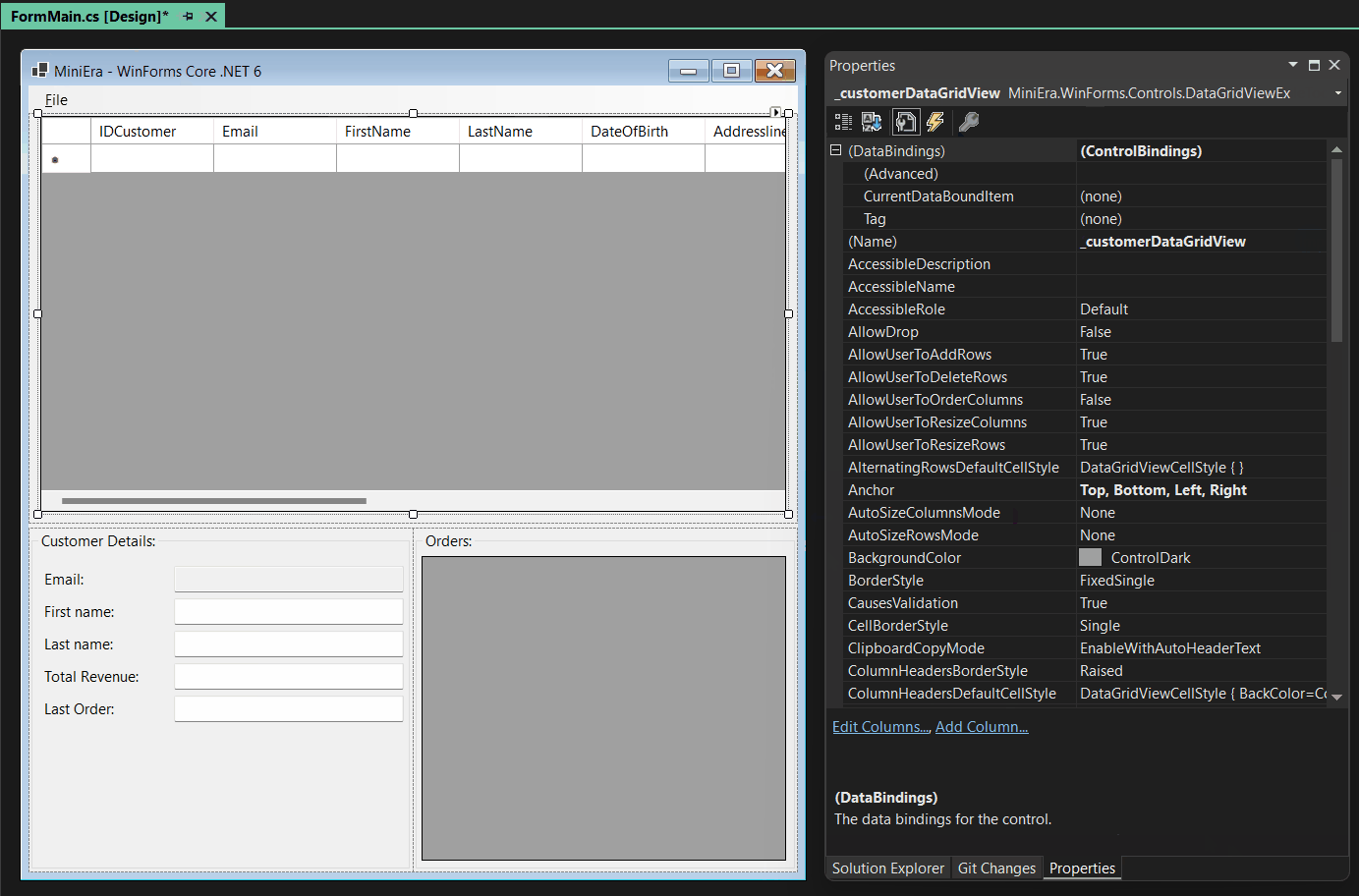
Here you see that adding MainUIController as an Object Data Source and
then binding its Import command to the ImportExternalDataCommand
property automatically led to the adding of the
mainUiControllerBindingSource component: In the Design Binding Picker you
can then pick that component as the actual data source.
History lesson: why BindingSources as mediators and no direct binding?
Adding a BindingSource component for an Object Data Source as a mediator
between the data source and the target control/component is a concept which
WinForms adapted from the early beginning (.NET 2.0 back in 2005). The
BindingSource component acts as the so-called currency manager. Currency
in this context means, the BindingSource component manages which data item
in a list of items is the current one. This way of binding is also done for
scenarios, for which the data source is or provides only one object instance – a
UI-controller or a single data source item for a data entry form for example.
This principle is being kept for backwards compatibility reasons, which means
that any attempt to bind the first property to a newly added (object) data
source will always add a respective BindingSource component to the
component tray. The actual binding will then be hooked up to that
BindingSource component rather than to the data source directly.
Note: It is important to know in this context, that WinForms doesn’t
natively know the concept of type conversion based on the IValueConverter
interface as it is used in WPF, UWP or WinUI. Rather, a conversion during
binding can be done by handling the events, such as Format and Parse,
which are provided by the actual binding instances generated by the designer for
the binding in InitializeComponent. Like this:
public FormMain()
{
InitializeComponent();
// Current version of WinForms Databinding doesn't allow yet
// IValueConverter, we do this instead:
var totalRevenueBinding = _totalRevenueTextBox.DataBindings[0];
// ConvertTo, here Decimal to String as an example:
totalRevenueBinding.Format += (sender, eventArgs) =>
{
if (eventArgs.DesiredType != typeof(string))
{
return;
}
eventArgs.Value = ((decimal)eventArgs.Value!).ToString();
};
.
.
.In this sample code we are assuming there is only one DataSource/Control binding
for a TextBox named _totalRevenueTextBox. We’re getting its Binding
definition and wire up to its Format event, where the actual conversion is
then handled at runtime.
Improvements to Advanced Databinding
We also made improvements to the Advanced Databinding Editor. You use the Advanced Databinding Editor for all properties which are not listed directly under Data Binding in the Property Browser. This dialog now shows what component or control you are binding to. It also shows what exact type of that control or component you are editing. Also, rather than picking the binding trigger from a drop-down list, you can now directly set that by clicking radio buttons, which is quicker and more accessible.
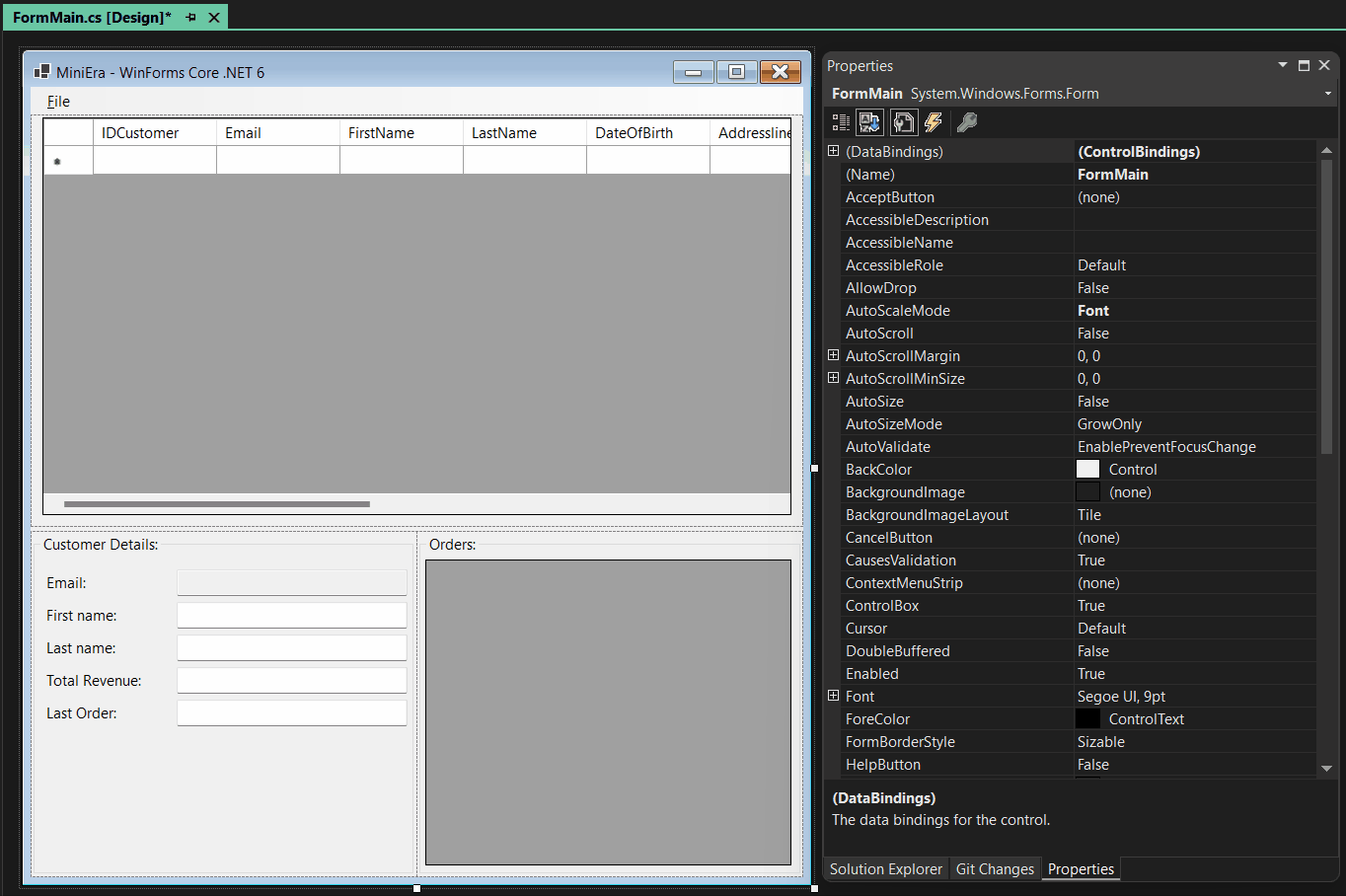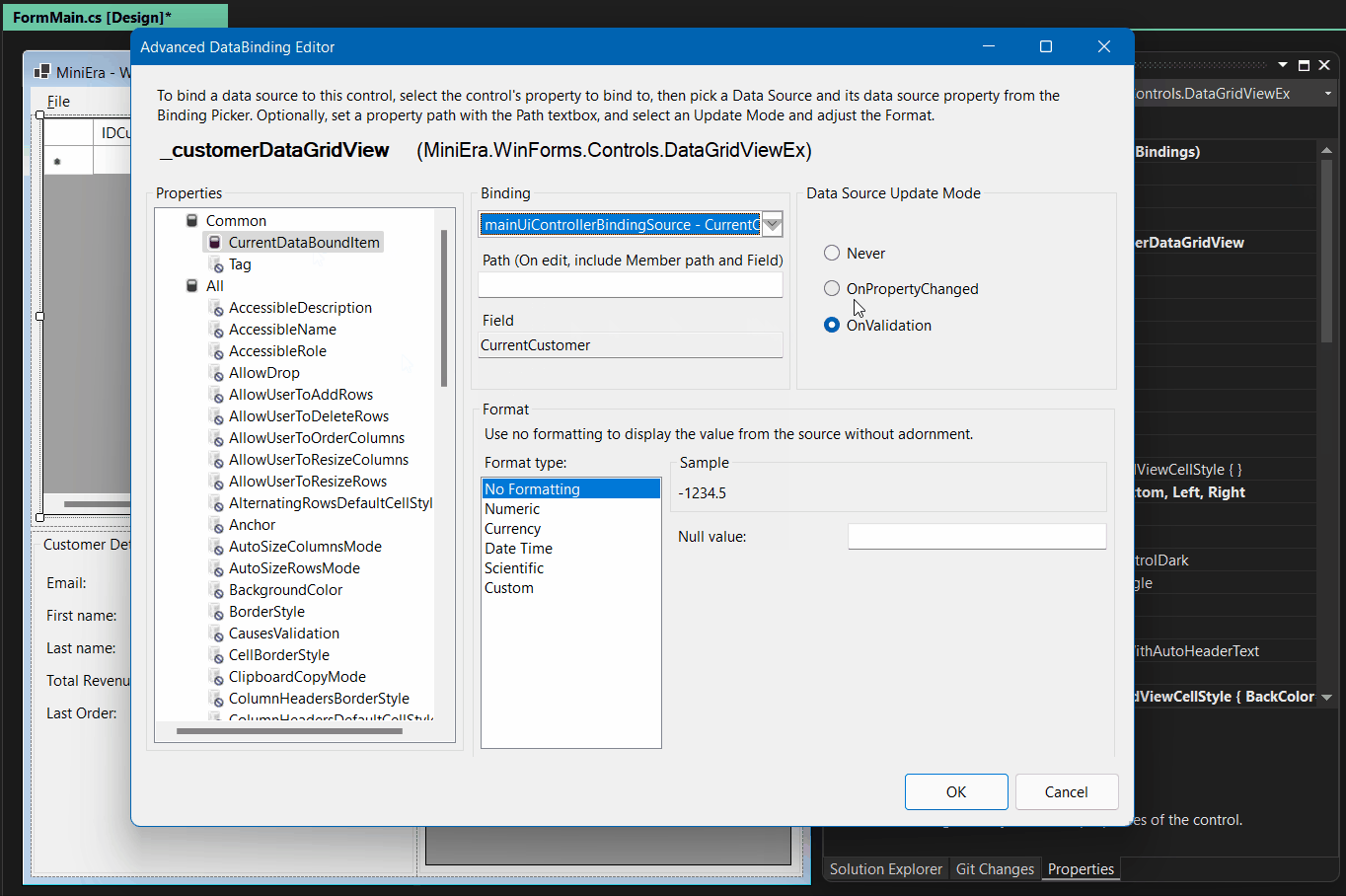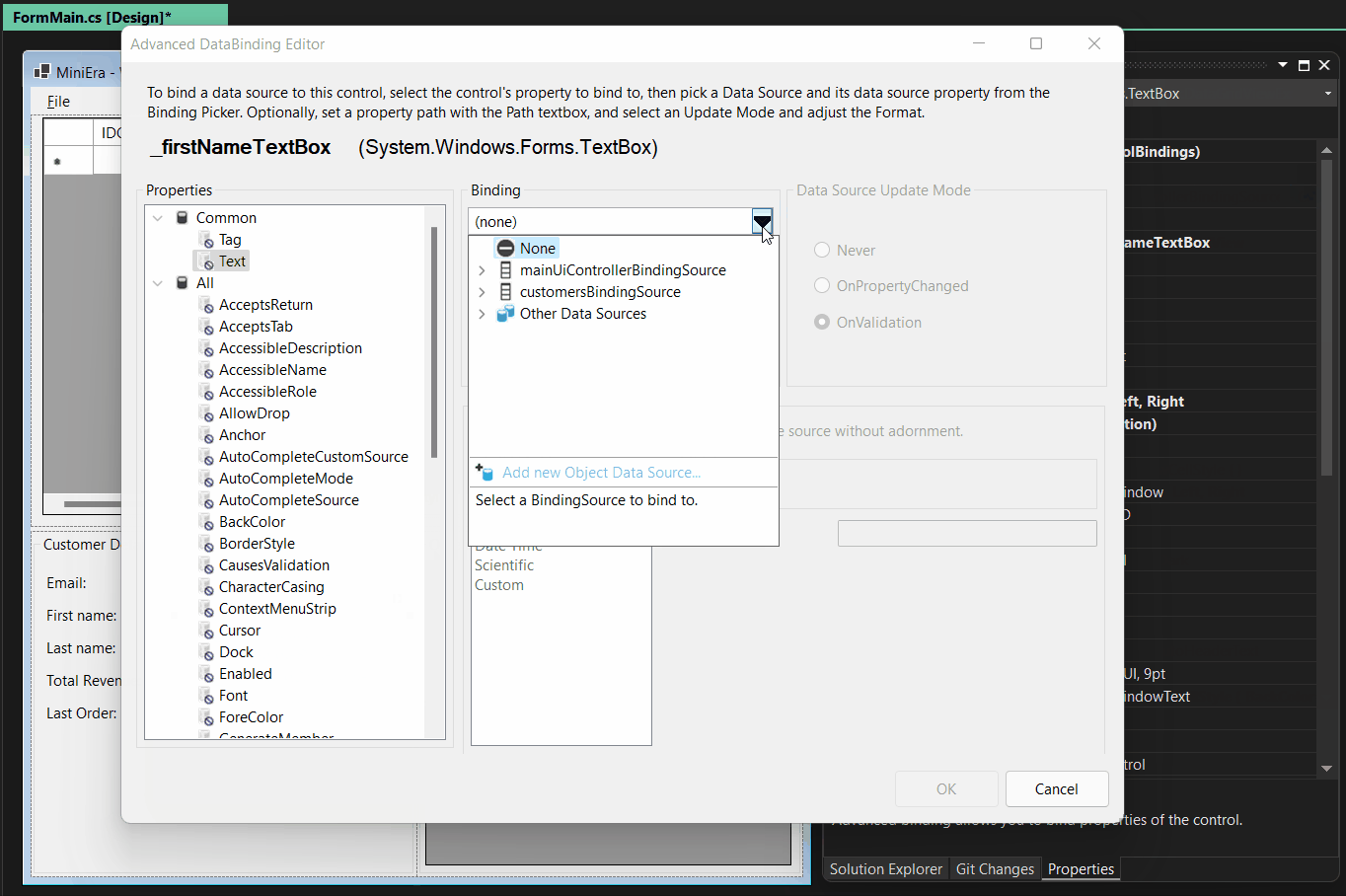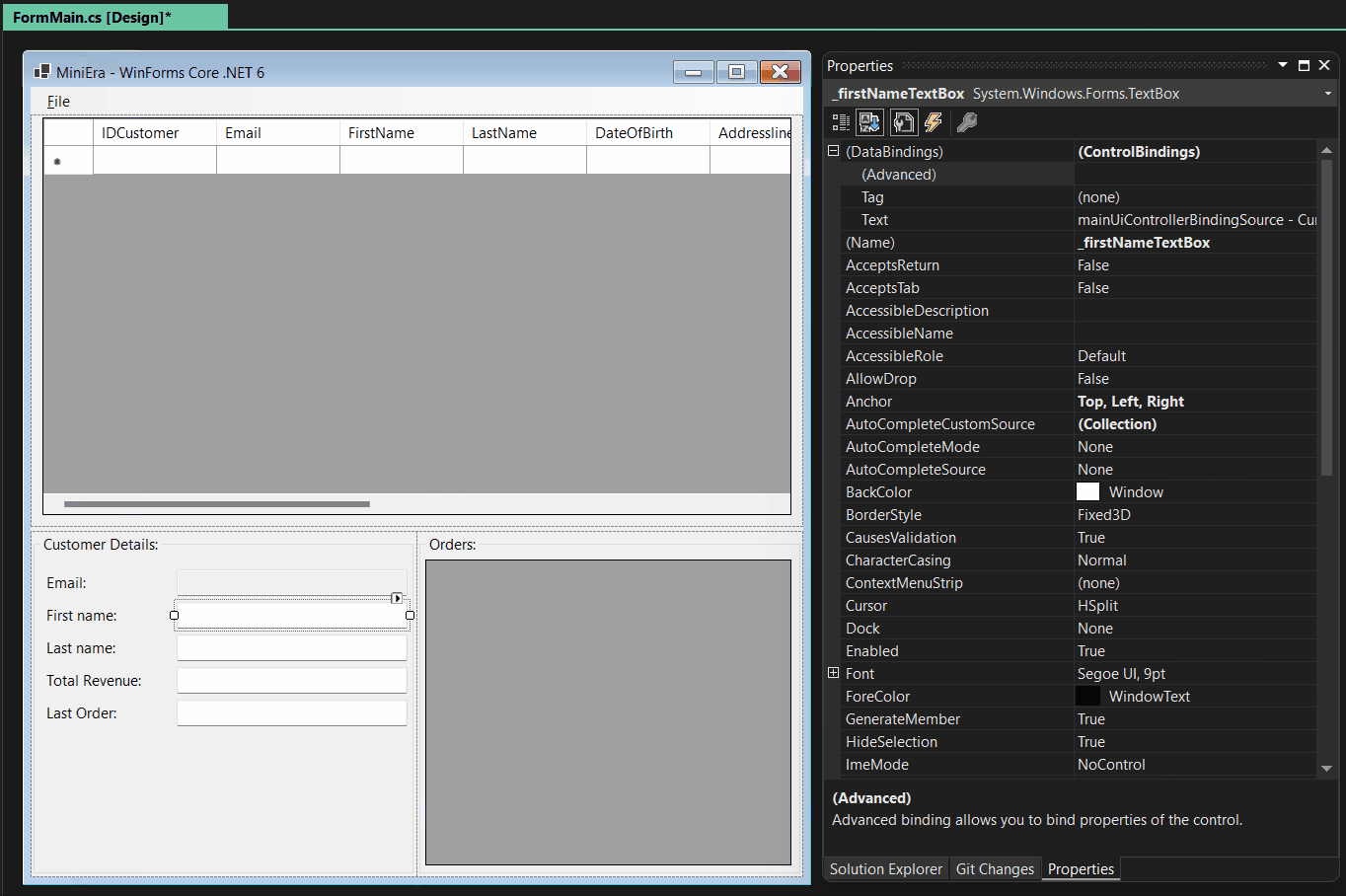
The Advanced Databinding Dialog now allows to set up another binding scenario:
Sometimes it’s necessary that you define a whole property path in complex
binding scenarios – which are scenarios, where you are binding to a list rather
than to a single object instance. In those cases, the correlating
BindingPath and BindingField of the Binding’s instance
BindingMemberInfo property can now easily be set in the Advanced Databinding
Editor by entering the whole path in the Path entry field. If this field gets
the focus, Path and Field are merged, and you can edit the property path as
a whole. When that entry field later loses the focus again, Path and Field
are separated in the same way as they would show up if you’d queried them at
runtime through the Binding’s correlating BindingMemberInfo property:
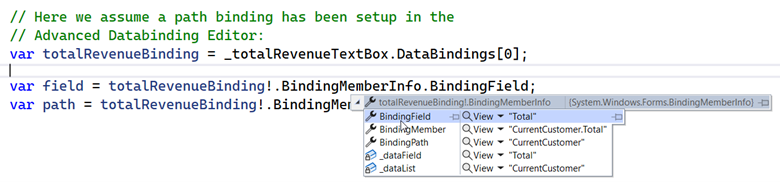
Summary and key takeaways
-
Databinding in WinForms .NET is focused on Object Data Binding. We encourage developers to explore modern ORM technologies like Entity Framework Core, which can be used in their latest versions in contrast to .NET Framework.
-
Databinding of legacy technologies (Typed DataSets) is still supported, albeit with some limitations. Typed DataSet definitions can be copied from Framework projects, but new Typed DataSets cannot be created in .NET projects, nor can their schemas interactively be changed.
Tip: Old and new database mapping technologies can coexist in a WinForms project, so there is a feasible way to gradually migrate the underlying data layer technologies, one Form at a time. -
Object Data Sources are defined for the project through the Design Binding Picker in the Property Browser by clicking on the Add New Object Data Source link. The Data Source Provider Service is at the time not available for .NET projects (neither WinForms nor WPF). That is also the case for the Data Sources tool window, which relies on the Data Source Provider Service.
-
Object Data Sources are a great tool migrating business “Code-behind” logic from Forms and UserControls into UI-stack-independent controller classes. This way, it becomes easier for WinForms apps to be unit tested or reuse business logic code in other contexts, and also have a clear migration path to introduce modern technologies in WinForms LOB Apps.
-
The Advanced Databinding Dialog is now easier to handle and more accessible. It now also allows the definition for entering property paths for complex binding scenarios.
As always, please tell us which features you would like to see in the Designer but also in the WinForms runtime around the databinding area.
Happy WinForms Coding!

Thank you so much. Is this project available on Github? I want to check it further for:
<code>
Hopefully i will get it there and do my research further.
Even we are not discussing your particular issue in that context (yet!), you might want to take a look here.
https://github.com/dotnet/winforms/issues/4895#issuecomment-1067106503
Whatever question you have about using this, please ask those in the context.
Also, this is a documented feature, and you’ll find more about this here:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/api/system.windows.forms.binding.format?view=windowsdesktop-6.0
I would like to describe my first experience with data binding to EF Core entities. My goal was to make master/detail data entry form with two DataGridView controls. For all entities i implemented IPropertyChanged and IPropertyChanging (with Fody). Enabled ChangeTrackingStrategy ChangingAndChangedNotifications to address some performance considerations. Than i tried to change list type of navigation properties to BindingList, and i could not do it because BindingList does not implement INotifyCollectionChanged. I was really baffled when...
BindingList predates the way, that DataBinding for example in WPF is done, based on INotifyPropertyChanged.
Please take a look here: EFCore has a way to provide compatible adapters, which provides the notification principles for both ObservableCollection and BindingList:
https://docs.microsoft.com/dotnet/api/microsoft.entityframeworkcore.changetracking.localview-1.tobindinglist?view=efcore-6.0
Thanks for that …
I feel happy when I see improvements to WinForms … It means it’s still alive .. still get updates .. I’m a big WF fan.
But will it be for long?
It’s here to stay! 🙂
Is this project available on GitHub?
I can’t find this on GitHub. I’d love to see this source code too. @Klaus can you publish it?
The "sample project" for this blog post doesn't have much more than already shown in the post. On top, this post was primarily targeted for showing the new Databinding UI in the new WinForms Designer. Now, I get also from the feedback which reaches me via email in addition, that more and more folks are interested in the Controller/ViewModel approach for WinForms, which this post only addresses partly. I think this is not the right...
Hi, thank you for this post. I’m so happy WinForms will have long life, I think it’s the best tech for building data/office-automation oriented clients.
Is this code example available in some repo which we can clone?
Office Automation oriented? I wonder if you’re using Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel package. Had problems with it with Office 365 and ended up switching to OpenXml
I’ll like to introduce some sample code in context of #4895 in the WinForms repo. Please also take part in the discussion, if you have additional ideas around that. Thomas already got engaged (thanks!) and had some pretty good ideas around that we should further discuss or consider.
Thanks for this post and sharing some news about the designer and the developer experience.
I am sad the DataSource browser Treeview in the property grid still doesn't sort the class properties alphabetically. When you have an object with a lot of them it makes the experience really painful. But it's been this way since the beginning, so I must be the only one mumbling about that :D
I just also discovered the issue #4895 about enhancing...
I did not have this on my radar, thanks for pointing this out. I’ll take a look, how we can improve this. Shouldn’t be too difficult!
It's awesome how much time your teem invests to migrate the WinForms-Designer.
At my actual work I have to use the WinForms-Designer with dotnet-framework 4.7.2. The designer is very buggy on that framework. It's a pain to work with it. For me it is no surprise that your team needs so much much time for migration because the old source is not well.
I must say, I don't understand why Microsoft invests so much resources for WinForms....
Thank you for the detailed report. I would like to disagree with the comments of Andi and Martin. I too have worked with the WinForms designer in Visual Studio for many years. I cannot confirm that it is buggy. On the contrary, I never had any issues with it. I don't see an issue in the fact that Microsoft has several UI technologies, all of which are maintained. On the contrary, we, the developers, have...
@Thorsten Sommer
I don’t see an issue in the fact that Microsoft has several UI technologies, all of which are maintained. On the contrary, we, the developers, have the choice and can select the best technology for each task.
You are right. In a good world it sounds very nice that we can decide a matching framework. But why you need 4 frameworks which solve the same problem (show something fancy on Windows-plattform).
What do you...
All these frameworks does the same thing. I cannot say which is the best. An official guide when to choose which one would be nice I think.
I don't agree. I think that each of those UI-Frameworks have different areas where they shine most, and on top address different team requirements, like design skills, ramp-up-times, accessibility advantages and much more. I wouldn't personally design a LOB app which needs let's more than 400 data...
I’ve been using WinForms on dotnet 3,4 extensively for 15 years, and nothing beats its productivity for UI-heavy apps, nothing! And I honestly do not remember when was the last time I encountered a bug or crash(and it’s a huge project). It just works!;) I am so happy MS decided to stick with, and modernise WinForms. Keep it up!
At my actual work I have to use the WinForms-Designer with dotnet-framework 4.7.2. The designer is very buggy on that framework. It’s a pain to work with it.
We should make what you say actionable! Please file a bug (or bugs) along with repros, so we can get that addressed - if it applies of course - in the WinForms Repo.
I must say, I don’t understand why Microsoft invests so much resources...
We all love the investment in WinForms. I have such fond memories of working with it and the improvements to data binding will give it a new lease of life. Seriously long live WinForms!!Read more
However please, please, please, show some love to WPF. Even the open source repo is barely supported. What's the point of open sourcing it if you're not going to staff the repo to allow the community to make the required updates.
We should make what you say actionable! Please file a bug (or bugs) along with repros, so we can get that addressed – if it applies of course – in the WinForms Repo.
Thanks for that info. I already created some issues for asp- and efcore on GitHub in the past. The GitHub plattform works realy good for contacting the MS-devs.
But sharing my WinForms problems is not possible for me because of two (or three)...
Hey Andi,
some thoughts:
The problems are not in runtime but on designer.
It's completely fine to report them in the WinForms repo, also because we need to assess if runtime or designer behavior are the root cause. Repros are important though. I know that bugs which only occur in big projects, which are using third party controls on top and probably custom Control Designers are hard to track down and the process can be frustrating...
<code>
I've seen viewModels with 10k+ code, just as abused as the code behind. If a developer can't make a difference in what belongs to UI code, and what doesn't, no binding class between View and Model would make his\hers code cleaner.
We had the architecture where the business logic is abstracted in separate libs, UI should just make calls to the database/webservice and represent the data.
<code>
I don't see the problem, you do not have to bind...
I agree with Andi. I appreciate your work and efforts on the WinForms-Designer, but on the other hand there is not so much invest in WPF.
We have switched a long time ago from WinForms to WPF. I understand that some people need to keep WinForms alive because they don't want to switch or the efforts to switch would be too high.
The problem also is that don't know how long WPF will live. Nowadays, there's...
I think the only real alternative to business application as a long term investment is WinForms, and is still maintained not because of the huge "legacy" application still around, but because is the best tool to implement data-entry intensive application in a sustainable timespan. It's just easy and powerfull.
WPF is made to implement media applications, and the complexity of xaml in complex interfaces is not sustainable.
All other framework just failed and are now...
It depends, what do you need to do? If you need a simple GUI for a windows business app, Winforms are still the best tool to use. Chose your tool, use the hammer appropriate for the nail.
As I said, I agree that for simple tools WinForms is pretty suitable, I have used it for a long time. Nowadays I always go with WPF even for smaller tools. But as you said hammer -> nail 😉 The only thing I’m “complaining” is the wide variety of frameworks do do not match and I hope they will merge back again in the future.
Yup, to many different hammers 😉 I actually agree. And I’m sad that Microsoft did not make something like Uno with a good designer. UI code should be UI code, wherever it runs.