Connecting the Dots: How Graph Databases Drive Innovation
In today’s data-rich world, organizations face challenges that go beyond simple tables and rows. Whether it’s uncovering hidden relationships in social networks, detecting fraud, or powering recommendation engines, graph databases offer a unique way to model and analyze complex connections.
JanusGraph, an open-source graph database, combined with Azure Managed Instance for Apache Cassandra, provides a scalable, secure, and flexible foundation for building graph-powered applications making it easier for teams to tackle problems that traditional databases struggle to solve.
From Problem to Solution: Building Scalable Graph Applications
The Challenge:
Traditional graph databases can be difficult to scale, manage, and secure especially in cloud environments. Azure Cosmos DB’s Gremlin API is powerful, but some use cases require deeper customization or open-source extensibility.
The Solution:
By integrating JanusGraph with Azure Managed Cassandra, organizations gain access to distributed and highly available graph storage, with data automatically replicated across nodes to ensure fault tolerance. This partnership delivers efficient graph traversal by mapping graph concepts onto Cassandra tables, significantly speeding up queries. In addition, managed service features such as automated scaling, seamless patching, continuous monitoring, and strengthened security posture enhance reliability and ease of use, making this combination a powerful, scalable foundation for graph applications.
How It Works
JanusGraph uses Cassandra as its storage backend, persisting vertices, edges, and properties in distributed tables. Queries are written in Gremlin (the open-source traversal language), translated into Cassandra CQL, and executed across the cluster.
Note: JanusGraph’s Gremlin implementation is open-source and runs on your Azure managed Cassandra cluster, while Cosmos DB’s Gremlin API is a fully managed Graph engine with its own operational model.
Key Benefits
Scalability: Both JanusGraph and Cassandra scale horizontally and vertically, handling large graphs and high write throughput.
High Availability: Cassandra’s replication ensures data durability.
Performance: Optimized for complex graph traversals and analytics.
Flexibility: Customize storage, queries, and indexing.
Active Community: Extensive documentation and support.
Typical Use Cases
Social networks: Modeling relationships between users and content.
Recommendation systems: Analysing user behaviour for personalized suggestions.
Fraud detection: Spotting suspicious patterns in financial transactions.
Knowledge graphs: Representing complex entity relationships.
IoT analytics: Understanding device interactions.
Getting Started: A Practical Guide
Provision an Azure Managed Instance for Apache Cassandra Cluster: Refer to the official Azure documentation for step-by-step instructions to establish a Cassandra cluster with your specified configuration, including node count, storage requirements, and network parameters.
Install JanusGraph: This guide describes how to use Azure Virtual Machines to run JanusGraph, connecting them to the Cassandra MI clusters established in Step 1.
QuickStart – Create a Linux VM in the Azure portal – Azure Virtual Machines | Microsoft Learn
Ensure that the Virtual Machine hosting JanusGraph is assigned to the same subnet within the Virtual Network created when setting up the Cassandra cluster in Step 1.
To install JanusGraph on Azure Linux VMs, refer to the following documentation: JanusGraph Local Installation
Configure Connections: Set up your JanusGraph instance to connect to the Cassandra cluster.
After completing the steps to install Cassandra MI and JanusGraph on Azure, log into your VM and create a configuration file to link the Cassandra cluster with JanusGraph.
You will find the configuration files for JanusGraph under /opt/janusgraph-1.1.0/conf/.
Create a new cql.properties file for Azure Cassandra MI; in this example, the file is named “janusgraph-azure-cql.properties”.

Below are the contents you should include in the “janusgraph-azure-cql.properties” file. Make sure your configuration matches this format.
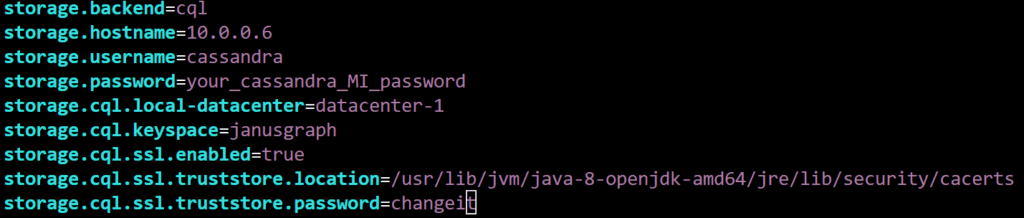
A key point to remember is to add the SSL Trust Store configuration details as required for your Virtual Machine. The default path and password for the trust store on an Ubuntu image should be similar, but update the file as needed and save it.
Once you’ve created the property file, start the JanusGraph server from the /opt/janusgraph-1.1.0/bin/ directory.
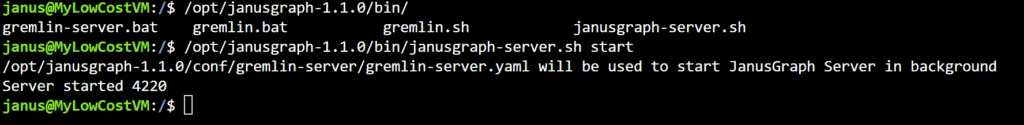
To launch the Gremlin process, use the gremlin.sh script located in the same /opt/janusgraph-1.1.0/bin/ folder.
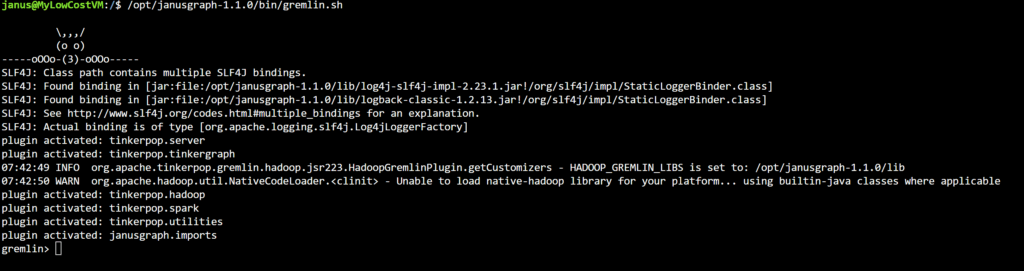
Load and Query Data: Populate the graph by utilizing Gremlin for data integration.
To connect the Gremlin console to Azure Cassandra MI, instantiate the Gremlin Factory as demonstrated below.
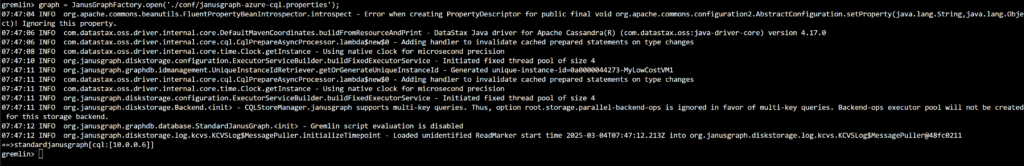
Once the Factory is instantiated, use Gremlin queries to access and analyze your graph data.
Note: JanusGraph leverages Apache TinkerPop’s Gremlin query language for graph traversals and analytics. Gremlin is an open-source, vendor-neutral language designed for property graph databases. When you use JanusGraph, you write Gremlin queries that are executed directly on your managed Cassandra backend.
Closing Notes & How Can You Get Started?
By combining JanusGraph with Azure Managed Cassandra, organizations gain access to a scalable, secure, and flexible platform for advanced graph analysis while benefiting from the conveniences of managed cloud services. Whether the goal is to develop social networks, build recommendation engines, or implement fraud detection systems, this approach empowers teams to unlock new possibilities in graph-powered applications.
Ready to begin your journey?
- Explore the JanusGraph documentation
- Follow Azure’s Cassandra MI setup guide
- Dive into JanusGraph installation steps
- Use Gremlin Query Language

0 comments
Be the first to start the discussion.