In big data solutions, compute is expected to takes place where the data resides, mainly due to the cost of moving very large scale data across clusters. However there exist scenarios where more compute capacity is needed than the on-premises cluster provides. To avoid moving large chunk of data around, the beneficial scenario consists of a comparable small dataset (in big data terms) that requires an indirect proportional amount of compute capacity. This is usually the case when building Monte Carlo models or calculating multiple models based on one dataset.
In this case study you will learn how take advantage of Microsoft Azure HDInsight to run a remote Hadoop MapReduce job using Apache Templeton.
Overview of the Solution
The solution realizes a simple data flow that extracts a dataset from an on-premises Hadoop cluster (in our case a Cloudera cluster running on Linux), runs an on-premises task to anonymize the data (if needed), then creates a Microsoft Azure HDInsight cluster, uploads the anonymized dataset, and runs a set of compute intense translation/modeling jobs in HDInsight. Once the translation/modeling has been completed, the data will be downloaded from the cloud to the on-premises Hadoop cluster where the previously anonymized data will be de-anonymized. (The case study Data Anonymizing in Hadoop describes our anonymizing approach in detail and comes with a code repository on GitHub)
For simplicity purposes, we decided to describe and execute the data flow using a bash script. It schedules the on-premises MapReduce jobs for data extraction, runs the PIG statements that anonymize the data, leverages the Azure Command-Line Interface (CLI) for data upload/download and the interaction with HDInsight.
At the heart of the solution is Apache Templeton: It provides a REST-like web API which can be used to make HTTP requests to MapReduce, Pig and Hive. Using the HDInsight Templeton endpoint allows us to start, monitor and stop our remote MapReduce jobs.
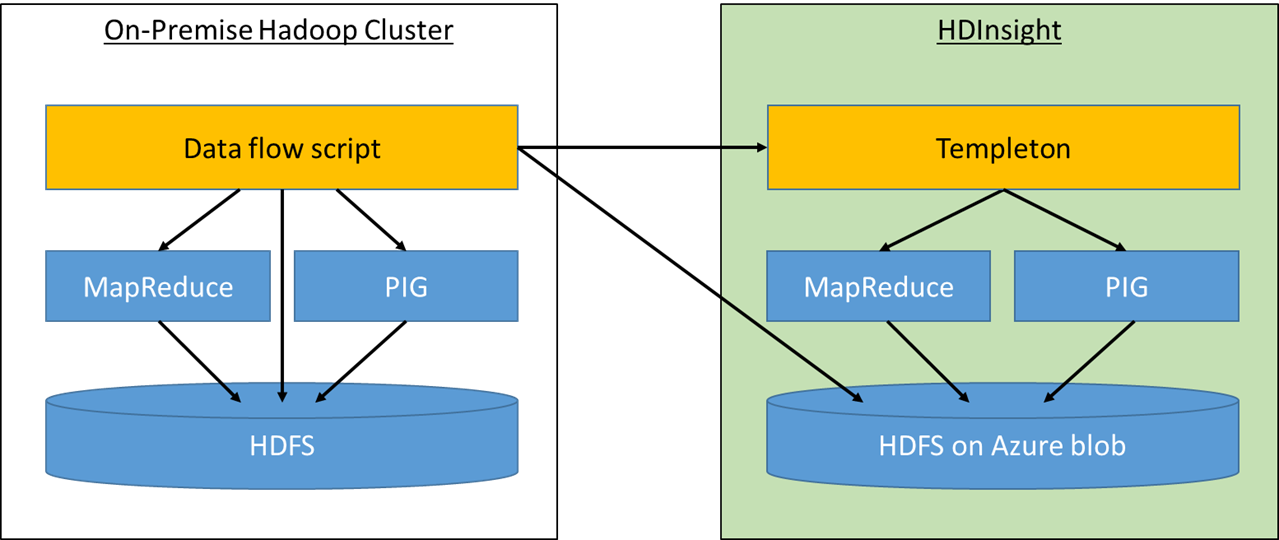
Figure 1: the data flow script runs on-premises and orchestrates all involved tasks
Code Artifacts
The bash script consists of a sequential flow of Azure CLI and Apache Templeton calls. While most of this is straight forward, starting and monitoring an HDInsight job from an on-premises Hadoop cluster required some trickery (the commands dealing with the HDInsight job are highlighted in bold):
# We copy the data and programs to blob store using the Azure CLI tools
# These blobs are mapped through the HDInsight cluster via wasb:// so they are available via
# the local cluster file system.
azure storage blob upload anonymized default "/user/jaglion/input/"
azure storage blob upload bin/jaglion.jar default "/user/jaglion/jaglion.jar"
# This part of the script is what launches and monitors the job through the “Templeton” interface
# HDInsight Endpoint for remote invocations
# API=https://jaglion.azurehdinsight.net/templeton/v1
# HDInsight credentials
CRED=”user.name=jaglion –u jaglion:<password>”
# Run the job in HDInsight
# This invocation sends a request to Hadoop via Templeton that requests the cluster to run
# the Jaglion.Job class with the arguments defined with ‘–d arg=’.
# The other arguments, specifically (jar, callback, statusdir, hdInsightJobName) are information # for Hadoop to successfully run the job requested.
#
JOBID=$(curl -d $CRED -d jar=$OUTPUTBASE/jaglion.jar -d hdInsightJobName=$BASEDIR
-d arg=$BASEDIR/input -d arg=$BASEDIR/output
-d arg=$BASEDIR/configuration.xml -d statusdir=$BASEDIR
-d callback=null -d class=Jaglion.Job '$API/mapreduce/jar' | jsawk 'return this.id')
# Monitor the job until it completes
STATUS=$(curl -s $CRED $API/jobs/$JOBID?user.name=jaglion | jsawk 'return this.status.state')
while [ "$STATUS" != "SUCCEEDED" ]; do
STATUS=$(curl -s $CRED $API/jobs/$JOBID?user.name=jaglion | jsawk 'return this.status.state')
done
# After this, we can copy the resulting data back to the local cluster from blob store because
# the HDInsight job writes the results back to blob store via the same wasb:// mapped file system
# used to setup the job.
mkdir -p $OUTPUTBASE/translated
azure storage blob download default "$OUTPUTBASE/output" $OUTPUTBASE/output
Opportunities for Reuse
The described way to run and monitor an HDInsight job from a Linux or Windows server can be used even without involving an on-premises Hadoop cluster. However for performance reasons, it is crucial that the amount of off-premises compute is highly indirect proportional to the size of the data which is moved between off- and on-premises. The following two formulas help to evaluate whether running jobs off-premises yield to a capacity and/or time gain:
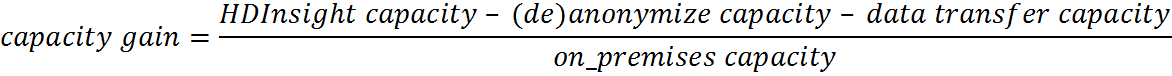
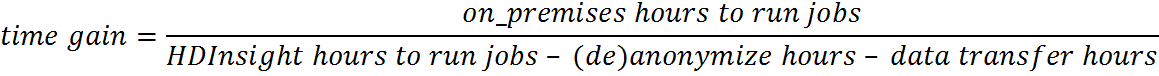
In the case of an on-premises Windows to HDInsight scenario, the Microsoft Azure Data Factory should be considered. It provides a reliable platform for building rich data processing pipelines across multiple data stores.
