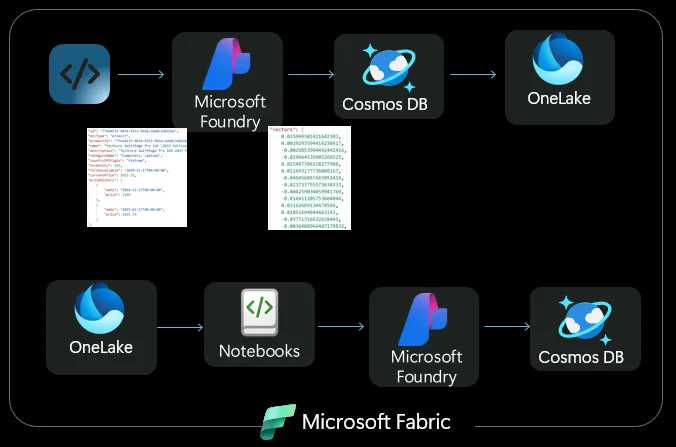
We’re excited to announce that Cosmos DB in Microsoft Fabric and Cosmos DB Mirroring are now Generally Available, uniting your operational and analytical data in one platform. You can now analyze live Cosmos DB data directly in Fabric—no complex or costly ETL required. Data stays in sync in OneLake, providing a single source of truth for real-time and historical insights. Write queries using T-SQL from a SQL Endpoint or use Python and Spark Notebooks in Fabric.
As a distributed NoSQL database Cosmos DB in Fabric brings support for semi or unstructured data to analytics and ML workloads as well as a host of additional new capabilities to Fabric, including vector indexing and search using DiskANN and reverse ETL capabilities allowing customers to serve analytics to users with incredible speed at massive scale.
Whether you’re building dashboards, running analytics, or training ML models, you can work on fresh operational data for faster, AI-ready insights. This GA release delivers production-grade performance, enterprise security, and the scale of Cosmos DB’s low-latency architecture within the unified Fabric experience. Let’s go into some of these benefits and how you can use Cosmos DB in Fabric in your workloads.
Cosmos DB in Fabric has been a home run for Kinectify. As a company, we store a lot of data in Cosmos DB, and being able to automatically, reliably and performantly move data with zero ETL into Fabric has allowed us to experiment with Fabric in ways that we simply would not have been able to if we had to setup the ETL ourselves.
Mike Calvin, CTO at Kinectify
Vector indexing support for AI and ML workloads
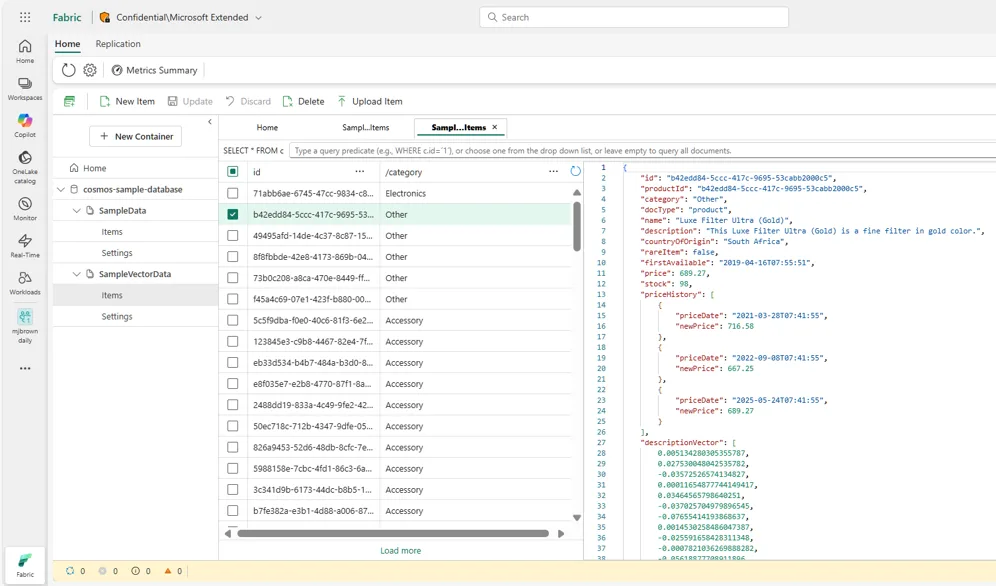
Cosmos DB in Microsoft Fabric is an AI-optimized NoSQL database and is the first database in Azure to offer DiskANN, a graph-based indexing and search system that can index, store, and search large sets of vector data on relatively small amounts of computational resources. DiskANN provides fast and efficient query filtering via pushdown to the index to enable fast and cost-effective hybrid queries. It also has support for full-text indexing and search with BM25 as well as hybrid search capability that combines vector search with full-text search scoring by using the Reciprocal Rank Fusion (RRF) function.
Cosmos DB in Fabric vector indexing enables efficient similarity searches across high-dimensional data, which is also beneficial for data science scenarios including:
- Anomaly detection where behaviors are vectorized and stored, combined with extremely fast similarity searches to identify anomalies enabling real-time anomaly flagging without scanning entire datasets in OneLake.
- Alternating Least Squares (ALS) where ALS generates user and item factor vectors. Vector indexing accelerates the recommendation pipeline by enabling fast nearest-neighbor lookups—finding similar users or items based on their factor vectors. Combined with the reverse ETL technique, this allows you to retrieve top-K recommendations or find similar users with millisecond latency without expensive distance computations across all vectors.
Both scenarios illustrate how Cosmos DB in Fabric goes from a document store into a vector database, letting you build ML-powered applications without maintaining separate vector stores.
With Cosmos DB natively available in Microsoft Fabric, we can now operationalize transactional data for near real-time analytics and GenAI use cases without complex ETL or duplication. This integration simplifies our architecture and reduces latency between our operational and analytical systems, enabling faster decisions and richer insights for our customers. It’s a game changer.
Enterprise Solution Architect, MAQ Software
User-data functions and translytical task flows
Cosmos DB in Microsoft Fabric is tightly integrated with user-data functions in Microsoft Fabric. Fabric User data functions provide a platform to write and host your business logic, internal algorithms, and libraries. You can also integrate it into your Fabric architectures to customize the behavior of your solutions.
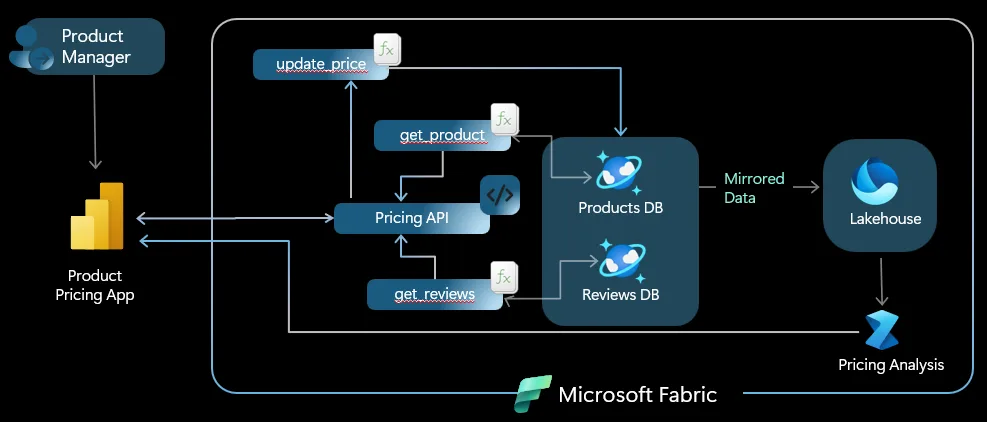
User-data functions in Fabric provides a simplified means for encapsulating operations on your data in Cosmos DB in Fabric. This enables translytical task flows by making published user-data functions available to Fabric artifacts such as Power BI reports, allowing users to write back to their operational data stored in Cosmos DB based upon the insights presented to the user.
Consider this scenario in which a product manager is working to ensure maximum revenue for their products. A user could build a Power BI report to analyze the pricing performance and from that report, then update the prices of their products directly back to their product database. This kind of scenario would have previously required extensive ETL and analytics. Translytical task flows utilizing Fabric’s user-data functions with Cosmos DB in Fabric makes this process much simpler.
Reverse ETL
Cosmos DB in Fabric provides zero-ETL integration between operational data in Cosmos DB and analytical data in OneLake. It also serves as a powerful, low-latency data layer capable of handling high concurrency across diverse data types—making it ideal for implementing reverse-ETL patterns in analytical workloads.
With reverse-ETL, Cosmos DB in Fabric can act as a serving layer that feeds analytical insights back into applications or reports. This enables developers to deliver real-time intelligence—such as purchase predictions, fraud detection, or personalization—to thousands of users simultaneously.
Reverse-ETL is typically implemented in a Fabric Notebook using Spark to write data back into a database for use in reports or applications. Cosmos DB’s Spark Connector simplifies this process by supporting reads, writes, queries, and container management, including throughput configuration.
Getting Started
To learn more about Cosmos DB in Fabric, here are some resources to help you get started.
- Cosmos DB in Fabric docs: The best place to get started is with our docs. You can start here, https://aka.ms/CosmosFabricDocs
- Cosmos DB in Fabric Samples: We have an extensive (and growing) set of samples ready for users to get started exploring Cosmos DB in Fabric. You can see our samples here, https://aka.ms/CosmosFabricSamples
- Cosmos DB in Fabric Videos: We also have a growing list of videos you can use to get more familiar with Cosmos DB in Fabric on YouTube: https://aka.ms/CosmosFabricVideos
Check out this video on how to get started with a Python Notebook with Cosmos DB in Fabric.
Whether you are an application developer, data engineer or analytics user, Cosmos DB in Fabric provides lots of benefits. Cosmos DB’s AI capabilities, support for semi or unstructured data, instant autoscale elasticity, fast performance and high availability make it a great companion for building workloads in Microsoft Fabric.
About Azure Cosmos DB
Azure Cosmos DB is a fully managed and serverless NoSQL and vector database for modern app development, including AI applications. With its SLA-backed speed and availability as well as instant dynamic scalability, it is ideal for real-time NoSQL and MongoDB applications that require high performance and distributed computing over massive volumes of NoSQL and vector data.
To stay in the loop on Azure Cosmos DB updates, follow us on X, YouTube, and LinkedIn.



0 comments
Be the first to start the discussion.