With the discontinuation of the popular InAppBillingPlugin, many .NET MAUI developers have been looking for guidance on implementing in-app purchases in their applications. Today, we’re sharing a comprehensive sample that demonstrates how to implement cross-platform billing for Android, iOS, Mac Catalyst, and Windows using platform-specific APIs with a unified interface.
The BillingService Sample
Our new BillingService sample shows you how to integrate platform-specific billing systems into your .NET MAUI applications while maintaining clean, maintainable code through dependency injection and the MVVM pattern. The sample includes complete implementations for:
- Android: Google Play Billing Client v7
- iOS & Mac Catalyst: StoreKit
- Windows: Microsoft Store APIs
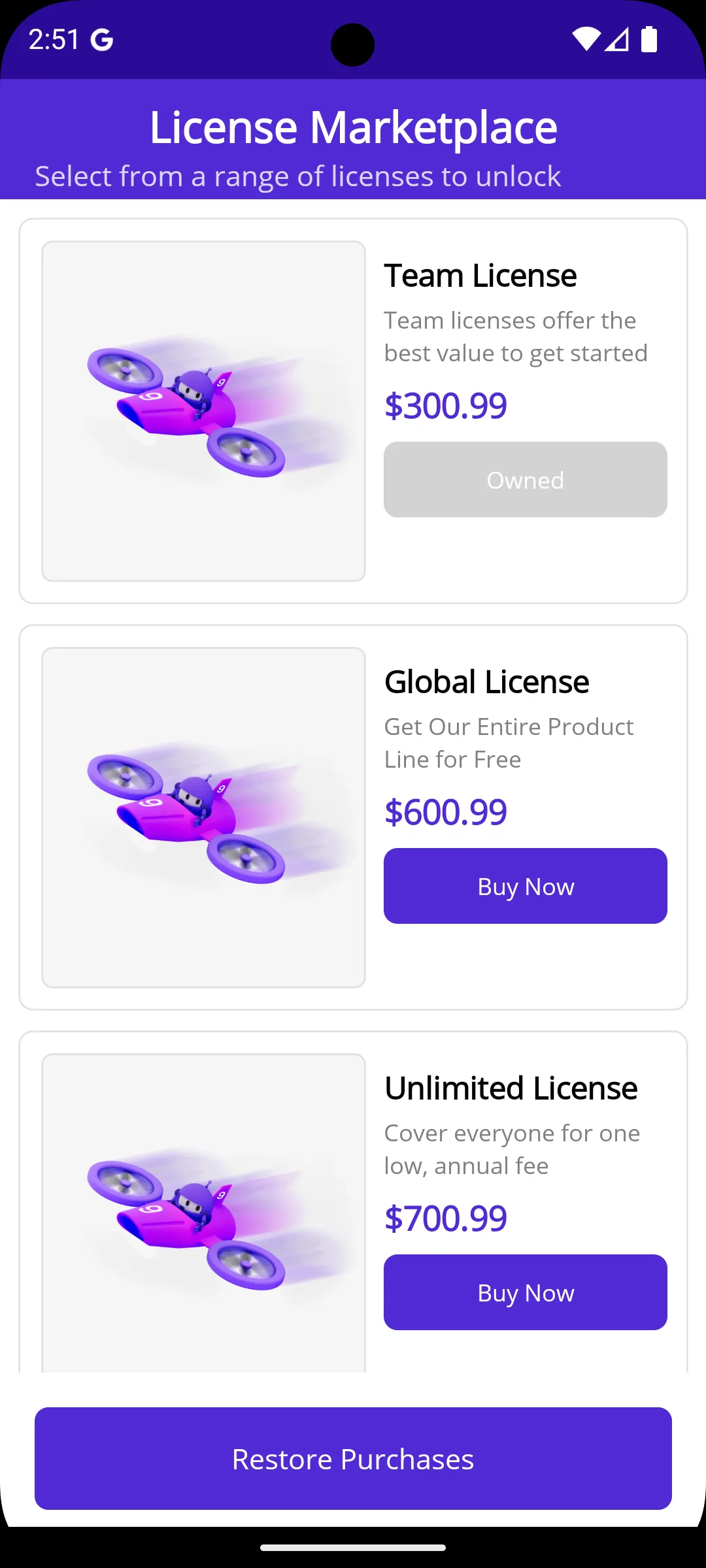
Architecture Overview
The sample demonstrates several important architectural patterns for cross-platform development:
Unified Interface
At the core of the implementation is a clean IBillingService interface that abstracts platform-specific billing operations:
public interface IBillingService
{
Task<bool> InitializeAsync();
Task<IEnumerable<Product>> GetProductsAsync();
Task<PurchaseResult> PurchaseAsync(string productId);
Task<bool> RestorePurchasesAsync();
bool IsProductOwned(string productId);
}Platform-Specific Implementations
Each platform has its own implementation file using conditional compilation:
BillingService.Android.cs– Google Play Billing integrationBillingService.iOS.cs– StoreKit implementation (shared between iOS and Mac Catalyst)BillingService.Windows.cs– Microsoft Store integration
The project file uses conditional compilation directives to include the appropriate implementation for each target platform, while iOS and Mac Catalyst share a single implementation since they both use identical StoreKit 1 APIs.
Dependency Injection
The billing service is registered in MauiProgram.cs and automatically resolves to the correct platform-specific implementation at runtime:
builder.Services.AddSingleton<IBillingService, Services.BillingService>();
builder.Services.AddTransient<ProductsViewModel>();A Note on StoreKit Implementation
The current iOS and Mac Catalyst implementation uses StoreKit 1, which continues to work on all current iOS versions, including iOS 18, 26, and beyond. At WWDC 2024, Apple announced the deprecation of StoreKit 1 in favor of StoreKit 2, which offers enhanced features and modern Swift-first APIs with async/await support. While StoreKit 1 remains functional for existing implementations, Apple has indicated that future enhancements and new features will be exclusive to StoreKit 2.
This sample provides a production-ready implementation you can use in your apps today. We are still working on Swift interop for .NET and plan to update this sample once full StoreKit 2 support is available in .NET for iOS. The migration to StoreKit 2 will bring improvements like better transaction handling, enhanced subscription management, and modern async patterns, but your apps using StoreKit 1 will continue to function properly in the meantime.
Important
For production applications, you should implement server-side purchase validation and receipt verification to ensure security and prevent fraud. This sample focuses on the client-side implementation patterns.Getting Started
To explore the sample and see how each platform implements billing:
- Browse the complete source code in the .NET MAUI samples repository
- Check out the online samples browser to see the sample in action
- Clone the repository and run the sample on your development machine
The sample includes detailed README documentation with platform-specific setup instructions for Google Play Console, App Store Connect, and Microsoft Partner Center.
Configuration Requirements
Before testing in-app purchases, you’ll need to configure products in each platform’s developer console:
- Android: Set up products in Google Play Console and configure license testers
- iOS/Mac Catalyst: Create products in App Store Connect and set up sandbox tester accounts
- Windows: Configure add-ons in Microsoft Partner Center and associate your app with the Store
Each platform has specific requirements for testing, and the sample documentation provides step-by-step guidance for each.
Learn More
The BillingService sample demonstrates patterns you can adapt for your own applications. Key takeaways include:
- How to create a unified interface for platform-specific billing operations
- Proper use of conditional compilation for platform-specific code
- Integration with dependency injection and MVVM patterns
- Error handling and user feedback for billing operations
- Testing strategies for in-app purchases
Visit the .NET MAUI samples browser to explore this and other samples that help you build better cross-platform applications.
Resources
- BillingService Sample – Complete source code
- Google Play Billing Documentation
- Apple StoreKit Documentation
- Microsoft Store In-App Purchases
- .NET MAUI Documentation
We hope this sample helps you implement in-app purchases in your .NET MAUI applications! Share your feedback and questions in the comments below.




I am encountering difficulties implementing social authentication (Google and Facebook) with Firebase in a .NET MAUI application for my main academic project. I respectfully request concise, authoritative resources—such as step-by-step written instructions or YouTube tutorials—and any configuration notes specific to MAUI (including Android/iOS platform setup, OAuth redirect handling, and required SHA fingerprints) that will enable a correct and secure integration. Thank you.