Large Language Models (LLMs) have reached a point where general intelligence is no longer the bottleneck. The real challenge in enterprise AI systems behavioral alignment ensuring models that produce consistent, reliable, policy-compliant outputs on a scale. Prompt engineering and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) are powerful but they do not change model behavior. Fine-tuning will solve this by customizing a pretrained AI model with additional training on a specific task or dataset to improve performance, add new skills, or enhance accuracy.
This post explores what Microsoft Foundry fine-tuning is, when using it, the fine-tuning approaches it supports and code examples on how to run Fine-tuning on Microsoft Foundry.
What Is Microsoft Foundry Fine-Tuning:
Microsoft Foundry fine-tuning allows you to customize pre-trained foundation models (OpenAI and open models) using task-specific datasets, producing a specialized model that behaves predictably for your use case while maintaining Azure’s enterprise-grade security, governance, and observability.
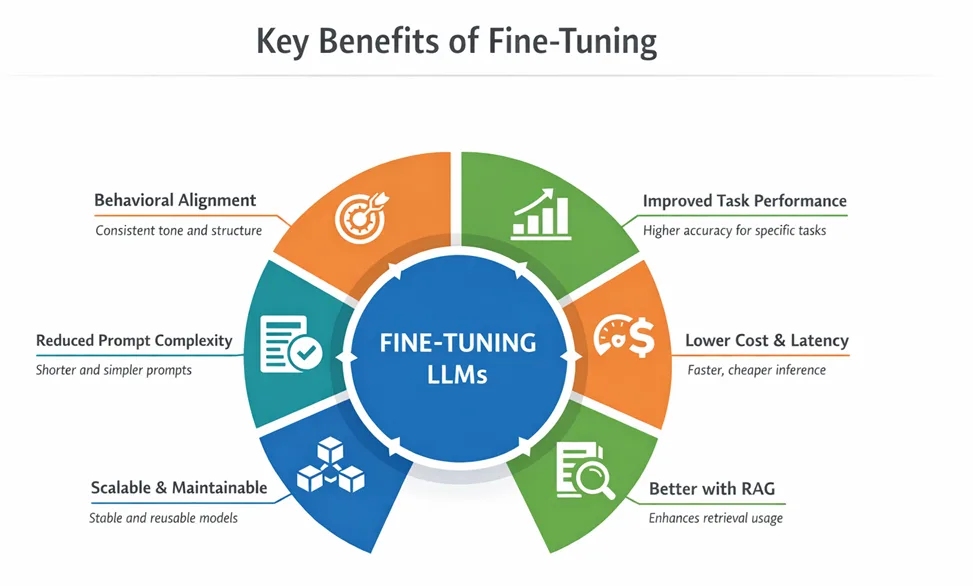
Key Benefits and top use cases of Fine-tuning:
- Domain Specialization: Adapt a language model for specialized domains like medicine, finance, or law to understand technical jargon and deliver more accurate, domain-specific responses.
- Task Performance: Optimize a model for tasks like sentiment analysis, code generation, translation, or summarization to achieve higher performance than a general-purpose model.
- Style and Tone: Fine-tune the model to match your preferred communication style, such as formal business, brand voice, or technical writing.
- Instruction Following: Enhance the model’s ability to follow formatting rules, multi-step instructions, and structured outputs, including selecting the right agent in multi-agent workflows.
- Compliance and Safety: Train a fine-tuned model to adhere to organizational policies, regulatory requirements, or other guidelines unique to your application.
- Language or Cultural Adaptation: Tailor a language model to a specific language, dialect, or cultural context when general-purpose models fall short, without the cost of training from scratch.
Supported Finetuning Methods:
- Supervised Finetuning
- Direct Preference Optimization
- Reinforcement Finetuning
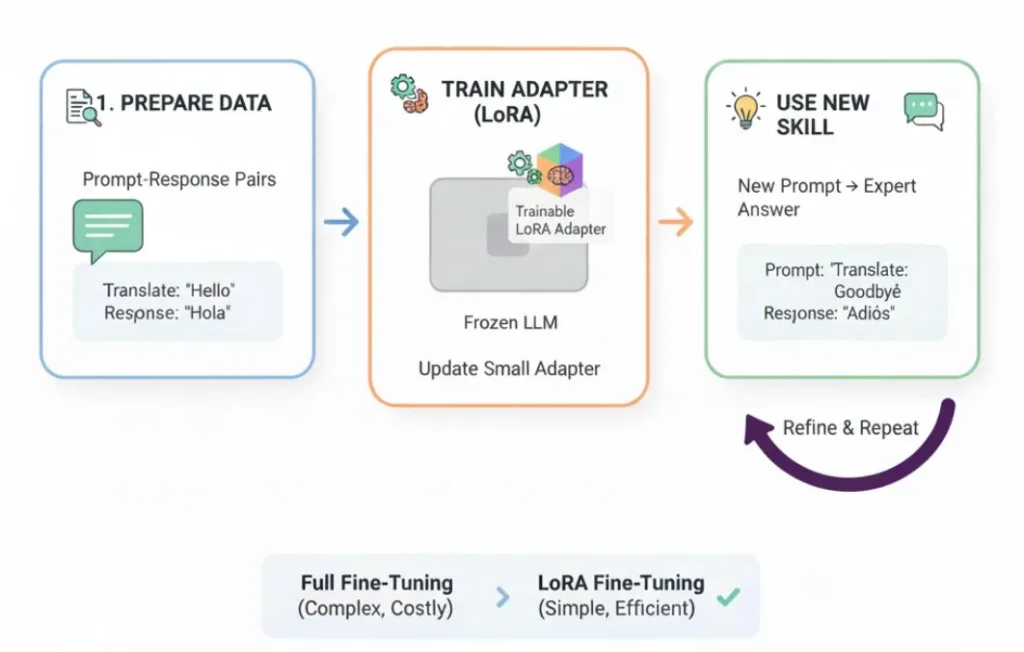
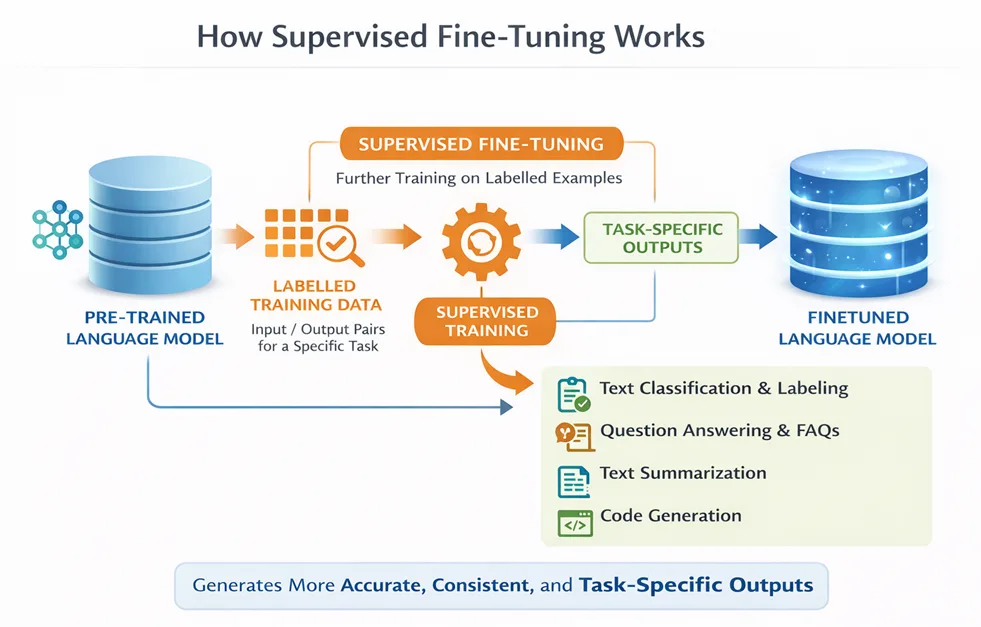
Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) is foundational training technique that trains a pre-trained model on input-output pairs for a specific task. It helps the model give more accurate, consistent, and task-specific responses, such as summarizing text, answering questions, or generating code, while keeping the knowledge from the original base model.
Best use cases for SFT:
- Text Classification & Labeling
- Question Answering & Knowledge Extraction
- Text Summarization
- Code Generation & Analysis
- Structured Output & Formatting
- Domain-Specific Language or Style Alignment
- Multi-Agent or Tool-Calling Workflows
How it works: You provide the model with a fixed set of examples, and it learns to produce the desired output for a given input. It’s a “learn by example” approach.
Supervised Finetuning Code Snippet: It is supported by Microsoft Foundry SDK and Foundry UI. This demonstrates the code snipped using Microsoft Foundry SDK:
import os from dotenv import load_dotenv from azure.identity import DefaultAzureCredential from azure.ai.projects import AIProjectClient load_dotenv() endpoint = os.environ.get("AZURE_AI_PROJECT_ENDPOINT") model_name = os.environ.get("MODEL_NAME") # Define dataset file paths training_file_path = "training.jsonl" validation_file_path = "validation.jsonl" credential = DefaultAzureCredential() project_client = AIProjectClient(endpoint=endpoint, credential=credential) openai_client = project_client.get_openai_client() with open(validation_file_path, "rb") as f: validation_file = openai_client.files.create(file=f, purpose="fine-tune") openai_client.files.wait_for_processing(validation_file.id) with open(training_file_path, "rb") as f: train_file = openai_client.files.create(file=f, purpose="fine-tune") openai_client.files.wait_for_processing(train_file.id) fine_tune_job = openai_client.fine_tuning.jobs.create( model=model_name, training_file=train_file.id, validation_file=validation_file.id, method={ "type": "supervised", "supervised": {"hyperparameters": {"n_epochs": 3, "batch_size": 1, "learning_rate_multiplier": 1.0}}, }, suffix="pubmed-summarization" )
Data Format Example: The training data sample should contain min. of 10 lines
{ "messages": [ { "role": "system", "content": "You are a medical research summarization assistant. Create concise, accurate abstracts of medical research articles that capture the key findings and methodology." }, { "role": "user", "content": "Summarize this medical research article:\n\n[full article text]" }, { "role": "assistant", "content": "[generated abstract]" } ] }Cookbooks: SFT with PubMed Medical Research Summarization Dataset
This cookbook fine-tuning/Demos/SFT_PubMed_Summarization at main · microsoft-foundry/fine-tuning demonstrates how to fine-tune language models using Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) with the PubMed Medical Research Summarization dataset on Azure AI.
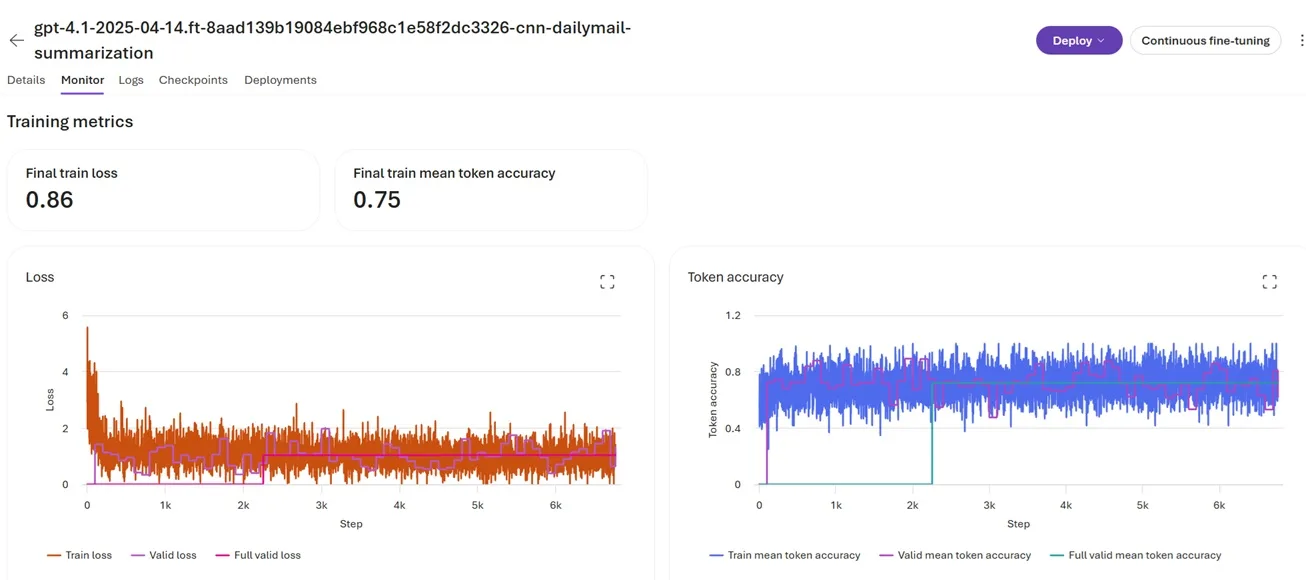
After executing the cookbook, one can navigate to Foundry Portal to monitor the job details.
Fine-tuning job view in Microsoft Foundry:
Navigate to Microsoft Foundry at https://ai.azure.com then the fine-tuning section to view the job details and execution progress
Key highlights:
- This cookbook uses GPT4.1 as the base model and PubMed Article Summarization Dataset on Kaggle as the reference training data set.
- Prerequisites: Ensure you have Azure subscription with Microsoft Foundry project; you must have Azure AI User role, have access to the required models and set up an AI Foundry project
- Dataset Preparation: Finetuning expects the datasets in JSONL formats, the JSONL can be found here: Use the training.jsonl and validation.jsonl available in this Cookbook sample
- Finetune Job: Configure with default hyper parameters and run the finetune job
- Deployment: Optionally, deploy the finetuned model to a serverless endpoint and perform sample inferences.
Results of Finetuning
| Metric | Base Model | Fine-Tuned Model |
|---|---|---|
| Task Accuracy | 70–80% | 88–95% |
| Prompt Length | 800–1200 tokens | 200–400 tokens |
| Inference Cost | Baseline (1.0x) | 0.5–0.7x |


Thank you for the blog post. However, the code blocks aren’t showing as multiline text. This makes it pretty hard to read.
Platform: iPhone 13 Pro Max
System: iOS
Browser: Chrome