Announcing TypeScript 3.9 Beta
Today we’re announcing the availability of TypeScript 3.9 Beta!
To get started using the beta, you can get it through NuGet, or use npm with the following command:
npm install typescript@beta
You can also get editor support by
- Downloading for Visual Studio 2019/2017
- Following directions for Visual Studio Code and Sublime Text.
For this release our team been has been focusing on performance, polish, and stability. We’ve been working on speeding up the compiler and editing experience, getting rid of friction and papercuts, and reducing bugs and crashes. We’ve also received a number of useful and much-appreciated features and fixes from the external community!
- Improvements in Inference and
Promise.all - Speed Improvements
// @ts-expect-errorComments- Uncalled Function Checks in Conditional Expressions
- Editor Improvements
- Breaking Changes
Improvements in Inference and Promise.all
Recent versions of TypeScript (around 3.7) have had updates to the declarations of functions like Promise.all and Promise.race. Unfortunately, that introduced a few regressions, especially when mixing in values with null or undefined.
interface Lion {
roar(): void
}
interface Seal {
singKissFromARose(): void
}
async function visitZoo(lionExhibit: Promise<Lion>, sealExhibit: Promise<Seal | undefined>) {
let [lion, seal] = await Promise.all([lionExhibit, sealExhibit]);
lion.roar(); // uh oh
// ~~~~
// Object is possibly 'undefined'.
}
This is strange behavior! The fact that sealExhibit contained an undefined somehow poisoned type of lion to include undefined.
Thanks to a pull request from Jack Bates, this has been fixed with improvements in our inference process in TypeScript 3.9. The above no longer errors. If you’ve been stuck on older versions of TypeScript due to issues around Promises, we encourage you to give 3.9 a shot!
What About the awaited Type?
If you’ve been following our issue tracker and design meeting notes, you might be aware of some work around a new type operator called awaited. This goal of this type operator is to accurately model the way that Promise unwrapping works in JavaScript.
We initially anticipated shipping awaited in TypeScript 3.9, but as we’ve run early TypeScript builds with existing codebases, we’ve realized that the feature needs more design work before we can roll it out to everyone smoothly. As a result, we’ve decided to pull the feature out of our main branch until we feel more confident. We’ll be experimenting more with the feature, but we won’t be shipping it as part of this release.
Speed Improvements
TypeScript 3.9 ships with many new speed improvements. Our team has been focusing on performance after observing extremely poor editing/compilation speed with packages like material-ui and styled-components. We’ve dived deep here, with a series of different pull requests that optimize certain pathological cases involving large unions, intersections, conditional types, and mapped types.
- https://github.com/microsoft/TypeScript/pull/36576
- https://github.com/microsoft/TypeScript/pull/36590
- https://github.com/microsoft/TypeScript/pull/36607
- https://github.com/microsoft/TypeScript/pull/36622
- https://github.com/microsoft/TypeScript/pull/36754
- https://github.com/microsoft/TypeScript/pull/36696
Each of these pull requests gains about a 5-10% reduction in compile times on certain codebases. In total, we believe we’ve achieved around a 40% reduction in material-ui’s compile time!
We also have some changes to file renaming functionality in editor scenarios. We heard from the Visual Studio Code team that when renaming a file, just figuring out which import statements needed to be updated could take between 5 to 10 seconds. TypeScript 3.9 addresses this issue by changing the internals of how the compiler and language service caches file lookups.
While there’s still room for improvement, we hope this work translates to a snappier experience for everyone!
// @ts-expect-error Comments
Imagine that we’re writing a library in TypeScript and we’re exporting some function called doStuff as part of our public API. The function’s types declare that it takes two strings so that other TypeScript users can get type-checking errors, but it also does a runtime check (maybe only in development builds) to give JavaScript users a helpful error.
function doStuff(abc: string, xyz: string) {
assert(typeof abc === "string");
assert(typeof xyz === "string");
// do some stuff
}
So TypeScript users will get a helpful red squiggle and an error message when they misuse this function, and JavaScript users will get an assertion error. We’d like to test this behavior, so we’ll write a unit test.
expect(() => {
doStuff(123, 456);
}).toThrow();
Unfortunately if our tests are written in TypeScript, TypeScript will give us an error!
doStuff(123, 456);
// ~~~
// error: Type 'number' is not assignable to type 'string'.
That’s why TypeScript 3.9 brings a new feature: // @ts-expect-error comments. When a line is prefixed with a // @ts-expect-error comment, TypeScript will suppress that error from being reported; but if there’s no error, TypeScript will report that // @ts-expect-error wasn’t necessary.
As a quick example, the following code is okay
// @ts-expect-error
console.log(47 * "octopus");
while the following code
// @ts-expect-error
console.log(1 + 1);
results in the error
Unused '@ts-expect-error' directive.
We’d like to extend a big thanks to Josh Goldberg, the contributor who implemented this feature. For more information, you can take a look at the ts-expect-error pull request.
ts-ignore or ts-expect-error?
In some ways // @ts-expect-error can act as a new suppression comment, similar to // @ts-ignore. The difference is that // @ts-ignore comments will do nothing if the following line is error-free.
You might be tempted to switch existing // @ts-ignore comments over to // @ts-expect-error, and you might be wondering which is appropriate for future code. While it’s entirely up to you and your team, we have some ideas of which to pick in certain situations.
Pick ts-expect-error if:
- you’re writing test code where you actually want the type system to error on an operation
- you expect a fix to be coming in fairly quickly and you just need a quick workaround
- you’re in a reasonably-sized project with a proactive team that wants to remove suppression comments as soon affected code is valid again
Pick ts-ignore if:
- you have an a larger project and and new errors have appeared in code with no clear owner
- you are in the middle of an upgrade between two different versions of TypeScript, and a line of code errors in one version but not another.
- you honestly don’t have the time to decide which of these options is better.
Uncalled Function Checks in Conditional Expressions
In TypeScript 3.7 we introduced uncalled function checks to report an error when you’ve forgotten to call a function.
function hasImportantPermissions(): boolean {
// ...
}
// Oops!
if (hasImportantPermissions) {
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
// This condition will always return true since the function is always defined.
// Did you mean to call it instead?
deleteAllTheImportantFiles();
}
However, this error only applied to conditions in if statements. Thanks to a pull request from Alexander Tarasyuk, this feature is also now supported in ternary conditionals (i.e. the cond ? trueExpr : falseExpr syntax).
declare function listFilesOfDirectory(dirPath: string): string[];
declare function isDirectory(): boolean;
function getAllFiles(startFileName: string) {
const result: string[] = [];
traverse(startFileName);
return result;
function traverse(currentPath: string) {
return isDirectory ?
// ~~~~~~~~~~~
// This condition will always return true
// since the function is always defined.
// Did you mean to call it instead?
listFilesOfDirectory(currentPath).forEach(traverse) :
result.push(currentPath);
}
}
https://github.com/microsoft/TypeScript/issues/36048
Editor Improvements
The TypeScript compiler not only powers the TypeScript editing experience in most major editors, it also powers the JavaScript experience in the Visual Studio family of editors and more. Using new TypeScript/JavaScript functionality in your editor will differ depending on your editor, but
- Visual Studio Code supports selecting different versions of TypeScript. Alternatively, there’s the JavaScript/TypeScript Nightly Extension to stay on the bleeding edge (which is typically very stable).
- Visual Studio 2017/2019 have the SDK installers above and MSBuild installs.
- Sublime Text 3 supports selecting different versions of TypeScript
CommonJS Auto-Imports in JavaScript
One great new improvement is in auto-imports in JavaScript files using CommonJS modules.
In older versions, TypeScript always assumed that regardless of your file, you wanted an ECMAScript-style import like
import * as fs from "fs";
However, not everyone is targeting ECMAScript-style modules when writing JavaScript files. Plenty of users still use CommonJS-style require(...) imports like so
const fs = require("fs");
TypeScript now automatically detects the types of imports you’re using to keep your file’s style clean and consistent.
For more details on the change, see the corresponding pull request.
Code Actions Preserve Newlines
TypeScript’s refactorings and quick fixes often didn’t do a great job of preserving newlines. As a really basic example, take the following code.
const maxValue = 100;
/*start*/
for (let i = 0; i <= maxValue; i++) {
// First get the squared value.
let square = i ** 2;
// Now print the squared value.
console.log(square);
}
/*end*/
If we highlighted the range from /*start*/ to /*end*/ in our editor to extract to a new function, we’d end up with code like the following.
const maxValue = 100;
printSquares();
function printSquares() {
for (let i = 0; i <= maxValue; i++) {
// First get the squared value.
let square = i ** 2;
// Now print the squared value.
console.log(square);
}
}
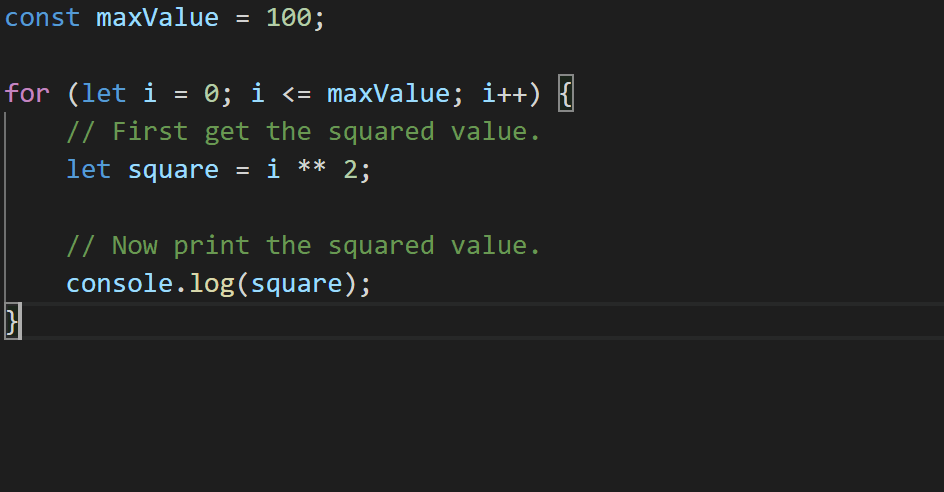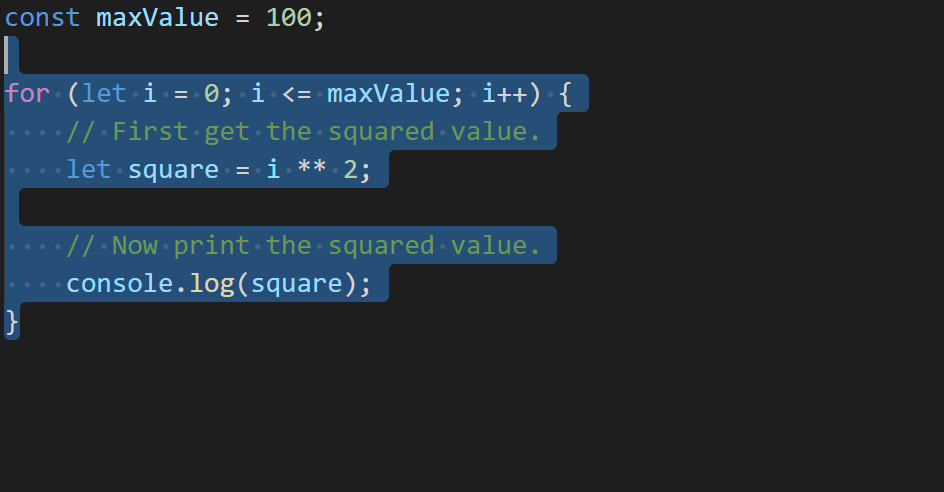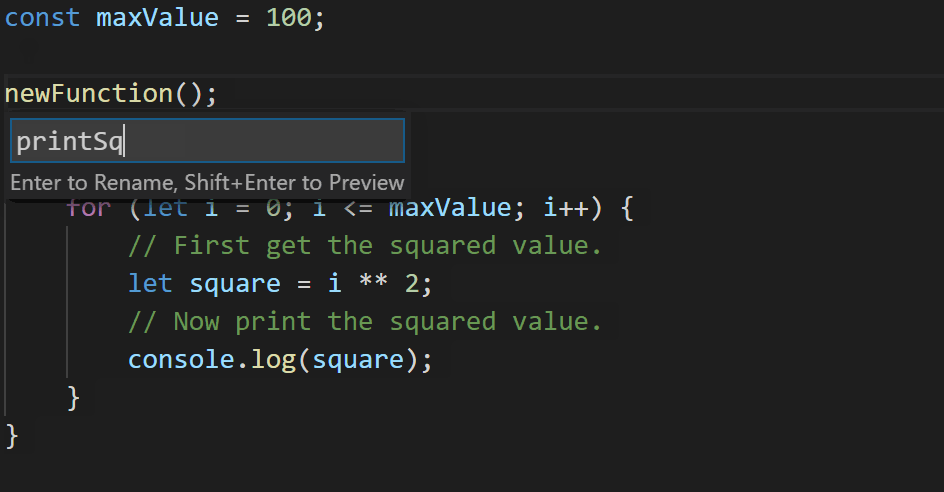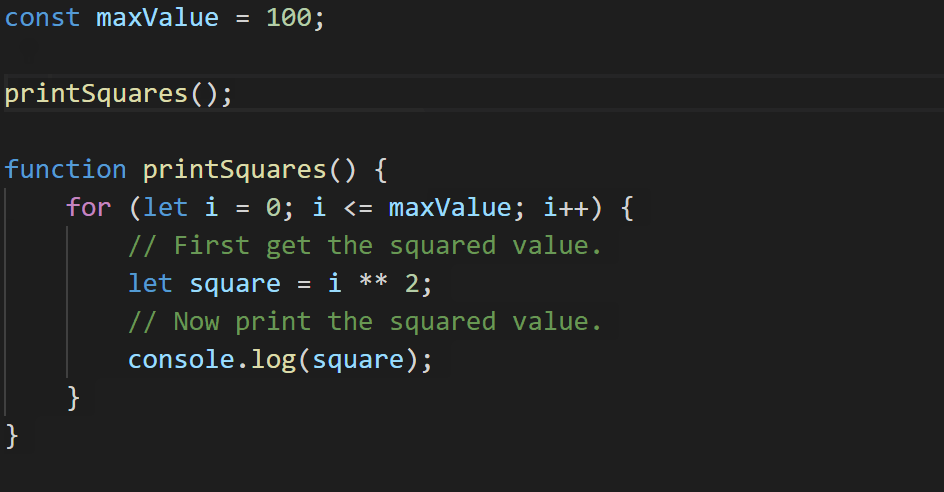
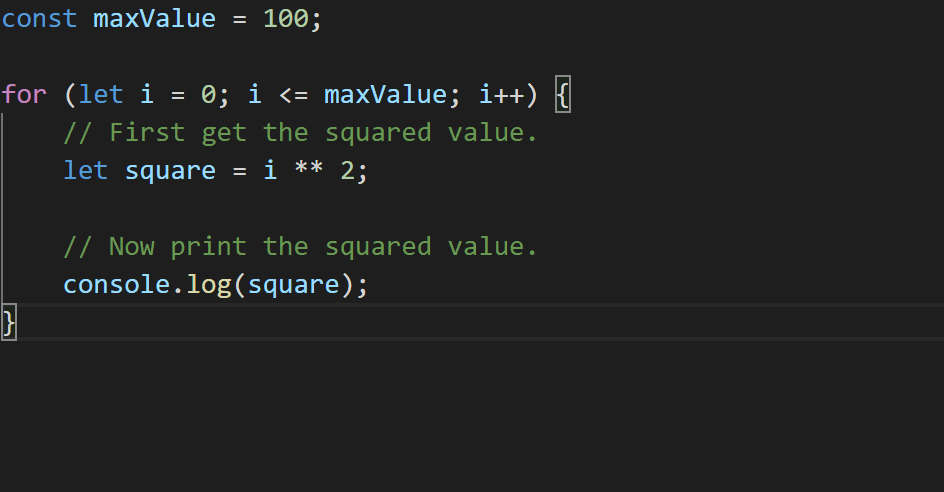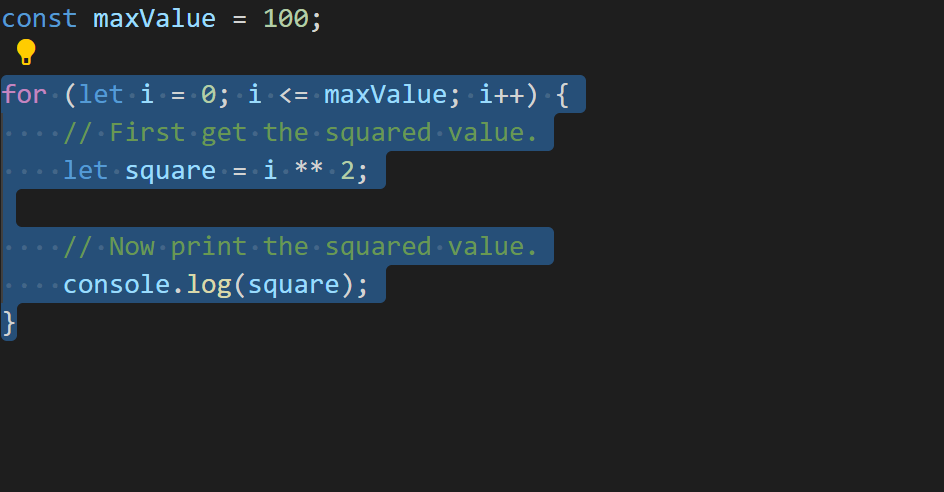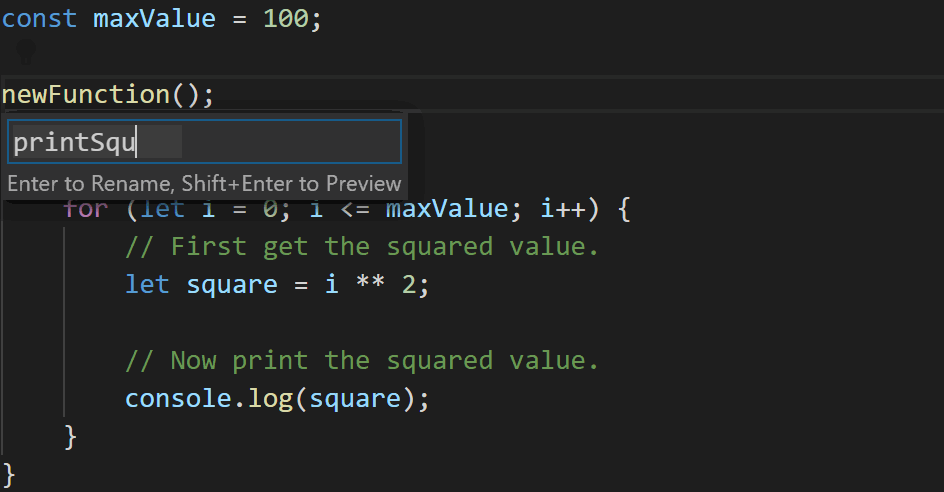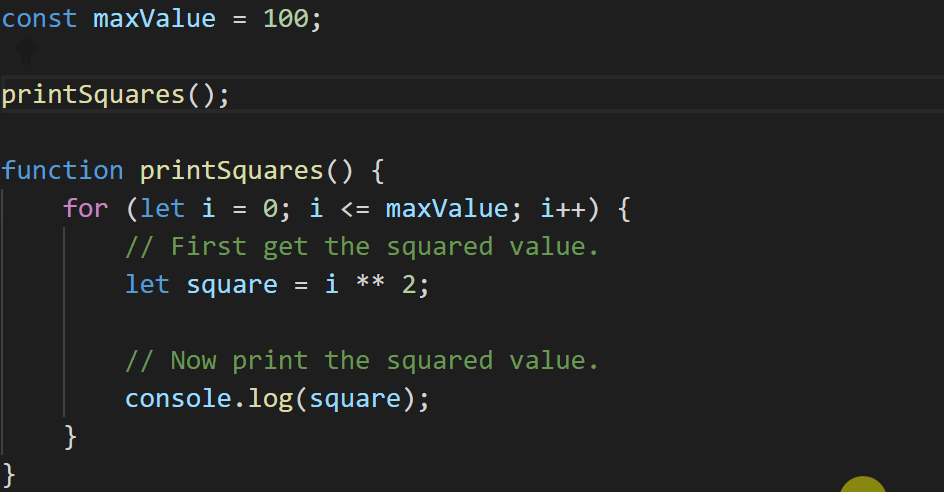
That’s not ideal – we had a blank line between each statement in our for loop, but the refactoring got rid of it! TypeScript 3.9 does a little more work to preserve what we write.
const maxValue = 100;
printSquares();
function printSquares() {
for (let i = 0; i <= maxValue; i++) {
// First get the squared value.
let square = i ** 2;
// Now print the squared value.
console.log(square);
}
}
You can see more about the implementation in this pull request
Support for “Solution Style” tsconfig.json Files
Editors need to figure out which configuration file a file belongs to so that it can apply the appropriate options and figure out which other files are included in the current “project”. By default, editors powered by TypeScript’s language server do this by walking up each parent directory to find a tsconfig.json.
One case where this slightly fell over is when a tsconfig.json simply existed to reference other tsconfig.json files.
// tsconfig.json
{
"files": [],
"references": [
{ "path": "./tsconfig.shared.json" },
{ "path": "./tsconfig.frontend.json" },
{ "path": "./tsconfig.backend.json" },
]
}
This file that really does nothing but manage other project files is often called a “solution” in some environments. Here, none of these tsconfig.*.json files get picked up by the server, but we’d really like the language server to understand that the current .ts file probably belongs to one of the mentioned projects in this root tsconfig.json.
TypeScript 3.9 adds support to editing scenarios for this configuration. For more details, take a look at the pull request that added this functionality.
Breaking Changes
Parsing Differences in Optional Chaining and Non-Null Assertions
TypeScript recently implemented the optional chaining operator, but we’ve received user feedback that the behavior of optional chaining (?.) with the non-null assertion operator (!) is extremely counter-intuitive.
Specifically, in previous versions, the code
foo?.bar!.baz
was interpreted to be equivalent to the following JavaScript.
(foo?.bar).baz
In the above code the parentheses stop the “short-circuiting” behavior of optional chaining, so if foo is undefined, accessing baz will cause a runtime error.
The Babel team who pointed this behavior out, and most users who provided feedback to us, believe that this behavior is wrong. We do too! The thing we heard the most was that the ! operator should just “disappear” since the intent was to remove null and undefined from the type of bar.
In other words, most people felt that the original snippet should be interpreted as
foo?.bar.baz
which just evaluates to undefined when foo is undefined.
This is a breaking change, but we believe most code was written with the new interpretation in mind. Users who want to revert to the old behavior can add explicit parentheses around the left side of the ! operator.
(foo?.bar)!.baz
} and > are Now Invalid JSX Text Characters
The JSX Specification forbids the use of the } and > characters in text positions. TypeScript and Babel have both decided to enforce this rule to be more comformant. The new way to insert these characters is to use an HTML escape code (e.g. <div> 2 > 1 </div>) or insert an expression with a string literal (e.g. <div> 2 {">"} 1 </div>).
Luckily, thanks to the pull request enforcing this from Brad Zacher, you’ll get an error message along the lines of
Unexpected token. Did you mean `{'>'}` or `>`?
Unexpected token. Did you mean `{'}'}` or `}`?
For example:
let directions = <div>Navigate to: Menu Bar > Tools > Options</div>
// ~ ~
// Unexpected token. Did you mean `{'>'}` or `>`?
That error message came with a handy quick fix, and thanks to Alexander Tarasyuk, you can apply these changes in bulk if you have a lot of errors.
Stricter Checks on Intersections and Optional Properties
Generally, an intersection type like A & B is assignable to C if either A or B is assignable to C; however, sometimes that has problems with optional properties. For example, take the following:
interface A {
a: number; // notice this is 'number'
}
interface B {
b: string;
}
interface C {
a?: boolean; // notice this is 'boolean'
b: string;
}
declare let x: A & B;
declare let y: C;
y = x;
In previous versions of TypeScript, this was allowed because while A was totally incompatible with C, B was compatible with C.
In TypeScript 3.9, so long as every type in an intersection is a concrete object type, the type system will consider all of the properties at once. As a result, TypeScript will see that the a property of A & B is incompatible with that of C:
Type 'A & B' is not assignable to type 'C'.
Types of property 'a' are incompatible.
Type 'number' is not assignable to type 'boolean | undefined'.
For more information on this change, see the corresponding pull request.
Intersections Reduced By Discriminant Properties
There are a few cases where you might end up with types that describe values that just don’t exist. For example
declare function smushObjects<T, U>(x: T, y: U): T & U;
interface Circle {
kind: "circle";
radius: number;
}
interface Square {
kind: "square";
sideLength: number;
}
declare let x: Circle;
declare let y: Square;
let z = smushObjects(x, y);
console.log(z.kind);
This code is slightly weird because there’s really no way to create an intersection of a Circle and a Square – they have two incompatible kind fields. In previous versions of TypeScript, this code was allowed and the type of kind itself was never because "circle" & "square" described a set of values that could never exist.
In TypeScript 3.9, the type system is more aggressive here – it notices that it’s impossible to intersect Circle and Square because of their kind properties. So instead of collapsing the type of z.kind to never, it collapses the type of z itself (Circle & Square) to never. That means the above code now errors with:
Property 'kind' does not exist on type 'never'.
Most of the breaks we observed seem to correspond with slightly incorrect type declarations. For more details, see the original pull request.
Getters/Setters are No Longer Enumerable
In older versions of TypeScript, get and set accessors in classes were emitted in a way that made them enumerable; however, this wasn’t compliant with the ECMAScript specification which states that they must be non-enumerable. As a result, TypeScript code that targeted ES5 and ES2015 could differ in behavior.
Thanks to a pull request from GitHub user pathurs, TypeScript 3.9 now conforms more closely with ECMAScript in this regard.
Type Parameters That Extend any No Longer Act as any
In previous versions of TypeScript, a type parameter constrained to any could be treated as any.
function foo<T extends any>(arg: T) {
arg.spfjgerijghoied; // no error!
}
This was an oversight, so TypeScript 3.9 takes a more conservative approach and issues an error on these questionable operations.
function foo<T extends any>(arg: T) {
arg.spfjgerijghoied;
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
// Property 'spfjgerijghoied' does not exist on type 'T'.
}
export * is Always Retained
In previous TypeScript versions, declarations like export * from "foo" would be dropped in our JavaScript output if foo didn’t export any values. This sort of emit is problematic because it’s type-directed and can’t be emulated by Babel. TypeScript 3.9 will always emit these export * declarations. In practice, we don’t expect this to break much existing code.
What’s Next?
You can keep posted on the progress of the TypeScript 3.9 release on our official Iteration Plan. We’d love to get your feedback to make sure that TypeScript 3.9 ships smoothly and makes you more productive, so give it a shot and if you run into anything please feel free to file an issue on our issue tracker.
Happy Hacking!
– Daniel Rosenwasser and the TypeScript Team

 Light
Light Dark
Dark
0 comments